Are Enzymes Consumed During A Chemical Reaction
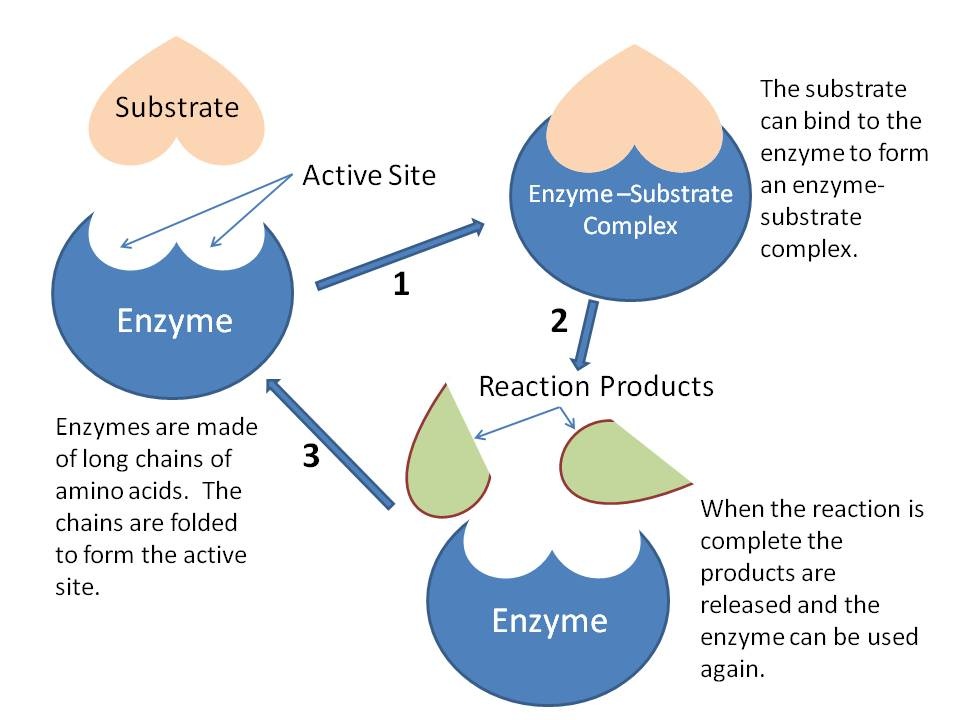
Enzymes Do Chemical Reaction At Anna Schofield Blog Explanation: enzymes are biological catalysts. catalysts are not consumed in a chemical reaction, they just speed up the rate of the chemical reaction without being used up. well, technically, they give an alternative pathway for a reaction to happen and are used up at some point, but then a second chemical reaction with the alternative pathway. An enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. a systematic process is used to name and classify … 5.1: enzymes chemistry libretexts.
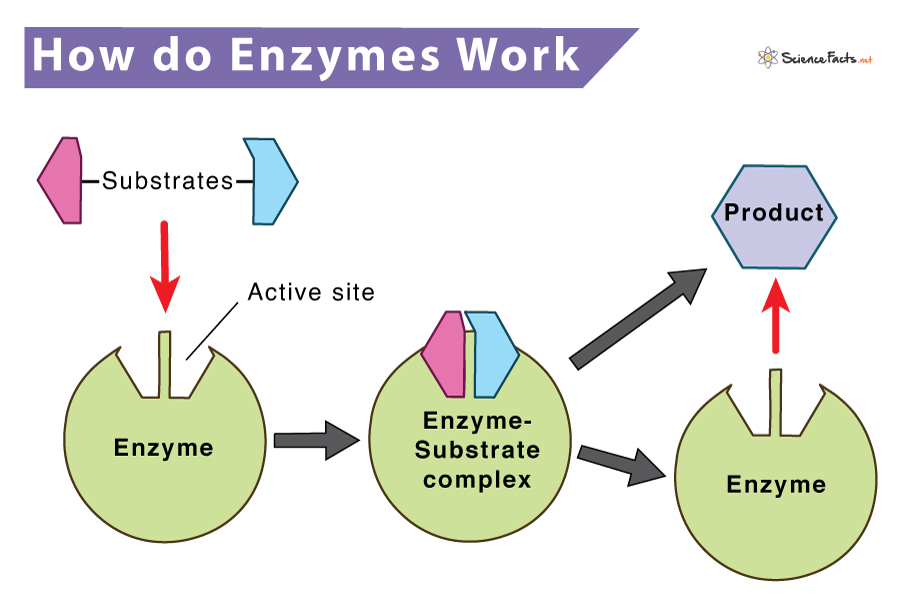
Enzyme Definition Types Structure Functions Diagram Enzymes. a substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are called enzymes.almost all enzymes are proteins, made up of chains of amino acids, and they perform the critical task of lowering the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell. These are not consumed in overall reactions. enzymes are required in a few amounts during chemical reactions. these have active sites where the interaction with the substrate occurs. enzymes are extremely specific to their substrate. structure of enzymes. as discussed earlier, most enzymes are proteins. Enzymes are proteins that speed up reactions by reducing the activation energy. each enzyme typically binds only one substrate. enzymes are not consumed during a reaction; instead they are available to bind new substrates and catalyze the same reaction repeatedly. The cell responds to the abundance of specific products by slowing down production during anabolic or catabolic reactions. such reaction products may inhibit the enzymes that catalyzed their production through the mechanisms described above. figure \(\pageindex{7}\): metabolic pathways are a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes.
