Aural Skills Learning Simplified By Professional Teachers

Aural Skills Learning Simplified By Professional Teachers Our music aural training programme, your teacher will be able to identify your areas of weakness, focus on them, so as to ensure you are up to standard and ready to take your examination. with aural skills training classes available throughout the week, our students leave happy and satisfied, well aware of their weekly progress. Use music and songs. one of the best ways to teach auditory learners is music and song. you can use songs to teach any subject, from math to history and language arts. the lyrics can be written by you or by students; sometimes, kids enjoy writing their lyrics because they feel they can express themselves better this way.

Aural Skills Learning Simplified By Professional Teachers Using foundations of aural skills as a supplement. foundations of aural skills is designed to help aural skills instructors move in new directions. nevertheless, curricula take time to change. one benefit of an open resource is that it can be used as a supplement to existing criteria without added cost to students. Play background music – when focussing, having background music playing will help you focus as an auditory learner. join in discussions – auditory learners are good at having conversations and debating. learning through others is a great activity. repetition – repeating facts and information out loud is a great way to study for auditory. In this section, we will explore some auditory learning techniques to use as a teacher to help students learn through auditory learning. 1. mnemonics. one of the easiest but effective auditory learning techniques to employ as a teacher is mnemonics. mnemonics are memory aids that use a combination of sounds, words, and phrases to help students. Strategies for teaching fundamentals. in teaching basic aural skills, grouping families of constructs that have some similarity but clear differences is a successful tactic. for example, work with upward intervals first, then downward. avoid overuse of a crutch, such as using the first two notes of a familiar tune, to form the basis of.

Aural Learning Strategies Mytecare In this section, we will explore some auditory learning techniques to use as a teacher to help students learn through auditory learning. 1. mnemonics. one of the easiest but effective auditory learning techniques to employ as a teacher is mnemonics. mnemonics are memory aids that use a combination of sounds, words, and phrases to help students. Strategies for teaching fundamentals. in teaching basic aural skills, grouping families of constructs that have some similarity but clear differences is a successful tactic. for example, work with upward intervals first, then downward. avoid overuse of a crutch, such as using the first two notes of a familiar tune, to form the basis of. This oer aural skills text is designed to support aural skills instruction at introductory levels, particularly college university conservatory classes with names like “aural skills 1,”“eartraining1,”“musicianship1,”“sight singing1,”etc. the text may also be useful for teachers of high school ap. The chapter closes with these recommendations: school music teachers should incorporate aural skills practice and assessment into multiple musical course offerings; infuse instruction and assessment with relevant musical material; begin aural skills instruction early in the music curriculum; and incorporate technological tools into instruction for assessment purposes when appropriate.
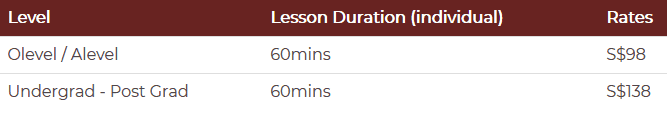
Aural Skills Learning Simplified By Professional Teachers This oer aural skills text is designed to support aural skills instruction at introductory levels, particularly college university conservatory classes with names like “aural skills 1,”“eartraining1,”“musicianship1,”“sight singing1,”etc. the text may also be useful for teachers of high school ap. The chapter closes with these recommendations: school music teachers should incorporate aural skills practice and assessment into multiple musical course offerings; infuse instruction and assessment with relevant musical material; begin aural skills instruction early in the music curriculum; and incorporate technological tools into instruction for assessment purposes when appropriate.

Aural Skills Learning Simplified By Professional Teachers

Comments are closed.