10 Different Types Of Viruses
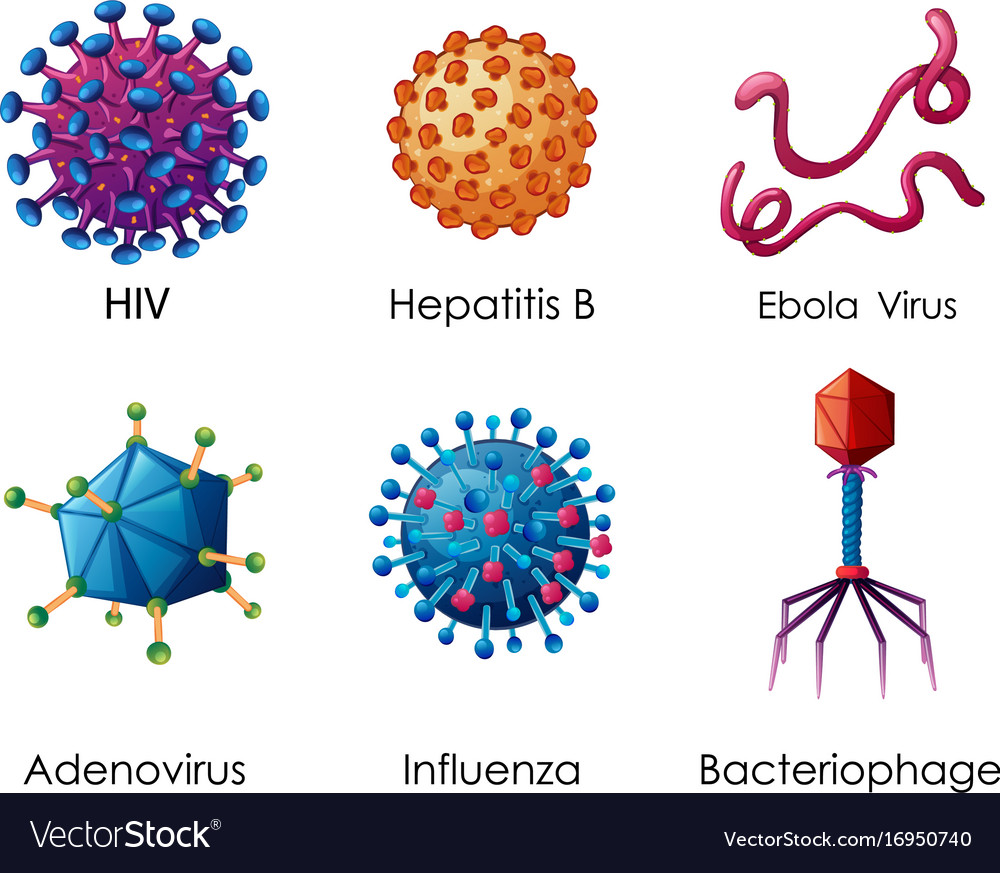
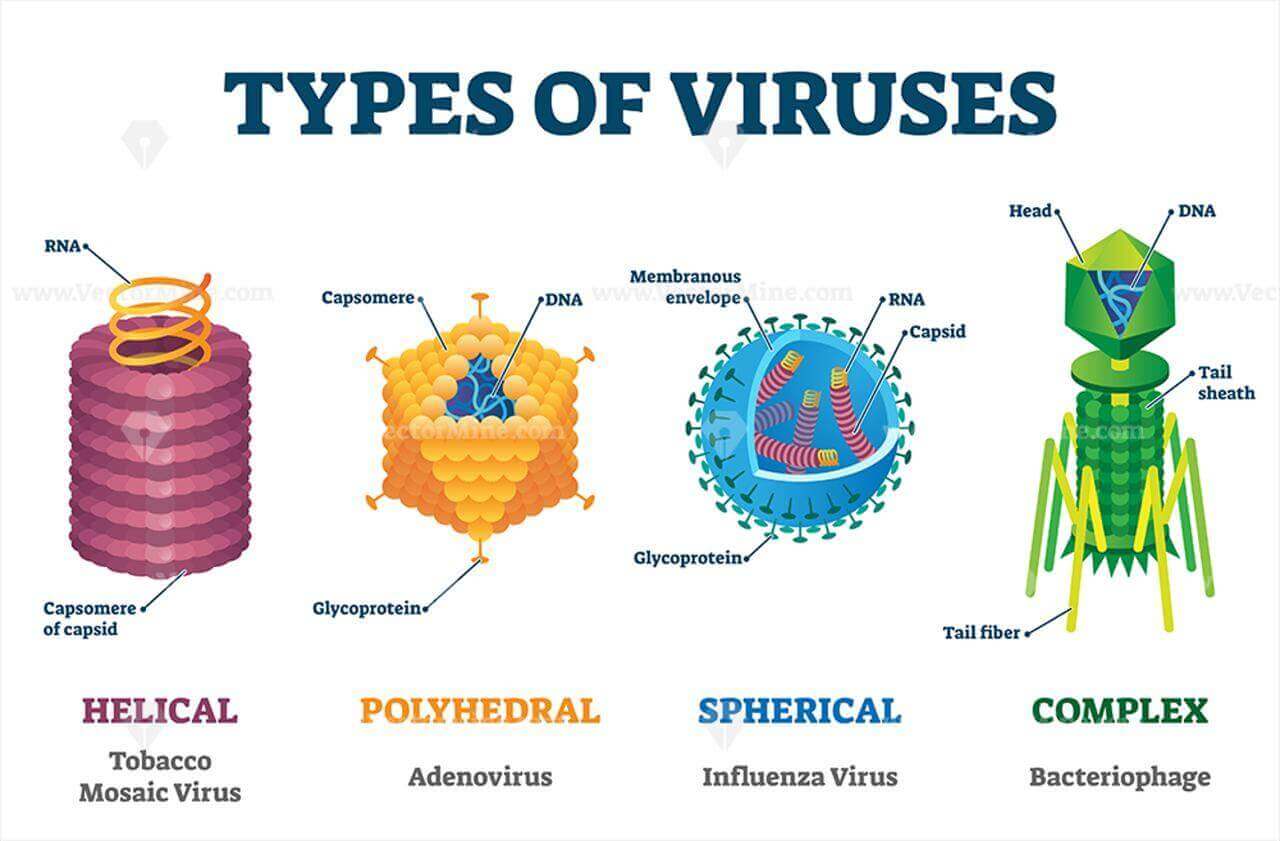
Virus Structure And Types Virus shapes. viruses can look very different from each other. scientists often described them by shape. types of virus shapes include: icosahedral or polyhedral. this is a geometric shape with many sides, similar to a soccer ball. most viruses that infect people are icosahedral. helical. this virus shape looks like a cylinder. This means they aren’t always spread from person to person. but many of them are. common examples of contagious viral diseases include the flu, the common cold, hiv, and herpes. other types of.
Virus Definition Discovery Characteristics And Structure Plantlet They can cause disease. some viruses cause sickness, like common colds, the flu, and food poisoning. symptoms of a viral infection include fever, pain, nausea, diarrhea, cough, congestion, shortness of breath, rashes, warts, and many others. the best treatment for most everyday viruses is rest, hydration, and time. Viruses can store their genetic information in six different types of nucleic acid which are named based on how that nucleic acid eventually becomes transcribed to the viral mrna (figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1) capable of binding to host cell ribosomes and being translated into viral proteins. figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1: transcription of viral nucleic acid. There are millions of different types of viruses, [8] although fewer than 7,000 types have been described in detail. [ 6 ] : 49 as of january 2021, the ncbi virus genome database has more than 193,000 complete genome sequences, [ 56 ] but there are doubtlessly many more to be discovered. Viruses are infectious units with diameters of about 16 nm (circoviruses) to over 300 nm (poxviruses; table 2.1). their small size makes them ultrafilterable, i.e. they are not retained by bacteria proof filters. viruses have evolved over longtime period, and have adapted to specific organisms or their cells. the infectious virus particles, or.
