6 1 Angles In Standard Position In Quadrant I
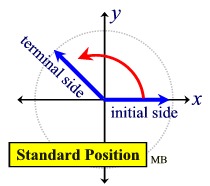
Standard Position And Reference Angles Mathbitsnotebook A2 Example of angles in standard position calculator. consider an angle of 150°. to find the reference angle using the calculator: identify the quadrant: 150° lies in the second quadrant. apply the formula: 180°−150°=30°. the reference angle is 30°. this example illustrates the calculator's utility in simplifying the process of finding. An angle in standard position is said to lie in the quadrant in which its terminal side lies. what are quadrantal angles? quadrantral angles are angles in standard position having their terminal sides along the x axis or y axis, such as angles with measures 90°, 180°, 270°, and so on.

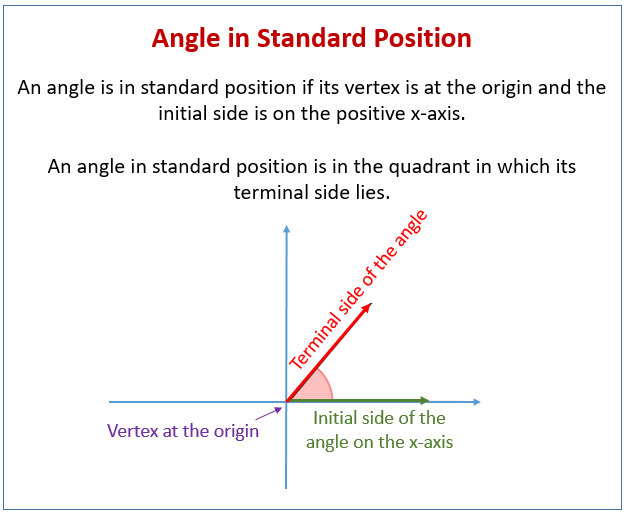
Reference Angle Chart The reference angle is the acute angle (the smallest angle) formed by the terminal side of the given angle and the x axis. reference angles may appear in all four quadrants. angles in quadrant i are their own reference angles. a reference angle is always positive and is always less than 90º. remember: the reference angle is measured from the. 6.1 angles in standard position in quadrant i name the coordinates of a point p on the coordinate plane can be described by its distance from the and the angle that op makes with the positive x axis. when the angle e, between angle is in of the angle and the point p is a is measured from the positive x axis, the the ray op is the for the angle. Standard position: an angle is in standard position if its vertex is located at the origin and one ray is on the positive x axis. the ray on the x axis is called the initial side and the other ray is called the terminal side. if the terminal side of an angle lies "on" the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal. A central angle is an angle formed at the center of a circle by two radii. because the total circumference equals 2π times the radius, a full circular rotation is 2π radians. so. 2π radians = 360 ∘ one complete rotation π radians = 360 ∘ 2 = 180 ∘ one half of a complete rotation 1 radian = 180 ∘ π ≈ 57.3 ∘.
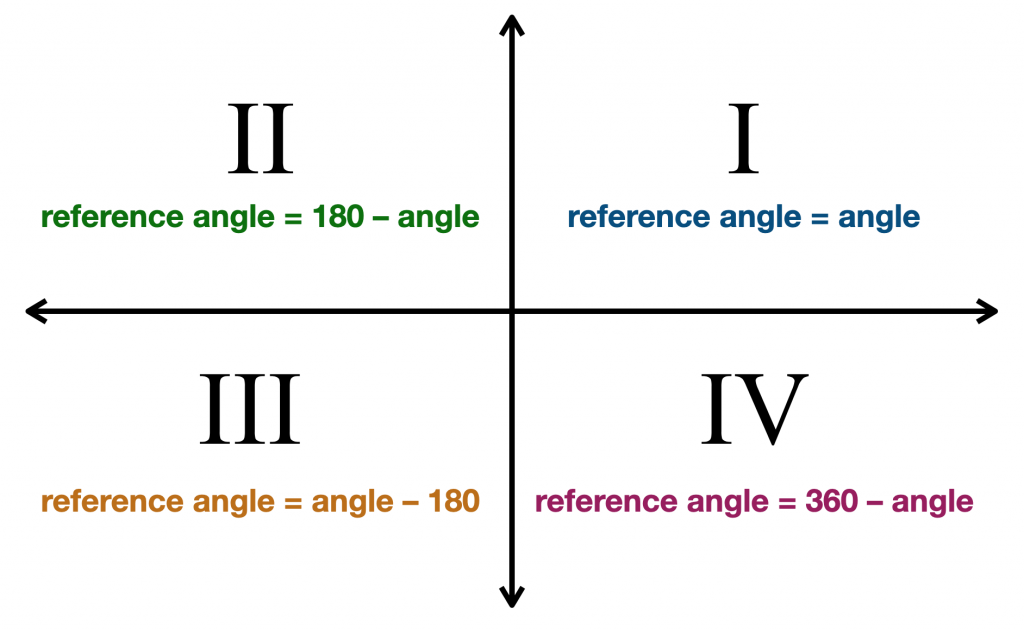
Reference Angle Calculator Pi Day Standard position: an angle is in standard position if its vertex is located at the origin and one ray is on the positive x axis. the ray on the x axis is called the initial side and the other ray is called the terminal side. if the terminal side of an angle lies "on" the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal. A central angle is an angle formed at the center of a circle by two radii. because the total circumference equals 2π times the radius, a full circular rotation is 2π radians. so. 2π radians = 360 ∘ one complete rotation π radians = 360 ∘ 2 = 180 ∘ one half of a complete rotation 1 radian = 180 ∘ π ≈ 57.3 ∘. The angles measuring 6 0 ∘ and 4 2 0 ∘ in standard position are other examples of coterminal angles, because their terminal sides are in the same position relative to the positive 𝑥 axis. in other words, the angles have the same terminal side. notice that the measure of the 4 2 0 ∘ angle is 3 6 0 ∘ more than the measure of the 6 0. Since we define an angle in standard position by its terminal side, we have a special type of angle whose terminal side lies on an axis, a quadrantal angle. this type of angle can have a measure of 0°, 90°, 180°, 270° or 360°. figure 7. quadrantal angles have a terminal side that lies along an axis. examples are shown.

6 1 Angles In Standard Position In Quadrant I Youtube The angles measuring 6 0 ∘ and 4 2 0 ∘ in standard position are other examples of coterminal angles, because their terminal sides are in the same position relative to the positive 𝑥 axis. in other words, the angles have the same terminal side. notice that the measure of the 4 2 0 ∘ angle is 3 6 0 ∘ more than the measure of the 6 0. Since we define an angle in standard position by its terminal side, we have a special type of angle whose terminal side lies on an axis, a quadrantal angle. this type of angle can have a measure of 0°, 90°, 180°, 270° or 360°. figure 7. quadrantal angles have a terminal side that lies along an axis. examples are shown.
Angles In Standard Position Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets

Comments are closed.