All About Protists
Protists Definition Types Characteristics And Examples Protist definition. protists are a group of loosely connected, mostly unicellular eukaryotic organisms that are not plants, animals or fungi. there is no single feature such as evolutionary history or morphology common to all these organisms and they are unofficially placed under a separate kingdom called protista. Protist, any member of a group of diverse eukaryotic, predominantly unicellular microscopic organisms. they may share certain morphological and physiological characteristics with animals or plants or both. the term protist typically is used in reference to a eukaryote that is not a true animal, plant, or fungus or in reference to a eukaryote.
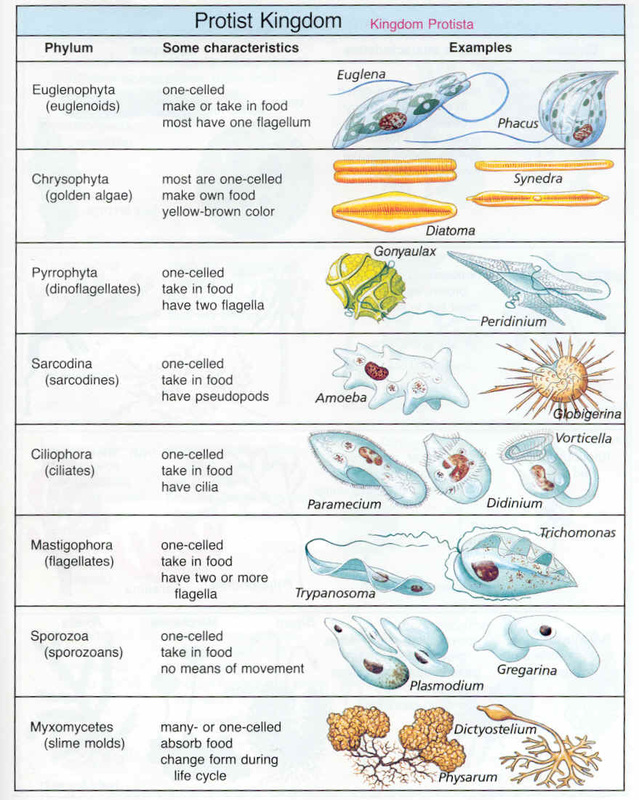
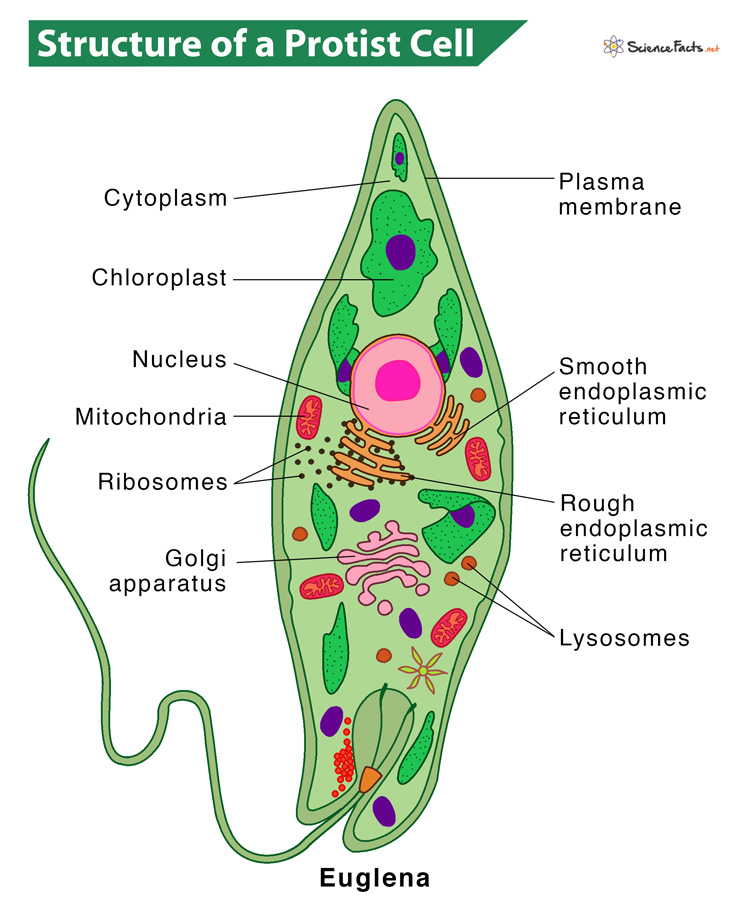
Protists Paramecium Some protists even have an eyespot, an organelle that helps them to detect light, so they can move toward or away from light as desired. all of their cellular components remain enveloped within a cell membrane or cell wall. in other protists, glassy silica based shells or pellicles of interlocking protein strips also encase them. Fungi. embryophyta (land plants) a protist ( ˈproʊtɪst proh tist) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a polyphyletic grouping of several independent clades that evolved from the last eukaryotic common ancestor. #protists #organisms #ngscience protists are a group of mostly single celled organisms, but some like giant kelp are large and multicellular. the strange thi. Protists are a diverse collection of organisms that do not fit into animal, plant, bacteria or fungi groups. while exceptions exist, they are primarily microscopic and made up of a single cell.

Comments are closed.