All About Blood Clot Treatment And Prevention
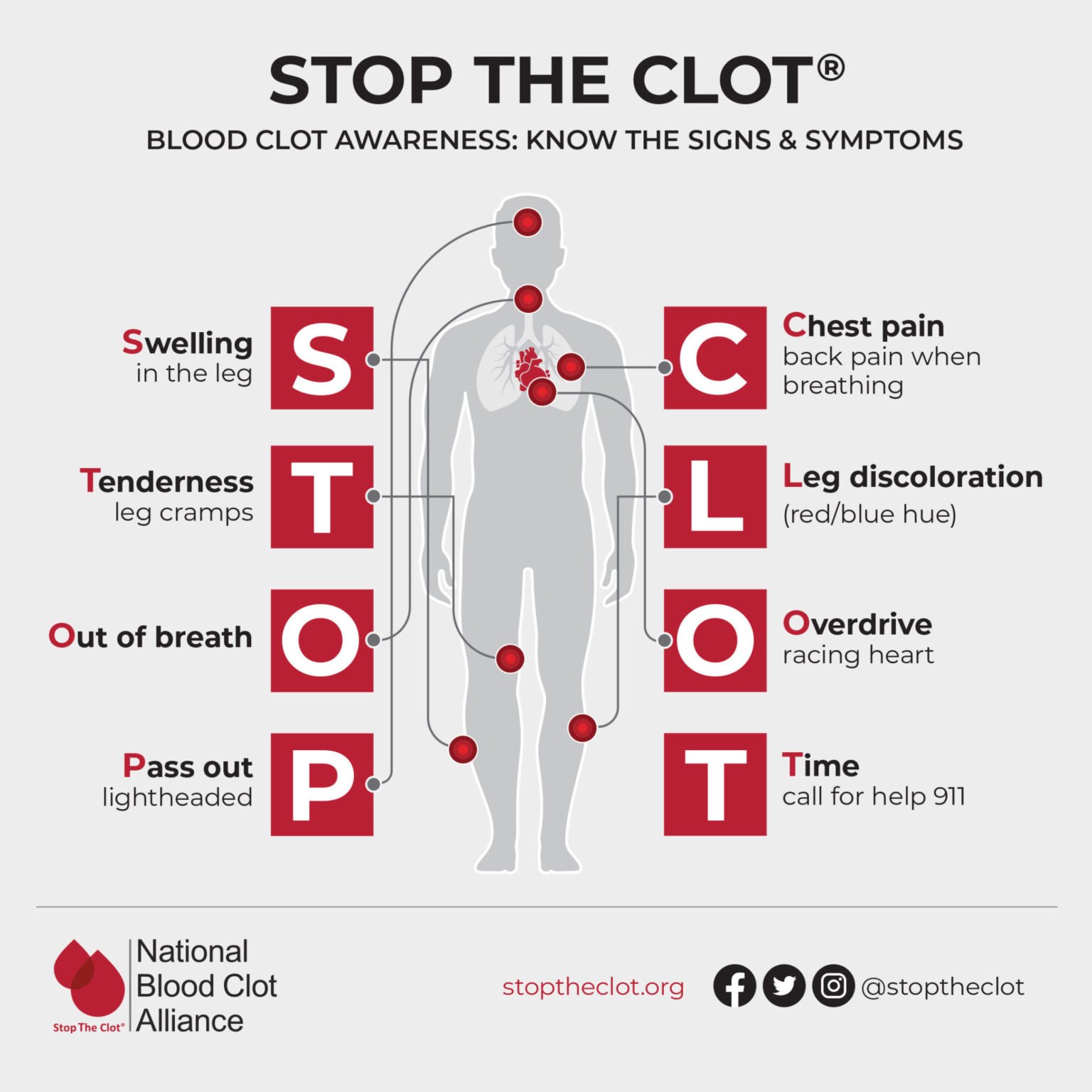
Blood Clot Info Risks Symptoms Treatment Prevention These types of blood clot are very serious and require urgent treatment. in this article, we outline the various treatments for blood clots and provide tips on the prevention and long term. Any blood clot may cause swelling, tingling, tenderness, or a feeling of warmth. if an artery that leads to the brain is clogged, neurological symptoms such as confusion or paralysis can occur, possibly indicating a stroke. a blood clot in the leg might cause the leg to swell so that it's noticeably larger than the other leg and may be a sign.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/treating-blood-clots-1746090_final-9a9eea79ed4542429fcbd319ba103f7d.jpg)
How Blood Clots Are Treated There are three general categories of drugs that are commonly used to prevent or treat blood clots (thrombosis): anticoagulants, fibrinolytics, and antiplatelet medications. some of these (pradaxa, angiomax, reopro) may be unfamiliar, while others (warfarin, heparin, aspirin) are generally household names. Prevent the clot from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs. reduce the chances of another dvt. dvt treatment options include: blood thinners. these medicines, also called anticoagulants, help prevent blood clots from getting bigger. blood thinners reduce the risk of developing more clots. blood thinners may be taken by mouth or given by. Preventing blood clots. you can help prevent blood clots if you: wear loose fitting clothes, socks, or stockings. raise your legs 6 inches above your heart from time to time. wear special stockings (called compression stockings) if your doctor prescribes them. do exercises your doctor gives you. A blood clot can affect any area of the body, but some regions are more susceptible to blood clots than others. the most common symptoms and regions of a blood clot are: in the arms or legs: deep vein thrombosis (dvt) causes swelling in the affected limb. in the heart: a heart attack can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, arm pain, jaw pain.

Blood Clot Prevention Preventing blood clots. you can help prevent blood clots if you: wear loose fitting clothes, socks, or stockings. raise your legs 6 inches above your heart from time to time. wear special stockings (called compression stockings) if your doctor prescribes them. do exercises your doctor gives you. A blood clot can affect any area of the body, but some regions are more susceptible to blood clots than others. the most common symptoms and regions of a blood clot are: in the arms or legs: deep vein thrombosis (dvt) causes swelling in the affected limb. in the heart: a heart attack can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, arm pain, jaw pain. If you have a high risk of a blood clot and a low risk of bleeding, a low dose, “blood thinning” medicine may help. traveling and blood clots. perform simple exercises. flex and extend the ankles and knees and contract the calf muscles at regular intervals. walk around. get up and walk while traveling every hour. consider compression. If you have a history of blood clots, your doctor may prescribe blood thinners. you may take blood thinner medicine by mouth (such as warfarin or aspirin) or as a shot (such as heparin). side effects of warfarin and heparin include heavy bleeding, severe headaches, and dizziness. warfarin also can interact with over the counter medicines such.

Comments are closed.