16 2 Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Biology Libretexts
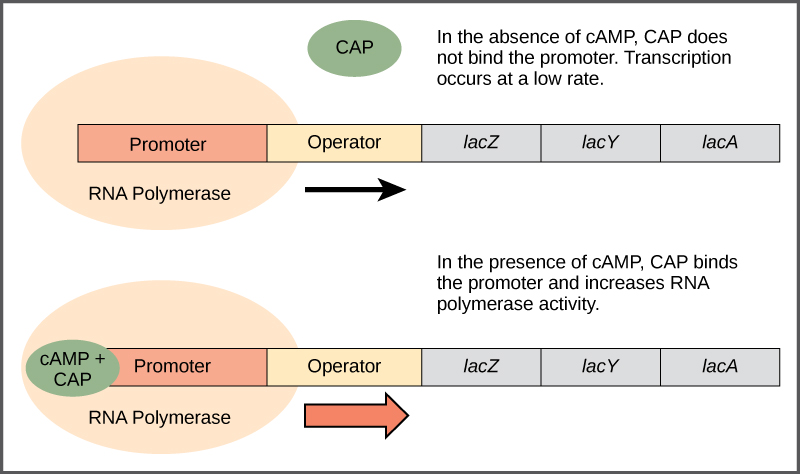
16 2 Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Biology Libretexts This increases the binding ability of rna polymerase to the promoter region and the transcription of the genes. figure 16.2.2 16.2. 2: when glucose levels fall, e. coli may use other sugars for fuel but must transcribe new genes to do so. as glucose supplies become limited, camp levels increase. Gene regulation is an important part of normal development. genes are turned on and off in different patterns during development to make a brain cell look and act different from a liver cell or a muscle cell, for example. gene regulation also allows cells to react quickly to changes in their environments.
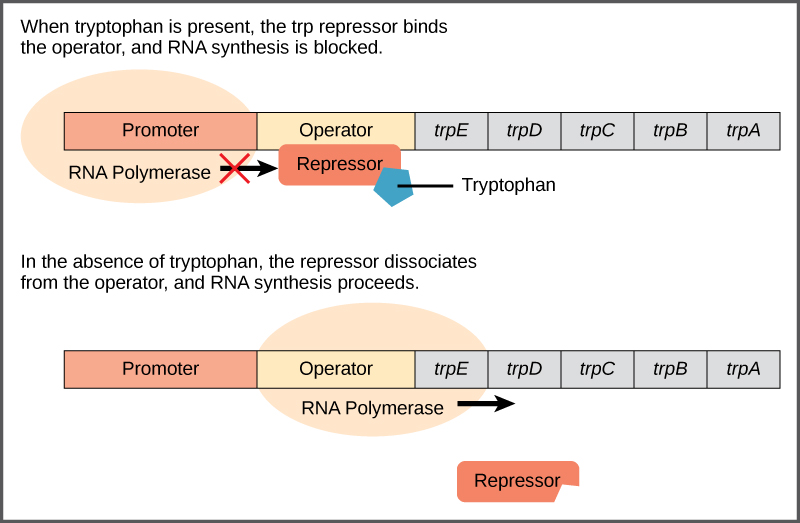
16 2 Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Biology Libretexts Art connection. figure 16.3.3 16.3. 3: transcription of the lac operon is carefully regulated so that its expression only occurs when glucose is limited and lactose is present to serve as an alternative fuel source. in e. coli, the trp operon is on by default, while the lac operon is off. The lac operon: an inducer operon. the third type of gene regulation in prokaryotic cells occurs through inducible operons, which have proteins that bind to activate or repress transcription depending on the local environment and the needs of the cell. Connection for ap. ®. courses. the regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. simply stated, if a cell does not transcribe the dna’s message into mrna, translation (protein synthesis), does not occur. bacterial genes are often organized into common pathways or processes called operons for more. The role of operons. regulation of transcription in prokaryotes typically involves operons. an operon is a region of dna that consists of one or more genes that encode the proteins needed for a specific function. the operon also includes a promoter and an operator. the operator is a region of the operon where regulatory proteins bind.
