Administer Intramuscular Subcutaneous And Intradermal Injections

Injection Medicine Wikipedia Subcutaneous. intraosseous. intradermal. side effects. summary. injections deliver liquid medications, fluids, or nutrients directly into a person’s body. different types of injections include. To administer an sc injection, a 25 to 30 gauge, 3 8 in. to 5 8 in. needle is used. some subcutaneous injections come prefilled with the syringe attached. always confirm that the right size needle is appropriate for the patient before use. subcutaneous injections are usually given at a 45 to 90 degree angle. the angle is based on the amount of.
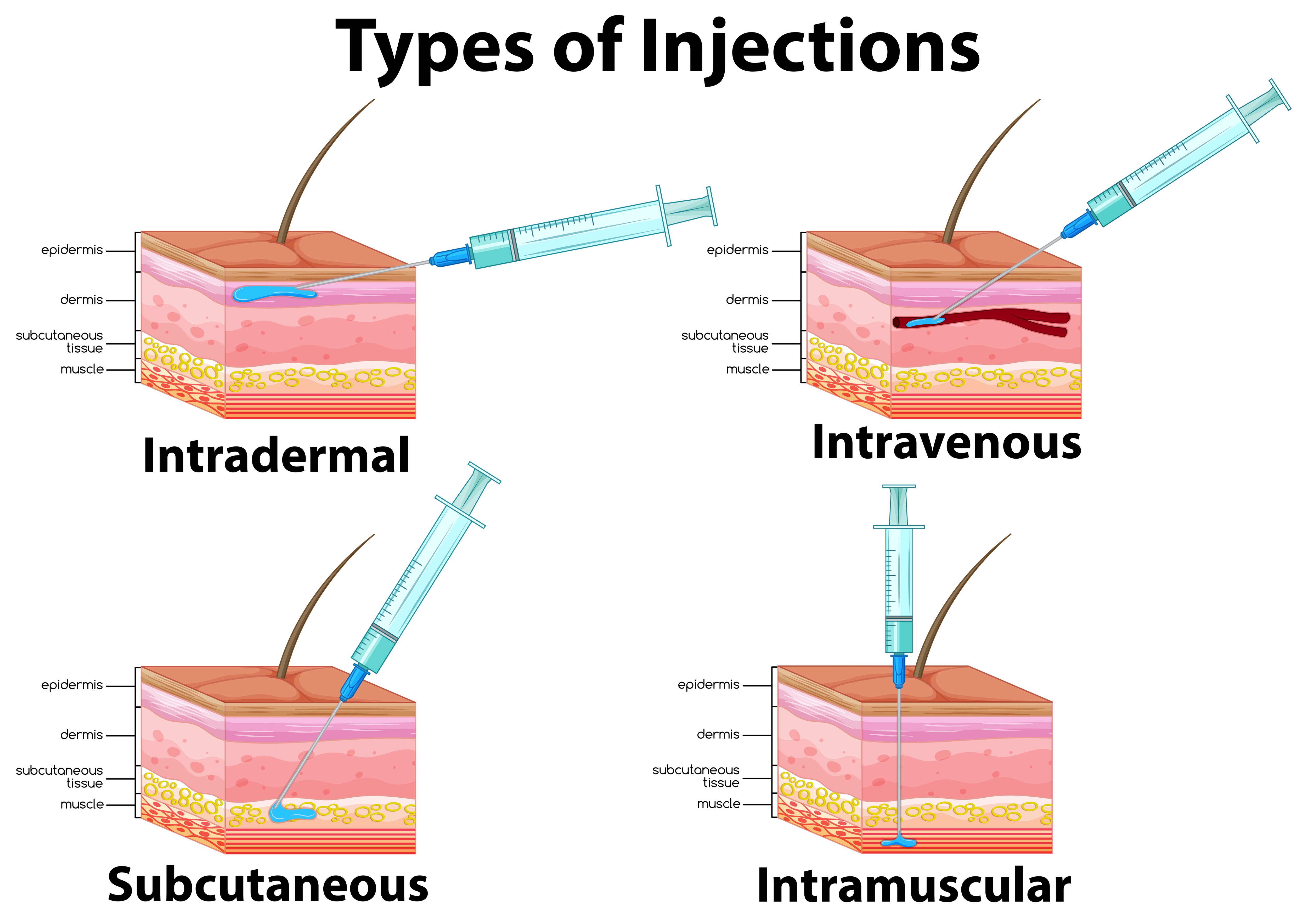
How To Do Deltoid Intramuscular Injections Balance My Hormones A video demonstrating administering a vaccine by subcutaneous injection can be found here. intramuscular route (im): intramuscular injections are administered into the muscle through the skin and subcutaneous tissue. the recommended site is based on age. use the correct needle length and gauge based on the age, weight, and gender of the. Intramuscular (im) injections. im injections are given deep into a muscle where the medication is then absorbed quickly by surrounding blood vessels. subcutaneous (sc) injections. sc injections are injected into the innermost layer of the skin called the subcutis or hypodermis, which is made up of a network of fat and collagen cells. Ellis demonstrates how to administer an intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injection.our critical nursing skills video tutorial series is taught by. Use a needle long enough to reach deep into the muscle. insert the needle at a 90° angle to the skin with a quick thrust. separate two injections given in the same deltoid muscle (or anterolateral thigh muscle, if using) by a minimum of 1". acromion process. • (bony prominence above deltoid).

Comments are closed.