Bernoulli S Equation
.PNG)
Derivation Applications Of Bernoulli Principal Presentation Physics Bernoulli's principle is a key concept in fluid dynamics that relates pressure, speed and height. Summary. bernoulli’s equation states that the sum on each side of the following equation is constant, or the same at any two points in an incompressible frictionless fluid: p1 1 2ρv2 1 ρgh1 = p2 1 2ρv2 2 ρgh2. bernoulli’s principle is bernoulli’s equation applied to situations in which depth is constant.
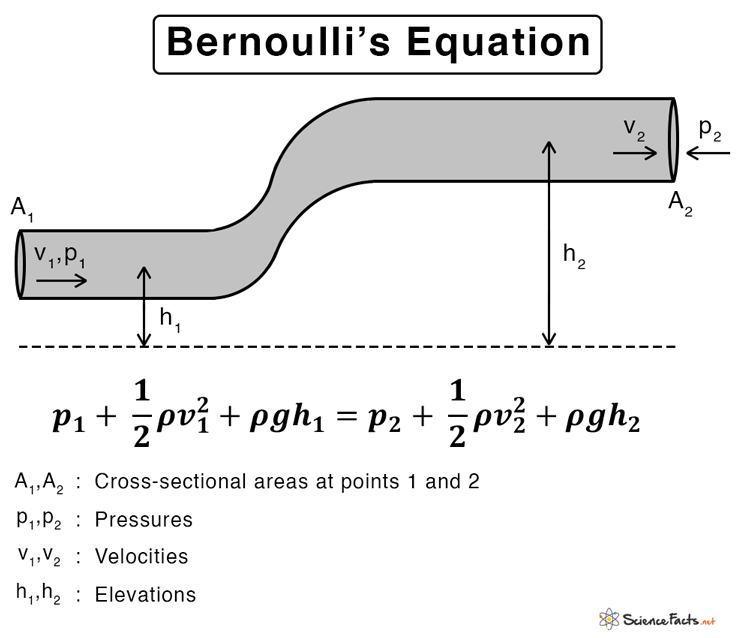
Bernoulli S Principle Equation Bernoulli’s equation formula is a relation between pressure, kinetic energy, and gravitational potential energy of a fluid in a container. the formula for bernoulli’s principle is given as follows: \ (\begin {array} {l}p \frac {1} {2} \rho v^2 \rho gh =constant\end {array} \). Rearranging the equation gives bernoulli’s equation: p1 1 2ρv2 1 ρgy1 = p2 1 2ρv2 2 ρgy2. this relation states that the mechanical energy of any part of the fluid changes as a result of the work done by the fluid external to that part, due to varying pressure along the way. Analyzing bernoulli’s equation. according to bernoulli’s equation, if we follow a small volume of fluid along its path, various quantities in the sum may change, but the total remains constant. bernoulli’s equation is, in fact, just a convenient statement of conservation of energy for an incompressible fluid in the absence of friction. The equation states that the static pressure ps in the flow plus the dynamic pressure, one half of the density rho (ρ) times the velocity v squared, is equal to a constant throughout the flow. we call this constant the total pressure pt of the flow. pt = ps ρ⋅v2 2.

Comments are closed.