5 Stages Of Sleep Psychology Cycle Sequence

5 Stages Of Sleep Psychology Cycle Sequence The five stages make one sleep cycle, which usually repeats every 90 to 110 minutes. stage 1 non rem sleep marks the transition from wakefulness to sleep. this stage typically lasts less than 10 minutes and is marked by a slowing of your heartbeat, breathing, eye movements, and the relaxation of your muscles. Stage 3. stage 3 sleep is also known as n3 or deep sleep, and it is harder to wake someone up if they are in this phase. muscle tone, pulse, and breathing rate decrease in n3 sleep as the body relaxes even further. the brain activity during this period has an identifiable pattern of what are known as delta waves.

Learn How To Sleep Better By Understanding Sleep Cycles Stages Stage r sleep lasts roughly 10 minutes the first time, increasing with each rem cycle. the final cycle of stage r may last roughly between 30 to 60 minutes. during this stage: eye movements become. Most people go through 4 or 5 sleep cycles per night. each cycle has 4 stages, with the first 3 being non rem (rapid eye movement): stage 1—where you transition from being awake to being asleep. it's when your heartbeat, breathing, and eye movement slow. your muscles may also twitch as you sink deeper into sleep towards stage 2. The human body cycles through 2 phases of sleep, (1) rapid eye movement (rem) and (2) nonrapid eye movement (nrem) sleep, which is further divided into 3 stages—n1 to n3. each phase and stage of sleep includes variations in muscle tone, brain wave patterns, and eye movements. the body cycles through all stages approximately 4 to 6 times each night, averaging 90 minutes for each cycle.[1]. Stage 3 and stage 4 are described as slow wave sleep that is marked by a predominance of delta waves. rem sleep involves rapid movements of the eyes, paralysis of voluntary muscles, and dreaming. both nrem and rem sleep appear to play important roles in learning and memory.
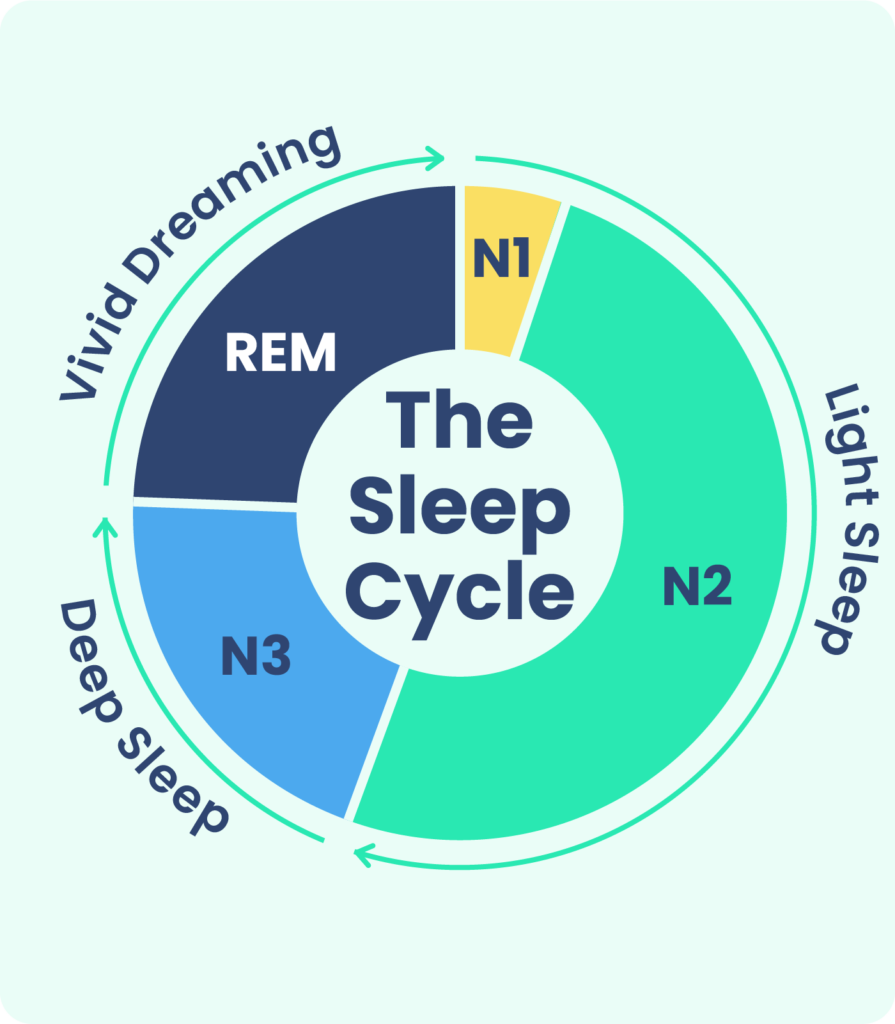
Stages Of Sleep Psychology Cycle Sequence 45 Off The human body cycles through 2 phases of sleep, (1) rapid eye movement (rem) and (2) nonrapid eye movement (nrem) sleep, which is further divided into 3 stages—n1 to n3. each phase and stage of sleep includes variations in muscle tone, brain wave patterns, and eye movements. the body cycles through all stages approximately 4 to 6 times each night, averaging 90 minutes for each cycle.[1]. Stage 3 and stage 4 are described as slow wave sleep that is marked by a predominance of delta waves. rem sleep involves rapid movements of the eyes, paralysis of voluntary muscles, and dreaming. both nrem and rem sleep appear to play important roles in learning and memory. Stage 1. stage one begins when a person shifts from wakefulness to sleep. it is a period of light non rem sleep that slows down a person’s heart rate, breathing, eye movements, and brain waves. The first stage of nrem sleep is known as stage 1 sleep. stage 1 sleep is a transitional phase that occurs between wakefulness and sleep, the period during which we drift off to sleep. during this time, there is a slowdown in both the rates of respiration and heartbeat. in addition, stage 1 sleep involves a marked decrease in both overall.

The Guide To Understanding Your Sleep Cycles And Stages Of Sleep Stage 1. stage one begins when a person shifts from wakefulness to sleep. it is a period of light non rem sleep that slows down a person’s heart rate, breathing, eye movements, and brain waves. The first stage of nrem sleep is known as stage 1 sleep. stage 1 sleep is a transitional phase that occurs between wakefulness and sleep, the period during which we drift off to sleep. during this time, there is a slowdown in both the rates of respiration and heartbeat. in addition, stage 1 sleep involves a marked decrease in both overall.

Comments are closed.