02 Food Webs Chains Trophic Levels Notes

02 Food Webs Chains Trophic Levels Notes Trophic level is the position within a food chain that is occupied by a group of organisms in an ecosystem. the classification of organisms into the different food chains is based on their feeding behavior. trophic level is a step in the nutritive series of food chains which in some cases might form a complicated path called a food web. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online Figure 10.3.2.1 10.3.2. 1: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the united states canada border. trophic levels with green algae as the primary producer, mollusks and snails are the primary consumers, and small fish (slimy sculpin) are the secondary consumers. the tertiary and apex consumer is chinook salmon. Draw a terrestrial food chain that includes four trophic levels. identify the trophic level of each organism in the food chain. this page titled 6.5: trophic levels is shared under a ck 12 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by ck 12 foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. A food web a food chain is one path through a food web. food chains use arrows to show energy flow. what are two food chains in this food web? a. grass snail bird eagle b. grass caterpillar lizard snc1d sustainable ecosystems rhsa energy flows through an ecosystem in a food chain. each step in a food chain is considered a higher trophic level. Mean chain length (chlen) = the average length of all observed chains in the food web. 1. calculate the length of every chain (= total length) 2. divide the total length by the total number of chains in the food length. figure 4. the length of all observed chains is summed for each trophic level in the above food web.
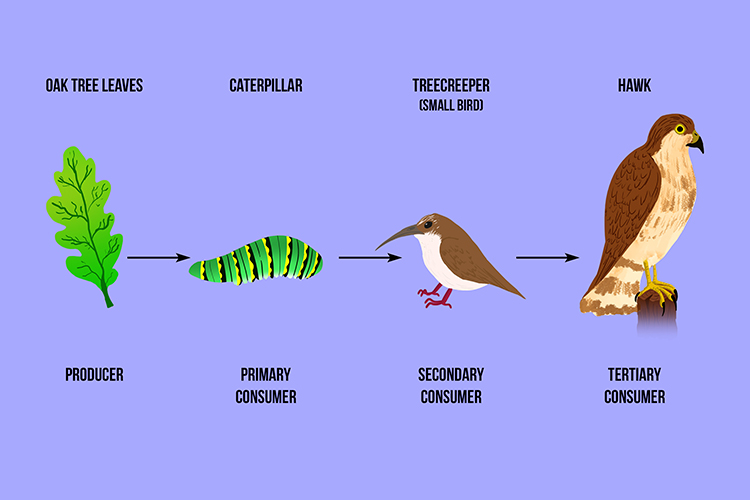
A Tropic Level Is A Nutritional Stage In Food Chain A food web a food chain is one path through a food web. food chains use arrows to show energy flow. what are two food chains in this food web? a. grass snail bird eagle b. grass caterpillar lizard snc1d sustainable ecosystems rhsa energy flows through an ecosystem in a food chain. each step in a food chain is considered a higher trophic level. Mean chain length (chlen) = the average length of all observed chains in the food web. 1. calculate the length of every chain (= total length) 2. divide the total length by the total number of chains in the food length. figure 4. the length of all observed chains is summed for each trophic level in the above food web. The above food chains coincide in the ecosystem with many others, where one organism has more than one prey. similarly, the same organism can have many predators forming an interconnected network of predator prey relationships across different trophic levels of the ecosystem – the food web. Summary. food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. they show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. a food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains. energy is passed up the food chain from one.
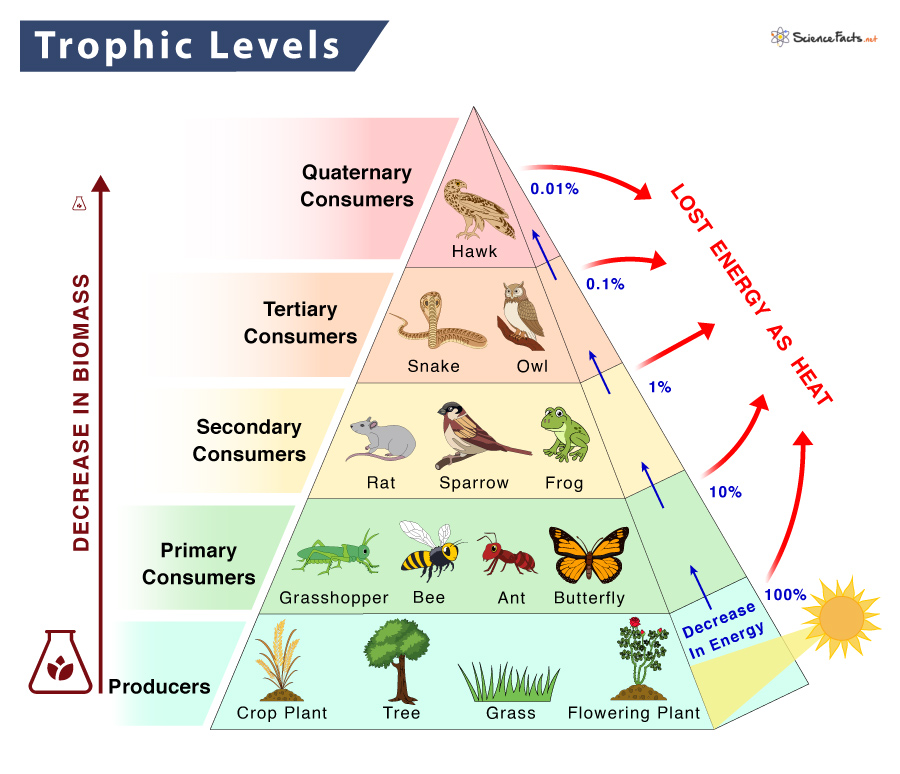
Food Chain Bulletin Board Energy Pyramid Food Chain F Vrogue Co The above food chains coincide in the ecosystem with many others, where one organism has more than one prey. similarly, the same organism can have many predators forming an interconnected network of predator prey relationships across different trophic levels of the ecosystem – the food web. Summary. food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. they show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. a food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains. energy is passed up the food chain from one.

Comments are closed.