Anomalous Origin Of The Left Coronary Artery From Pulmonary Artery Alcapa Repair By Translocation
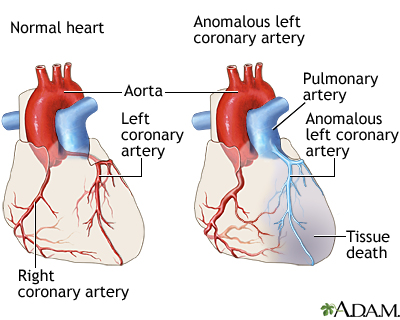
Anomalous Left Coronary Artery From The Pulmonary Artery Medline Anomalous means irregular. when the left coronary artery is attached to the pulmonary artery instead of the aorta, two main differences in the blood flow feeding the heart occur that can quickly cause the tissue of the heart to become damaged and die: not enough blood reaches the heart because of “coronary steal.”. Surgery is needed to treat anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (alcapa). options for repair include detaching the anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery and moving it over to the aorta directly (translocation) or creating a natural tunnel from its abnormal location to the aorta (takeuchi repair).

Anomalous Origin Of Left Coronary Artery From The Pulmonary A Anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (alcapa) syndrome is a rare congenital heart condition that affects approximately 1 in 300,000 live births [1]. it comprises between 0.24 and 0.46% of all congenital heart disease [2]. first clinically described in 1933 by edward bland, paul dudley white, and joseph garland. Anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (alcapa) is a rare but potentially fatal congenital coronary anomaly associated with early infant mortality and sudden adult death. by the development or lack of coronary collateral, it can be classified as infantile or adult type. Introduction. an anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (alcapa) is a rare congenital anomaly with an incidence of 1 in 300 000 live births, which corresponds to 0.25–0.5% of all congenital heart disease [1, 2]. Clinical presentation of alcapa depends on the magnitude of collateral vessels that develop to the lca territory. without a significant collateral blood supply, myocardial ischemia occurs in infancy when the neonatal elevated pulmonary vascular resistance normalizes, and blood flow in the lca is shunted toward the lower pressure pulmonary artery. 2 with the onset of ischemia, myocardial.

Comments are closed.