3d Phase Diagrams
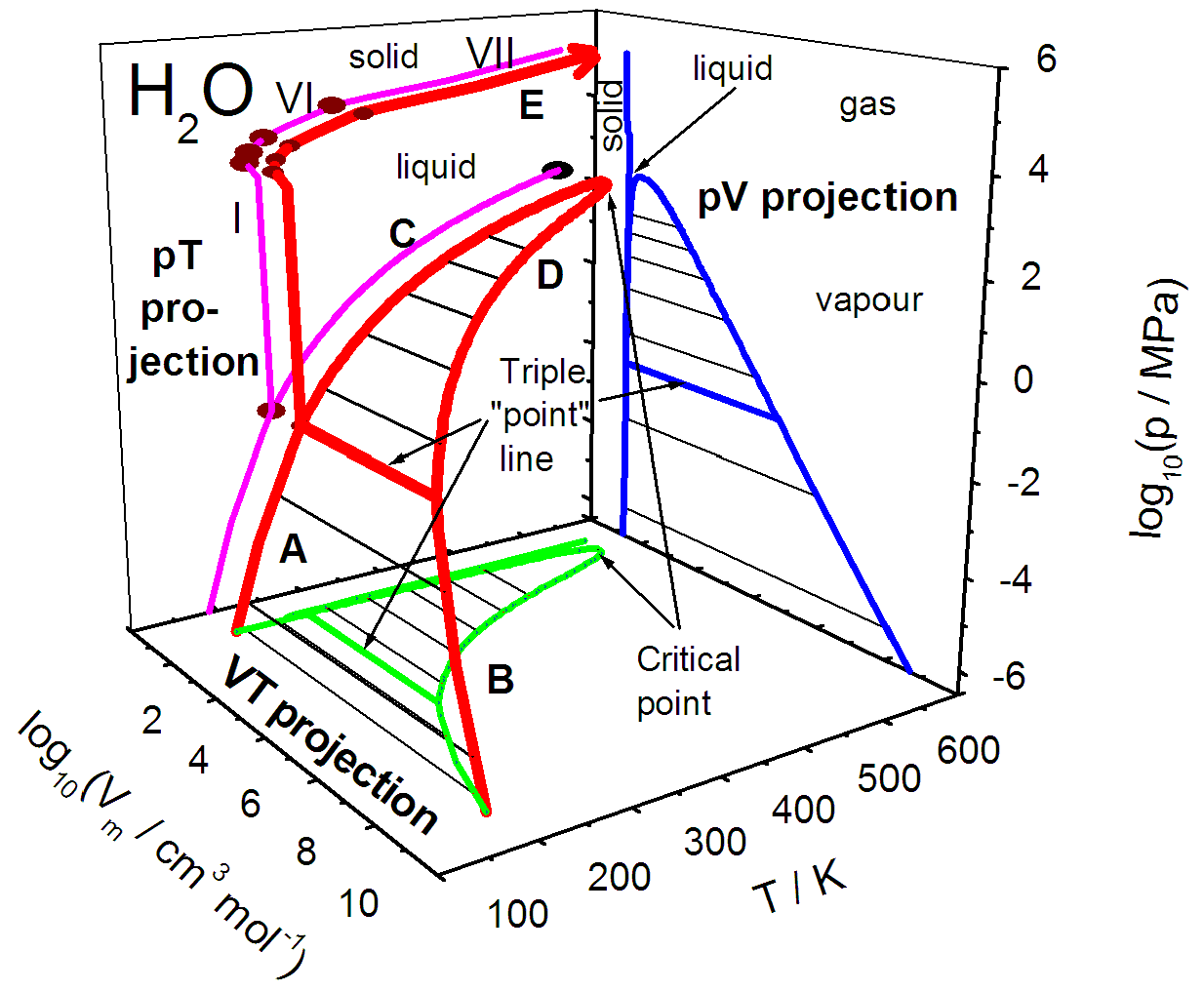
3d Phase Diagrams The critical point remains a point on the surface even on a 3d phase diagram. an orthographic projection of the 3d p–v–t graph showing pressure and temperature as the vertical and horizontal axes collapses the 3d plot into the standard 2d pressure–temperature diagram. when this is done, the solid–vapor, solid–liquid, and liquid. A 3d phase diagram is a type of graph in which three different conditions (such as p, v, t) are plotted along the cartesian axes. > it shows the conditions at which different phases occur and coexist at equilibrium. the equilibrium conditions are shown as curved surfaces in 3d, with areas for solid, liquid, and vapour phases and areas where two or three phases can coexist in equilibrium. for.
