Bohr Model Of The Hydrogen Atom

Bohr Model Description Hydrogen Development Facts Britannica The bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell model. as a theory, it can be derived as a first order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory . Historically, bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the very first model of atomic structure that correctly explained the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen. the model has a special place in the history of physics because it introduced an early quantum theory, which brought about new developments in scientific thought and later culminated in.

Bohr S Atomic Model вђ Overview Importance Expii Bohr model, description of the structure of atoms, especially that of hydrogen, proposed (1913) by the danish physicist niels bohr. the bohr model of the atom, a radical departure from earlier, classical descriptions, was the first that incorporated quantum theory and was the predecessor of wholly quantum mechanical models. the bohr model and. Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom also correctly predicts the spectra of some hydrogen like ions. hydrogen like ions are atoms of elements with an atomic number z larger than one (z = 1 for hydrogen) but with all electrons removed except one. for example, an electrically neutral helium atom has an atomic number z = 2. Learn about the bohr model of the hydrogen atom, which explains the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen using quantized orbits and energies. find out the equation, formula, limitations and examples of this model. The great danish physicist niels bohr (1885–1962) made immediate use of rutherford’s planetary model of the atom. (figure \ (\pageindex {1}\)). bohr became convinced of its validity and spent part of 1912 at rutherford’s laboratory. in 1913, after returning to copenhagen, he began publishing his theory of the simplest atom, hydrogen.
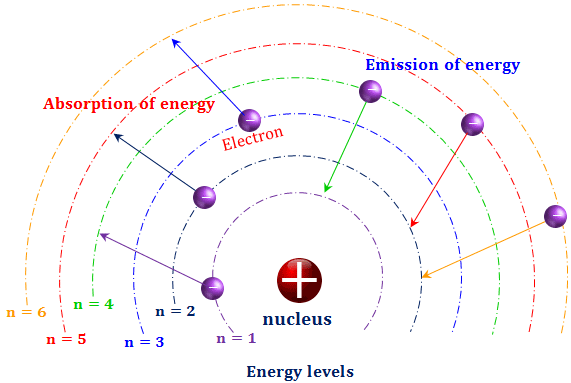
Bohr Model Hydrogen Atom Postulates Energy Levels Learn about the bohr model of the hydrogen atom, which explains the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen using quantized orbits and energies. find out the equation, formula, limitations and examples of this model. The great danish physicist niels bohr (1885–1962) made immediate use of rutherford’s planetary model of the atom. (figure \ (\pageindex {1}\)). bohr became convinced of its validity and spent part of 1912 at rutherford’s laboratory. in 1913, after returning to copenhagen, he began publishing his theory of the simplest atom, hydrogen. Bohr's model. in 1913, a danish physicist, niels bohr (1885–1962; nobel prize in physics, 1922), proposed a theoretical model for the hydrogen atom that explained its emission spectrum. bohr’s model required only one assumption: the electron moves around the nucleus in circular orbits that can have only certain allowed radii. 1 ry = e4me 8ϵ2 0h2 = 2.18 × 10 − 18 j. and this simplifies the allowed energies predicted by the bohr model (equation 1.8.11) as. en = − (2.18 × 10 − 18)z2 n2 j = − z2 n2 ry. hence, the energy of the electron in an atom also is quantized. equation 1.8.12 gives the energies of the electronic states of the hydrogen atom.

Comments are closed.