Anatomical Terms Of Movements

Anatomical Movements Of The Human Body Geeky Medics Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion are terms used to describe movements at the ankle. they refer to the two surfaces of the foot; the dorsum (superior surface) and the plantar surface (the sole). dorsiflexion refers to flexion at the ankle, so that the foot points more superiorly. dorsiflexion of the hand is a confusing term, and so is rarely used. Introduction. the movements produced at joints by muscles are given specific anatomical names, often referred to as “anatomical terms of motion”. we usually make the assumption that the body is in normal resting anatomical position, and that joint movement occurs from this resting position.
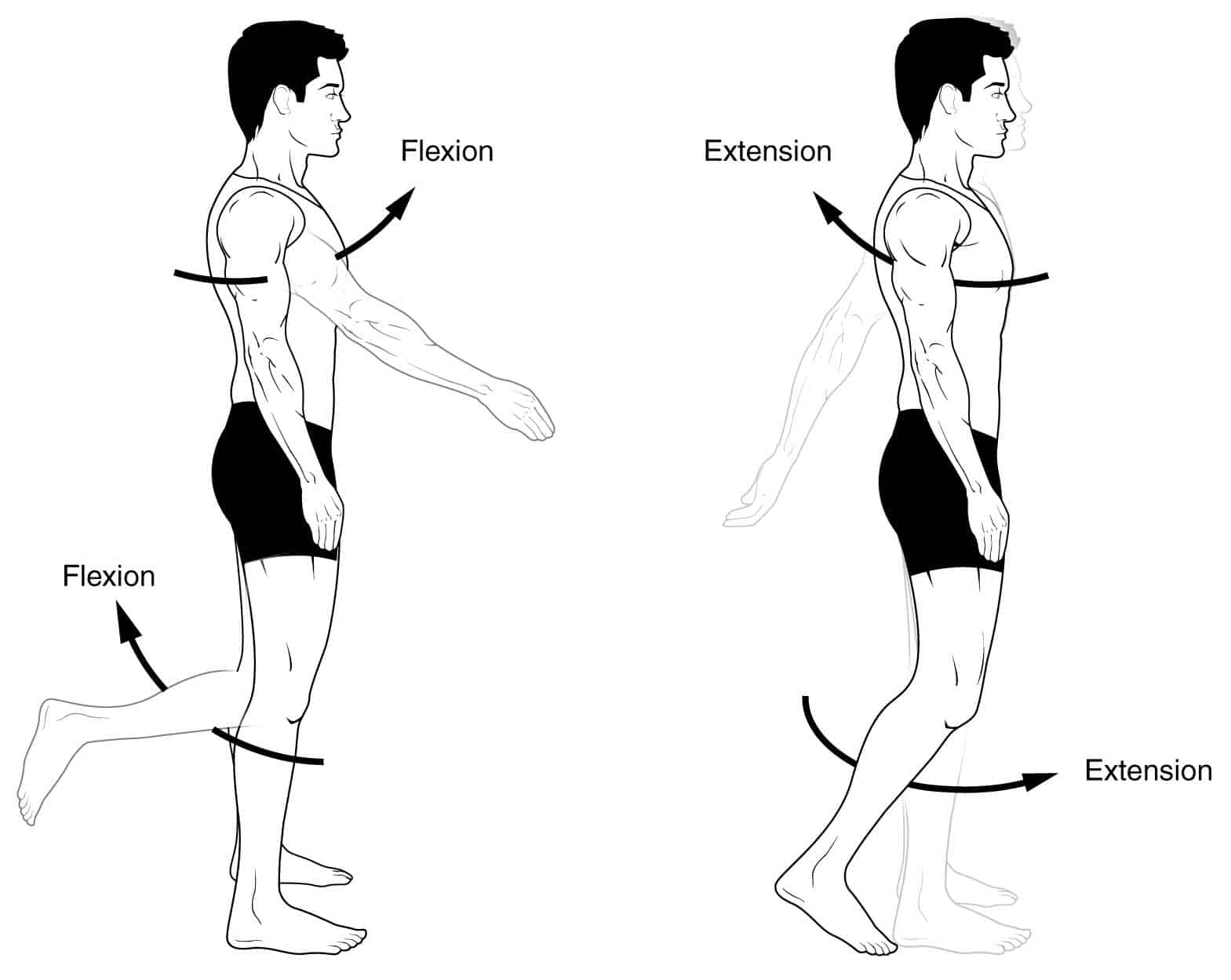
Anatomical Terms Of Movement Flexion Rotation Teachmeanatomy E. motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. the terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. anatomists and others use a unified set of. Circumduction is a special type of movement that is actually a combination of many other ones. the overall movement starts with flexion, followed by abduction, extension and finally adduction. the order must be sequential, but it can start from either flexion or adduction. the result is a circular movement. Figure 9.5.2 – movements of the body, part 2: (g) supination of the forearm turns the hand to the palm forward position in which the radius and ulna are parallel, while forearm pronation turns the hand to the palm backward position in which the radius crosses over the ulna to form an “x.” (h) dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle joint moves the top of the foot toward the leg, while. Figure 9.13 movements of the body, part 2 (g) supination of the forearm turns the hand to the palm forward position in which the radius and ulna are parallel, while forearm pronation turns the hand to the palm backward position in which the radius crosses over the ulna to form an "x." (h) dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle joint moves the top of the foot toward the leg, while plantar.

Comments are closed.