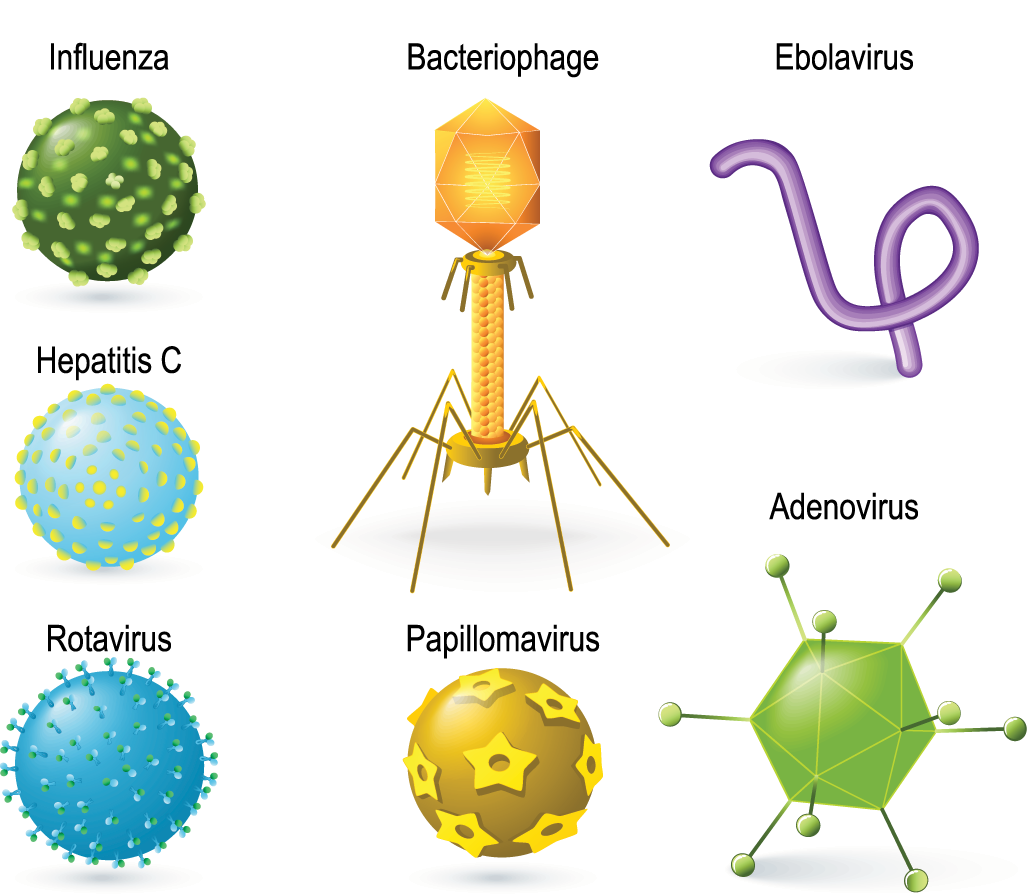
Explainer Virus Variants And Strains There are millions of different types of viruses, [8] although fewer than 7,000 types have been described in detail. [ 6 ] : 49 as of january 2021, the ncbi virus genome database has more than 193,000 complete genome sequences, [ 56 ] but there are doubtlessly many more to be discovered. Viruses are infectious units with diameters of about 16 nm (circoviruses) to over 300 nm (poxviruses; table 2.1). their small size makes them ultrafilterable, i.e. they are not retained by bacteria proof filters. viruses have evolved over longtime period, and have adapted to specific organisms or their cells. the infectious virus particles, or. Viruses have different shapes and sizes. scientists categorize viruses according to various factors, including: their shape and size, which may be rod shaped, almost spherical, or other shapes. Virus definition. a virus is a chain of nucleic acids (dna or rna) which lives in a host cell, uses parts of the cellular machinery to reproduce, and releases the replicated nucleic acid chains to infect more cells. a virus is often housed in a protein coat or protein envelope, a protective covering which allows the virus to survive between hosts.

Comments are closed.