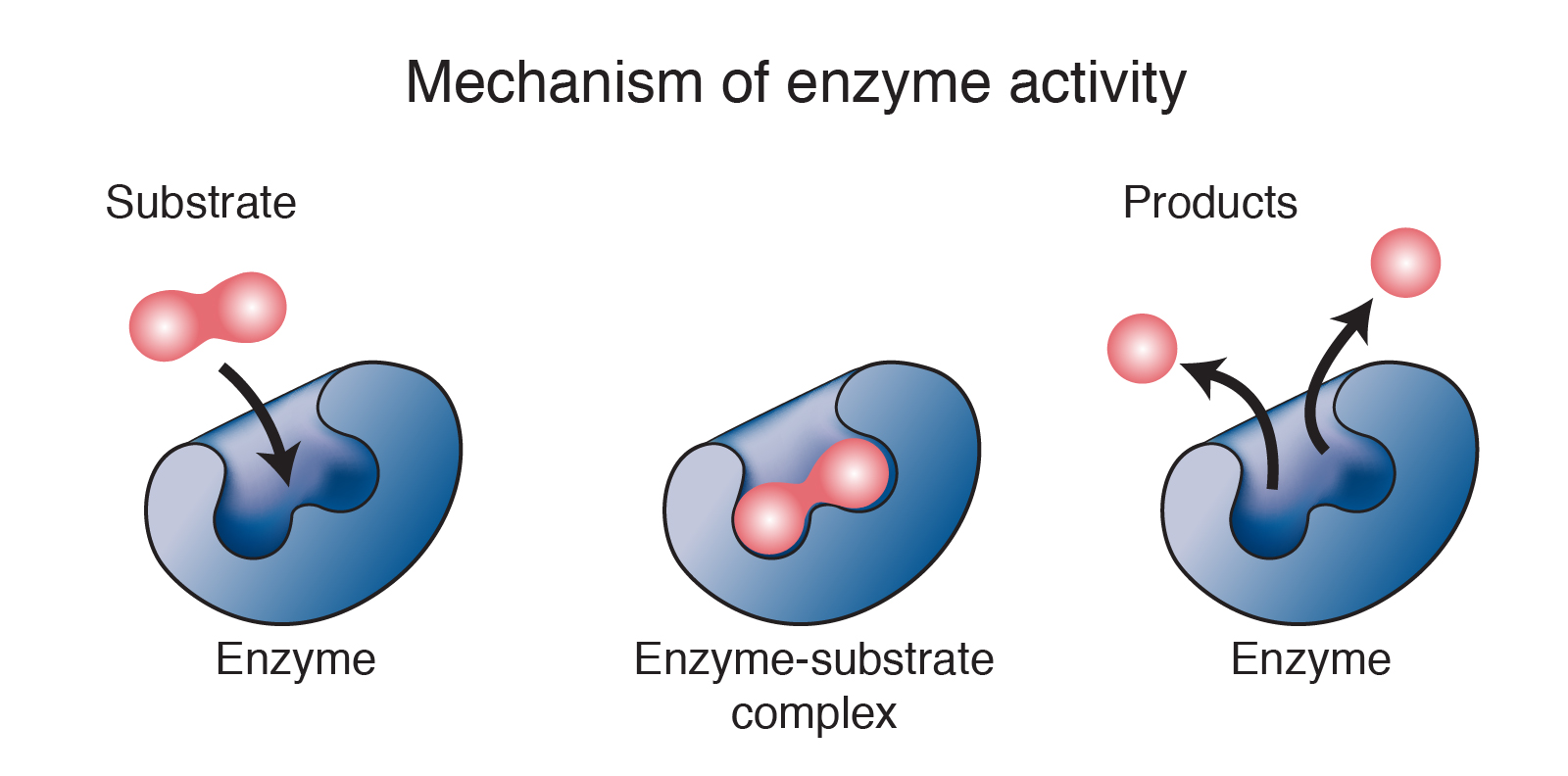
Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that speed up reactions by reducing the activation energy. each enzyme typically binds only one substrate. enzymes are not consumed during a reaction; instead they are available to bind new substrates and catalyze the same reaction repeatedly. The cell responds to the abundance of specific products by slowing down production during anabolic or catabolic reactions. such reaction products may inhibit the enzymes that catalyzed their production through the mechanisms described above. figure \(\pageindex{7}\): metabolic pathways are a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes. An enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. a systematic process is used to name and classify enzymes. a substrate binds to a specific region on an enzyme known as the active site, where the substrate can be converted to product. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. they are vital for life and.

Enzymes Chemical Reactions Ppt Download An enzyme is a biological catalyst, a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed or consumed in the reaction. a systematic process is used to name and classify enzymes. a substrate binds to a specific region on an enzyme known as the active site, where the substrate can be converted to product. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. they are vital for life and.

Enzymes Definition Classification Functions

Comments are closed.