3 2 Changes In Demand
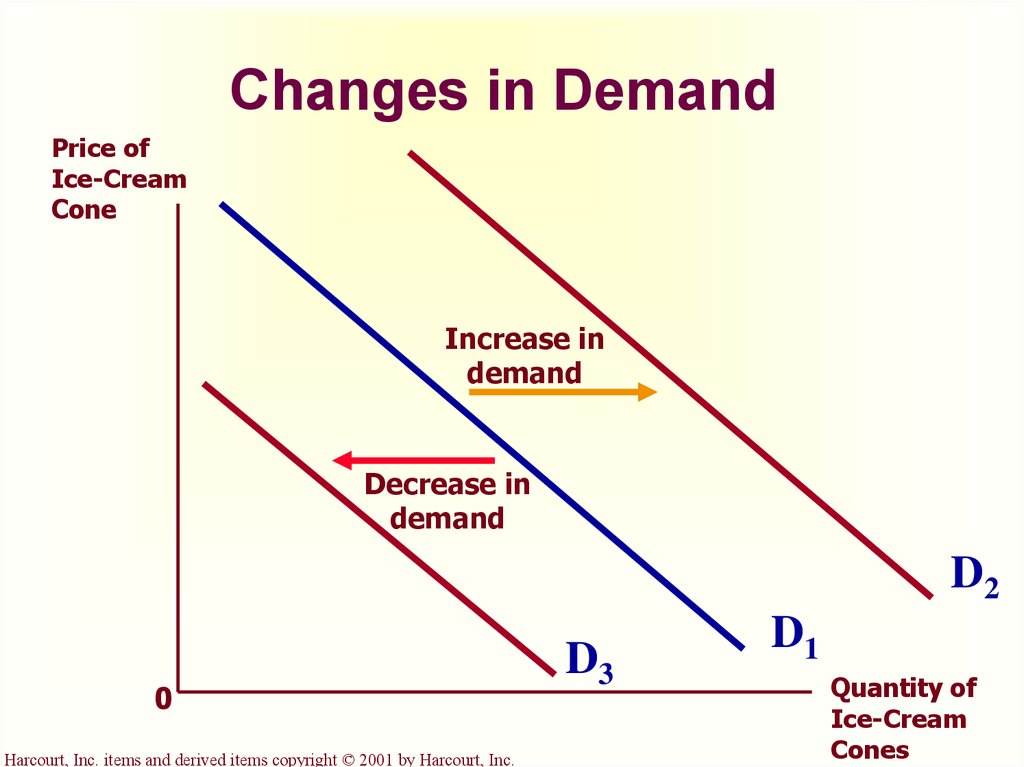
The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand Online Presentation Note, that a change in quantity demanded, ceteris paribus, refers to a movement along the demand curve, while a change in demand refers to a shift in the demand curve. a rightward shift of the demand curve is called an increase in demand. fig 3.2 “an increase in demand” by university of minnesota, cc by nc sa 4.0. An increase in price from $12 to $16 causes a movement along the demand curve, and quantity demand falls from 80 to 60. we say this is a contraction in demand. expansion in demand. a fall in price from $16 to $12 leads to an expansion (increase) in demand. as price falls, there is a movement along the demand curve and more is bought.

Changes In Supply And Demand Microeconomics A change in the price of a good or service causes a movement along a specific demand curve, and it typically leads to some change in the quantity demanded, but it does not shift the demand curve. figure 3.9 factors that shift demand curves (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from d 0 to d 1 . A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. A change in demand represents a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price. the change could be triggered by a shift in income. Figure 3.17 “changes in demand and supply” combines the information about changes in the demand and supply of coffee presented in figure 3.2 “an increase in demand” figure 3.3 “a reduction in demand” figure 3.9 “an increase in supply” and figure 3.10 “a reduction in supply” in each case, the original equilibrium price is $6.

A What Are The Six Major Factors That Cause Demand To Change B How A change in demand represents a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price. the change could be triggered by a shift in income. Figure 3.17 “changes in demand and supply” combines the information about changes in the demand and supply of coffee presented in figure 3.2 “an increase in demand” figure 3.3 “a reduction in demand” figure 3.9 “an increase in supply” and figure 3.10 “a reduction in supply” in each case, the original equilibrium price is $6. A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. A change in the price of a good or service causes a movement along a specific demand curve, and it typically leads to some change in the quantity demanded, but it does not shift the demand curve. figure 3.8 factors that shift demand curves (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from [latex]d 0[ latex] to [latex]d 1[ latex].

Changes In Demand And Movements Along Demand Curve Tutorial Sophia A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. A change in the price of a good or service causes a movement along a specific demand curve, and it typically leads to some change in the quantity demanded, but it does not shift the demand curve. figure 3.8 factors that shift demand curves (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from [latex]d 0[ latex] to [latex]d 1[ latex].

Comments are closed.