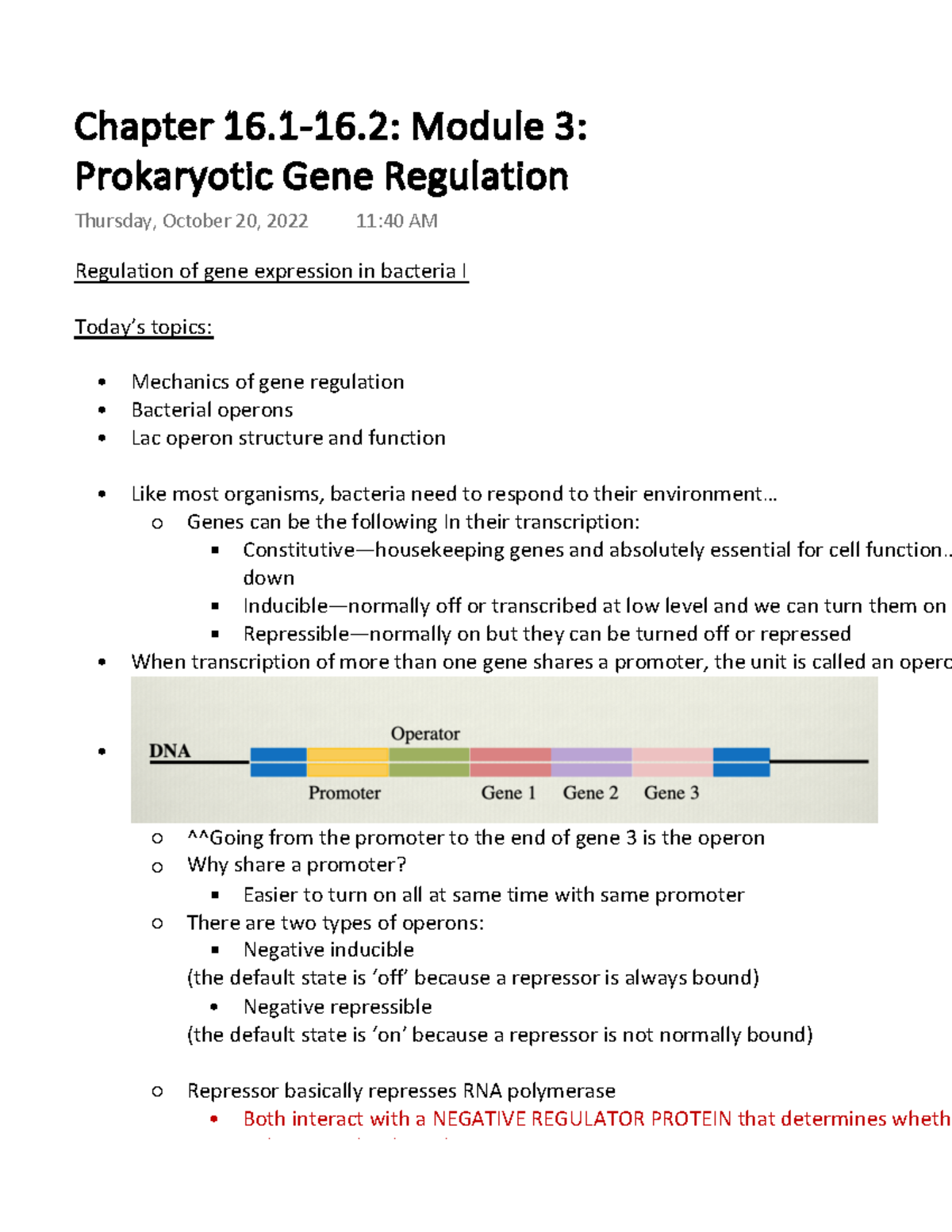
Module 3 Chapter 16 1 16 2 Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Lecture Connection for ap. ®. courses. the regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. simply stated, if a cell does not transcribe the dna’s message into mrna, translation (protein synthesis), does not occur. bacterial genes are often organized into common pathways or processes called operons for more. The role of operons. regulation of transcription in prokaryotes typically involves operons. an operon is a region of dna that consists of one or more genes that encode the proteins needed for a specific function. the operon also includes a promoter and an operator. the operator is a region of the operon where regulatory proteins bind. The regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. there are three ways to control the transcription of an operon: repressive control, activator control, and inducible control. 16.2 prokaryotic gene regulation. the regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. there are two majors kinds of proteins that control prokaryotic transcription: repressors and activators. repressors bind to an operator region to block the action of rna polymerase.

Gene Regulation In Prokaryotes The regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. there are three ways to control the transcription of an operon: repressive control, activator control, and inducible control. 16.2 prokaryotic gene regulation. the regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. there are two majors kinds of proteins that control prokaryotic transcription: repressors and activators. repressors bind to an operator region to block the action of rna polymerase.

Comments are closed.