Categorг A Divergent Boundary Geoscience Education

Divergent Boundary Definition Examples Lesson Study Depending on the conditions, rifts can grow into very large lakes and even oceans. figure 2.4.1 2.4. 1: normal faults that occur at divergent boundaries can result in horsts and grabens. (by gregors from usgs; public domain via wikimedia commons.) while seemingly occurring at random, rifting is dictated by two factors. Figure 2.4.1 2.4. 1: faulting that occurs in divergent boundaries. in places where the continental plates are very thick, they reflect so much heat back into the mantle it develops strong convection currents that push super heated mantle material up against the overlying plate, softening it. tensional forces created by this convective upwelling.
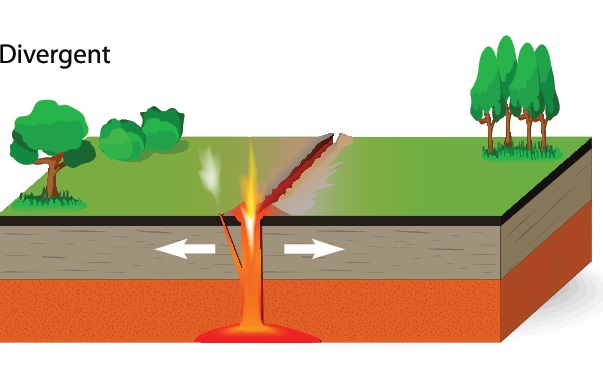
Divergent Boundary Map Most divergent boundaries are located along mid ocean oceanic ridges (although some are on land). the mid ocean ridge system is a giant undersea mountain range, and is the largest geological feature on earth; at 65,000 km long and about 1000 km wide, it covers 23% of earth’s surface (figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1). because the new crust formed at the. Allows you to view plate motions from the past 200 million years, as well as predicted motions 25 million years into the future. information on plate tectonics, including animations of plate motions for the past 750 million years. detailed maps showing the paleogeography from different periods and time slices for selected regions. A plate may contain both continent and ocean, but depending on the proportion, category of the plate is determined. generally, oceanic plates are denser than continental plates. where two plates come side by side, they can converge (called convergent boundary ), they may diverge from each other ( divergent boundary ) and may slide past each other ( transform boundary ). A transform plate boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other, horizontally. a well known transform plate boundary is the san andreas fault, which is responsible for many of california’s earthquakes. a single tectonic plate can have multiple types of plate boundaries with the other plates that surround it.

Divergent Boundary A plate may contain both continent and ocean, but depending on the proportion, category of the plate is determined. generally, oceanic plates are denser than continental plates. where two plates come side by side, they can converge (called convergent boundary ), they may diverge from each other ( divergent boundary ) and may slide past each other ( transform boundary ). A transform plate boundary occurs when two plates slide past each other, horizontally. a well known transform plate boundary is the san andreas fault, which is responsible for many of california’s earthquakes. a single tectonic plate can have multiple types of plate boundaries with the other plates that surround it. Deep ocean circulation. describes in a simple way the effects of temperature on density and the initiation of downward movement in the oceans. learn how bottom currents scour and sort sediments, thus affecting what kind of bottom develops in an area. describes the general circulation pattern of the earth’s oceans. The application of both of these lines of prior knowledge results in students concluding the two sides of a divergent boundary are the same plate. retention of these alternative concepts prevents conceptual change from occurring during the period of instruction and results in students not recognizing divergent boundaries as plate boundaries, leading them to incorrectly count the number of plates.
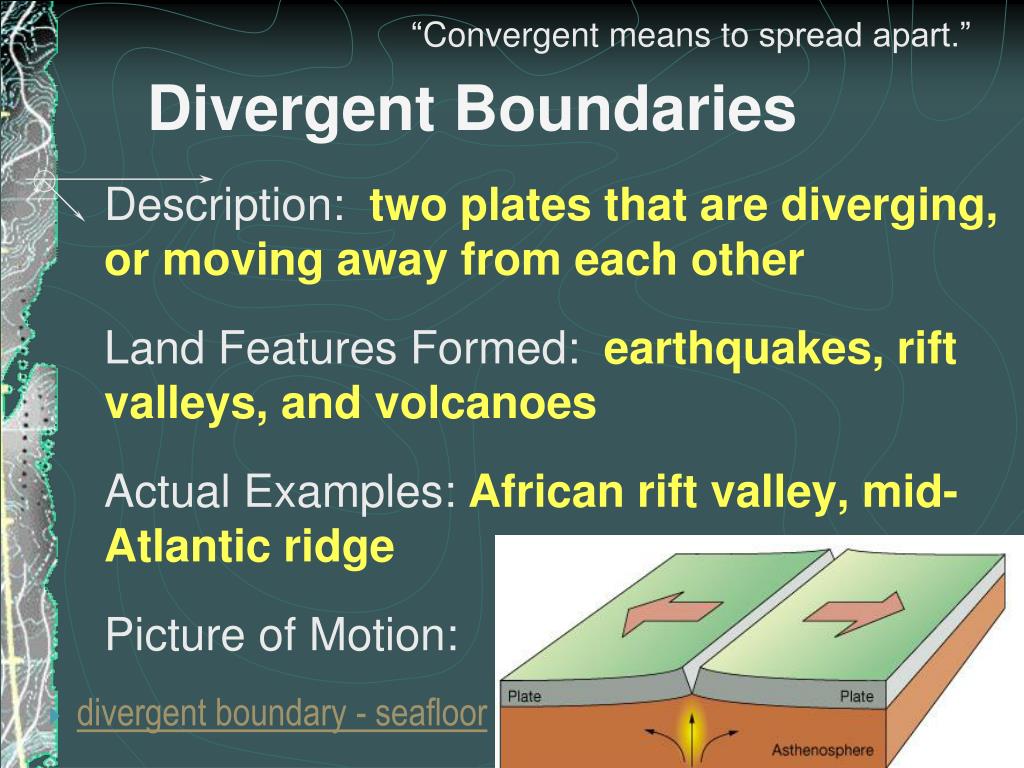
Divergent Plate Boundaries Examples Deep ocean circulation. describes in a simple way the effects of temperature on density and the initiation of downward movement in the oceans. learn how bottom currents scour and sort sediments, thus affecting what kind of bottom develops in an area. describes the general circulation pattern of the earth’s oceans. The application of both of these lines of prior knowledge results in students concluding the two sides of a divergent boundary are the same plate. retention of these alternative concepts prevents conceptual change from occurring during the period of instruction and results in students not recognizing divergent boundaries as plate boundaries, leading them to incorrectly count the number of plates.

Comments are closed.