Administering Subcutaneous Medication Nursing
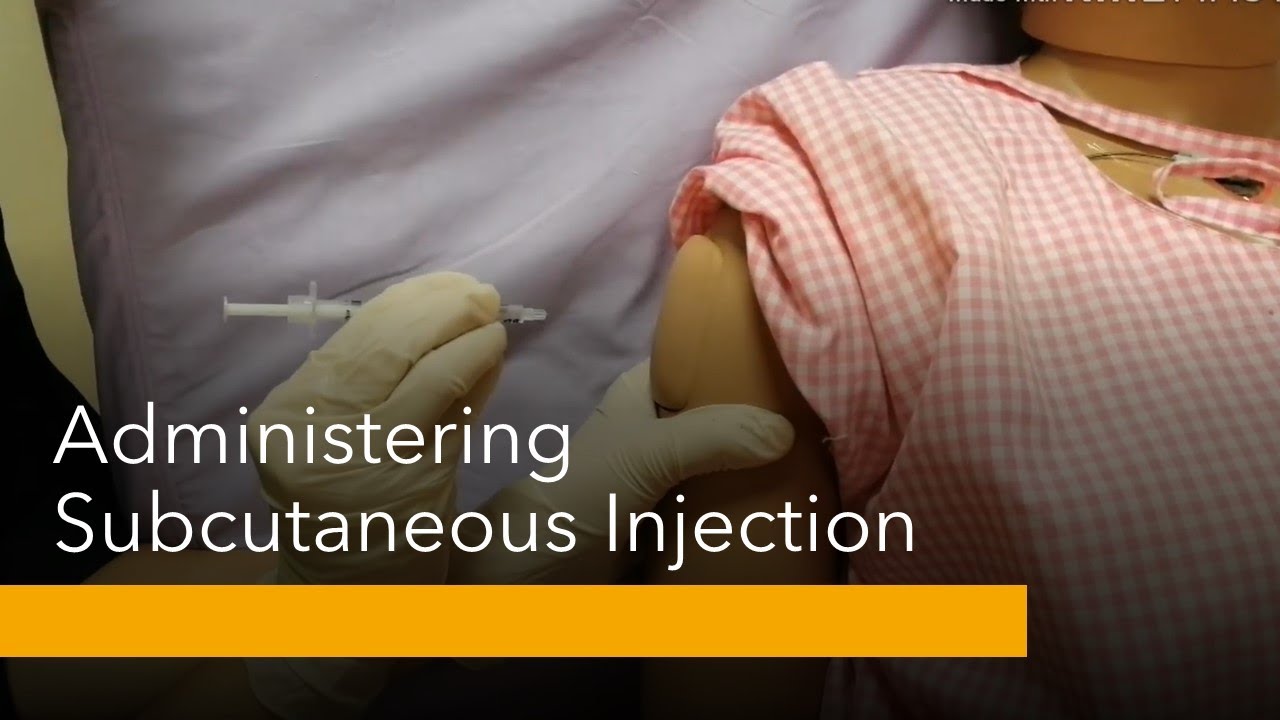
Pharmacological Nursing Administering Subcutaneous Injection Youtube Nurses can achieve safe and effective subcutaneous injections by following these steps: 1. wash hands thoroughly with soap and water or use an alcohol based hand sanitizer. decreases the risk of infection. 2. collect all necessary supplies and equipment: medication: correct dosage as prescribed. Figure 18.5.2 18.5. 2: common subcutaneous injection sites. prior to injecting the medication, inspect the skin area. avoid skin areas that are bruised, open, scarred, or over bony prominences. medical conditions that impair the blood flow to a tissue area contraindicate the use of subcutaneous injections in that area.

18 5 Administering Subcutaneous Medications Medicine Libretexts Nurses select the appropriate needle size for subcutaneous injection based on patient size. subcutaneous needles range in gauge from 25 31 and in length from ½ inch to ⅝ inch. prior to administering the injection, determine the amount of subcutaneous tissue present and use this information to select the needle length. Open resources for nursing (open rn) subcutaneous injections are administered into the adipose tissue layer called “subcutis” below the dermis. see an image of the subcutis (hypodermis) layer in figure 18.20. [1] medications injected into the subcutaneous layer are absorbed at a slow and steady rate. figure 18.20 subcutis layer of skin. To help prevent a wrong dose or wrong concentration error, two nurses are required to double check the medication before administration. the nurse should review laboratory results, such as partial thromboplastic time (ptt) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) that characterize blood coagulation, before administering heparin to. According to a recent study conducted by aarp and the national alliance for caregiving, many family caregivers experience stress when managing the complex care of older relatives, particularly in regard to the administration of medication. 1 advances in the management of diseases like diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune diseases—as well as in preventive care for conditions such as thrombosis.

Subcutaneous Injection Technique For Nurses To help prevent a wrong dose or wrong concentration error, two nurses are required to double check the medication before administration. the nurse should review laboratory results, such as partial thromboplastic time (ptt) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) that characterize blood coagulation, before administering heparin to. According to a recent study conducted by aarp and the national alliance for caregiving, many family caregivers experience stress when managing the complex care of older relatives, particularly in regard to the administration of medication. 1 advances in the management of diseases like diabetes, cancer, and autoimmune diseases—as well as in preventive care for conditions such as thrombosis. Administration of subcutaneous injections: nurses can help family caregivers enhance their knowledge, experience, and skill in managing injectable treatments minimize anxiety for the family caregiver and harm to the recipient. performing new procedures can be frightening, especially to family caregivers, who may not be. Transcript. subcutaneous medication administration is the method of delivering small volumes of medication less than 2 milliliters into the tissue layer just under the skin. it is a route commonly used for administering anticoagulant medications, epinephrine, insulin, and some immunizations. the absorption and onset of action are slower than.
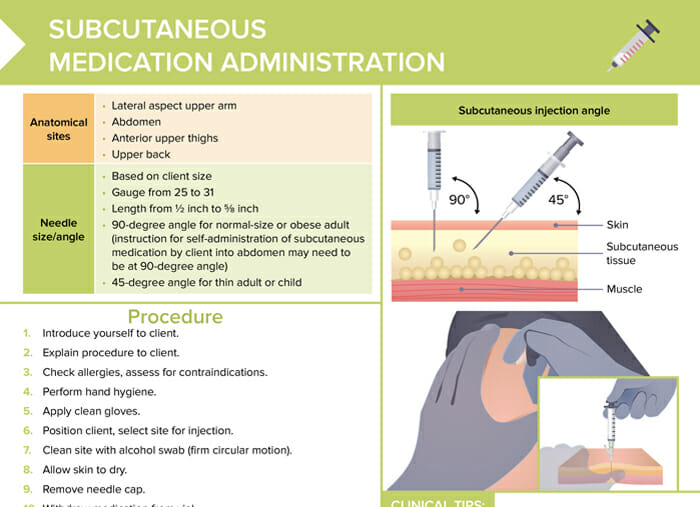
Subcutaneous Injections Free Cheat Sheet Lecturio Administration of subcutaneous injections: nurses can help family caregivers enhance their knowledge, experience, and skill in managing injectable treatments minimize anxiety for the family caregiver and harm to the recipient. performing new procedures can be frightening, especially to family caregivers, who may not be. Transcript. subcutaneous medication administration is the method of delivering small volumes of medication less than 2 milliliters into the tissue layer just under the skin. it is a route commonly used for administering anticoagulant medications, epinephrine, insulin, and some immunizations. the absorption and onset of action are slower than.

Comments are closed.