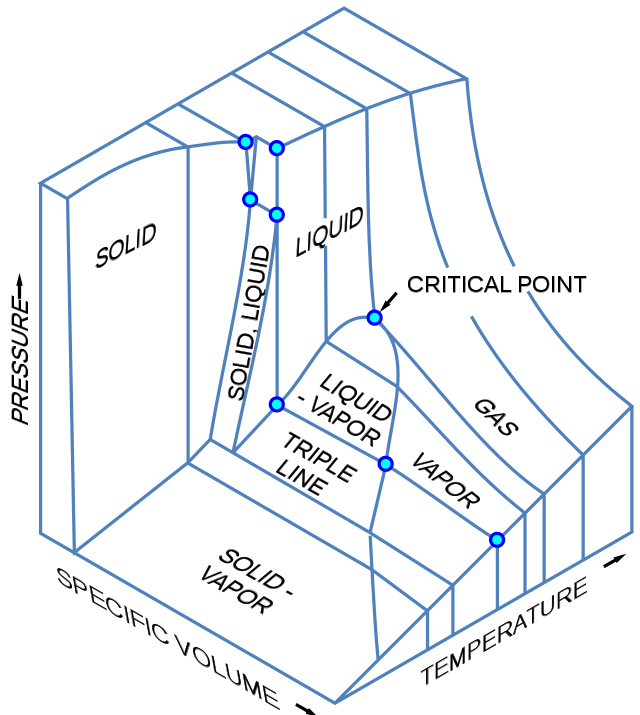
Phase Diagrams Chemtalk One component phase diagram. figure 1 illustrates the temperatures and pressures at which water can exist as a solid, liquid or vapor. the curves represent the points at which two of the phases coexist in equilibrium. at the point tt vapor, liquid and solid coexist in equilibrium. in the fields of the diagram (phase fields) only one phase exists. Three dimensional phase change diagrams plot three thermodynamic variables and show regions of space corresponding to different phases. in this type of diagram, we have a triple line instead of a triple point, and coexistence surfaces instead of coexistence curves. below is a generic 3d diagram plotting temperature, pressure, and specific volume. Such a p t graph is called a phase diagram. [1] [1] in the phase diagram, we can observe that the boiling point curve (the line that distinguishes liquid and vapour phases) ends at a point, which is called critical point. above the critical point, liquid and gas can no longer be distinguished and are classified as a supercritical fluid. 13.2.2 solid–liquid systems. figure 13.1 temperature–composition phase diagram for a binary system exhibiting a eutectic point. figure 13.1 is a temperature–composition phase diagram at a fixed pressure. the composition variable is the mole fraction of component b in the system as a whole.

3d Phase Diagrams Youtube Such a p t graph is called a phase diagram. [1] [1] in the phase diagram, we can observe that the boiling point curve (the line that distinguishes liquid and vapour phases) ends at a point, which is called critical point. above the critical point, liquid and gas can no longer be distinguished and are classified as a supercritical fluid. 13.2.2 solid–liquid systems. figure 13.1 temperature–composition phase diagram for a binary system exhibiting a eutectic point. figure 13.1 is a temperature–composition phase diagram at a fixed pressure. the composition variable is the mole fraction of component b in the system as a whole. The lines in a phase diagram correspond to the combinations of temperature and pressure at which two phases can coexist in equilibrium. in figure 12.4.1 12.4. 1, the line that connects points a and d separates the solid and liquid phases and shows how the melting point of a solid varies with pressure. the solid and liquid phases are in. 139. bi mass fraction of sn sn. 3 dimensional depiction of temperature composition phase diagram of bismuth, tin, and lead at 1atm. the diagram has been simplified by omission of the regions of solid solubility. each face of the triangular prism is a two component temperature composition phase diagram with a eutectic.

Comments are closed.