Are Phytoplankton Consumers

Animal Food Chain Ocean Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. they are eaten by primary consumers like zooplankton, small fish, and crustaceans. primary consumers are in turn eaten by fish, small sharks, corals, and baleen whales. top ocean predators include large sharks, billfish, dolphins, toothed whales, and large seals. Consumers are divided into herbivores and carnivores and are typically further divided into 1st, 2nd or 3rd level consumers. for example, many zooplankton in the marine environment are herbivorous consumers. they form the 2nd level of the trophic pyramid and consume phytoplankton.
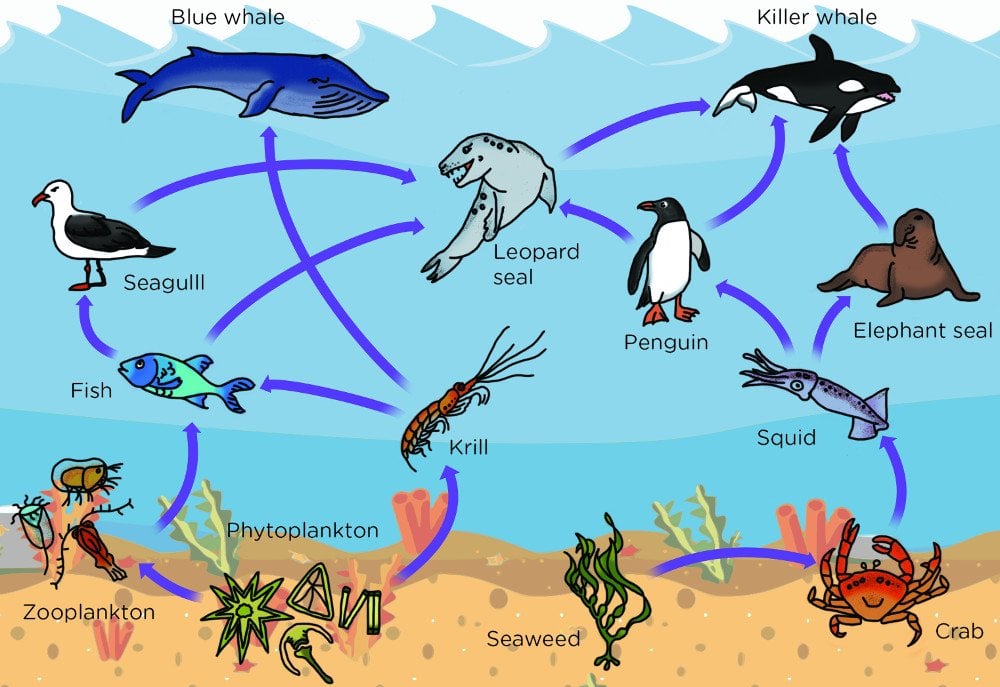
What Is Phytoplankton Phytoplankton ( ˌfaɪtoʊˈplæŋktən ) are the autotrophic (self feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. the name comes from the greek words φυτόν (phyton), meaning ' plant ', and πλαγκτός (planktos), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. [1][2][3] phytoplankton obtain their. Phytoplankton are the base of several aquatic food webs and provide food for many sea creatures. they are similar to plants and require sunlight and nutrients to grow, but they are not consumers themselves. A marine food web is a food web of marine life. at the base of the ocean food web are single celled algae and other plant like organisms known as phytoplankton. the second trophic level (primary consumers) is occupied by zooplankton which feed off the phytoplankton. higher order consumers complete the web. Phytoplankton are microscopic, single celled organisms that live near the ocean surface and produce oxygen and organic carbon via photosynthesis. they are the base of the marine food chain and play a key role in the carbon cycle and climate system.

Comments are closed.