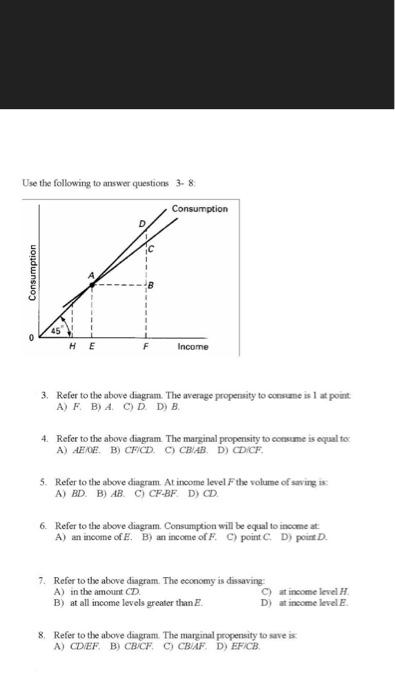
40 Refer To The Given Diagram The Marginal Propensity To Consume Is

40 Refer To The Given Diagram The Marginal Propensity To Consume Is Di signifies disposable income and c represents consumption expenditures. all figures are in billions of dollars. the marginal propensity to consume cannot be calculated from the data given. is highest in economy (1). is highest in economy (3). is highest in economy (2). 80. the multiplier = 1 ÷ mps = 1 ÷ 0.2 = 5. (5 × $20 billion = $100 billion). (1 − 0.2) × $100 billion = $80 billion. if disposable income is $800 billion when the average propensity to consume is 0.7, it can be concluded that saving is. $240 billion. (1 − 0.7) × $800 billion = $240 billion. suppose that an initial $10 billion increase.
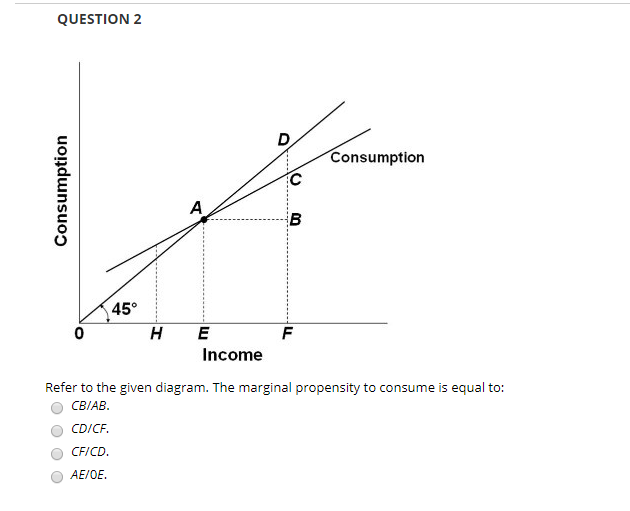
40 Refer To The Given Diagram The Marginal Propensity To Consume Is The marginal propensity to consume is equal to Δc Δy, where Δc is the change in consumption, and Δy is the change in income. if consumption increases by 80 cents for each additional dollar. To calculate the marginal propensity to consume, insert those changes into the formula: mpc = ∆c ∆y. mpc = 5,000 10,000. mpc = .5 or 50%. this means that for the given period, the individual. The mpc calculator is a simple tool designed to compute the marginal propensity to consume, a fraction strongly linked to a concept of marginal propensity to save, average propensity to consume, or the money multiplier. in the following, you can learn how to calculate mpc with the simple mpc formula and familiarize yourself with its importance. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) measures the proportion of extra income that is spent on consumption. for example, if an individual gains an extra £10, and spends £7.50, then the marginal propensity to consume will be £7.5 10 = 0.75. the mpc will invariably be between 0 and 1. the marginal propensity to consume measures the change.
40 Refer To The Given Diagram The Marginal Propensity To Consume Is The mpc calculator is a simple tool designed to compute the marginal propensity to consume, a fraction strongly linked to a concept of marginal propensity to save, average propensity to consume, or the money multiplier. in the following, you can learn how to calculate mpc with the simple mpc formula and familiarize yourself with its importance. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) measures the proportion of extra income that is spent on consumption. for example, if an individual gains an extra £10, and spends £7.50, then the marginal propensity to consume will be £7.5 10 = 0.75. the mpc will invariably be between 0 and 1. the marginal propensity to consume measures the change. Marginal propensity to consume (mpc) is defined as the share of additional income that a consumer spends on consumption. that means it describes the percenta. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) refers to how sensitive consumption in a given economy is to unitized changes in income levels. mpc as a concept works similar to price elasticity, where novel insights can be drawn by looking at the magnitude of change in consumption as a result of income fluctuations.
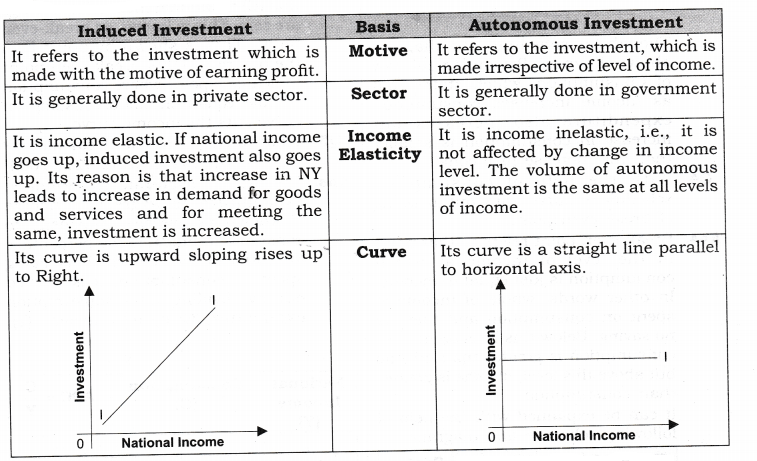
40 Refer To The Given Diagram The Marginal Propensity To Consume Is Marginal propensity to consume (mpc) is defined as the share of additional income that a consumer spends on consumption. that means it describes the percenta. The marginal propensity to consume (mpc) refers to how sensitive consumption in a given economy is to unitized changes in income levels. mpc as a concept works similar to price elasticity, where novel insights can be drawn by looking at the magnitude of change in consumption as a result of income fluctuations.

Comments are closed.