Benjamin Bloom S Taxonomy
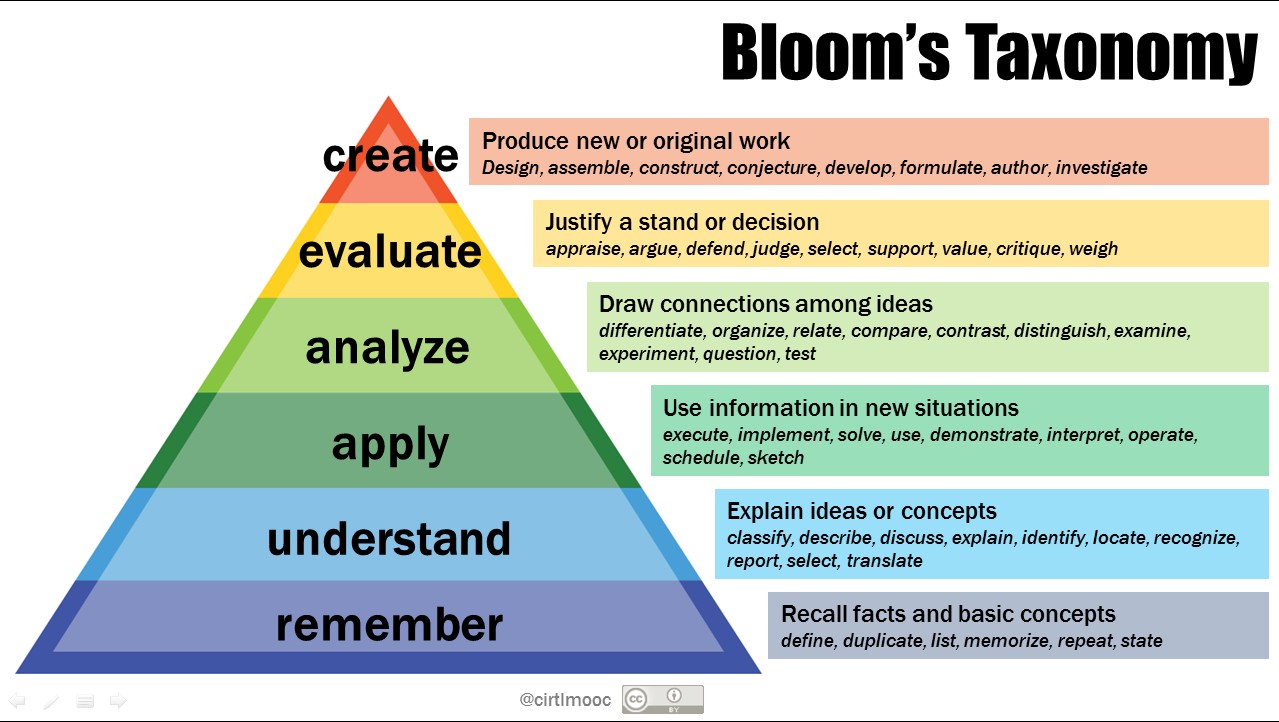
юааbloomтащsюаб юааtaxonomyюаб Center For Teaching Vanderbilt University This taxonomy was originally created by Benjamin Bloom in 1956 to categorize a continuum This document is a blank table with the categories for Bloom’s taxonomy marked on each axis You can use it The revised version of Benjamin Bloom’s taxonomy (Anderson and Krathwohl, 2001) categorizes the cognitive complexity of tasks These categories help determine the difficulty of learning outcomes,
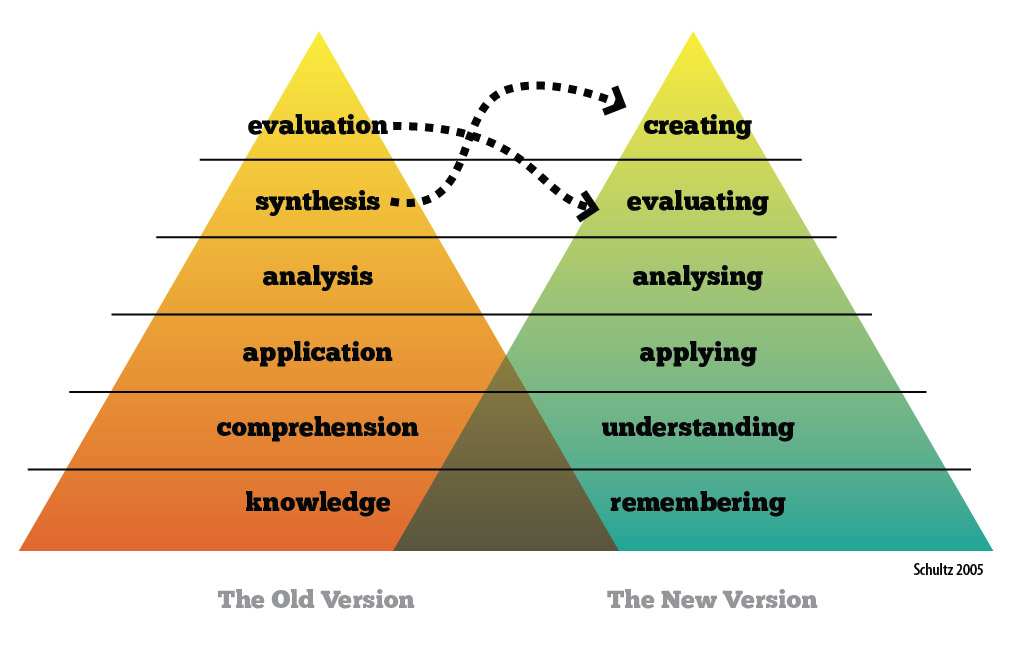
юааbloomтащsюаб юааtaxonomyюаб Levels Of Understanding тау Psia Aasi Northwest Careful design of questions can enable the testing of higher order skills Below is a graphic view of the Bloom's Taxonomy (developed by Benjamin Bloom in 1956) highlighting the correlation between Educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom identified categories of learning that His order of learning behaviours is called Bloom's Taxonomy, from the title of his influential publication Since This tenet also harkens back to Benjamin Bloom’s famous 2 Sigma Problem, where he demonstrates that students tutored in one-on-one settings perform two standard deviations better than those in For the Standard of Competency, the Forms of Comprehension are based on Benjamin Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives and the cognitive domain, which involves knowledge and the development of

Comments are closed.