Cell Division And Reproduction It S A Natural Universe

Cell Division And Reproduction It S A Natural Universe Cell division and reproduction. in order for cells to increase in number, either for growth or replacement of old cells, they go through the process of cell division – the cell cycle. although the cycle is generally considered to consist of three major phases, there is a fourth phase to cell life. cell cycles in various parts of the human. Haplontic – the organism’s life cycle is comprised of a dominant haploid stage. diplontic – the diploid stage is dominant (in humans, for example). haplodiplontic – the two stages alternate more or less equally (the case for most plants). the alternating stages of haplodiplontic organisms is called the alternation of generations.
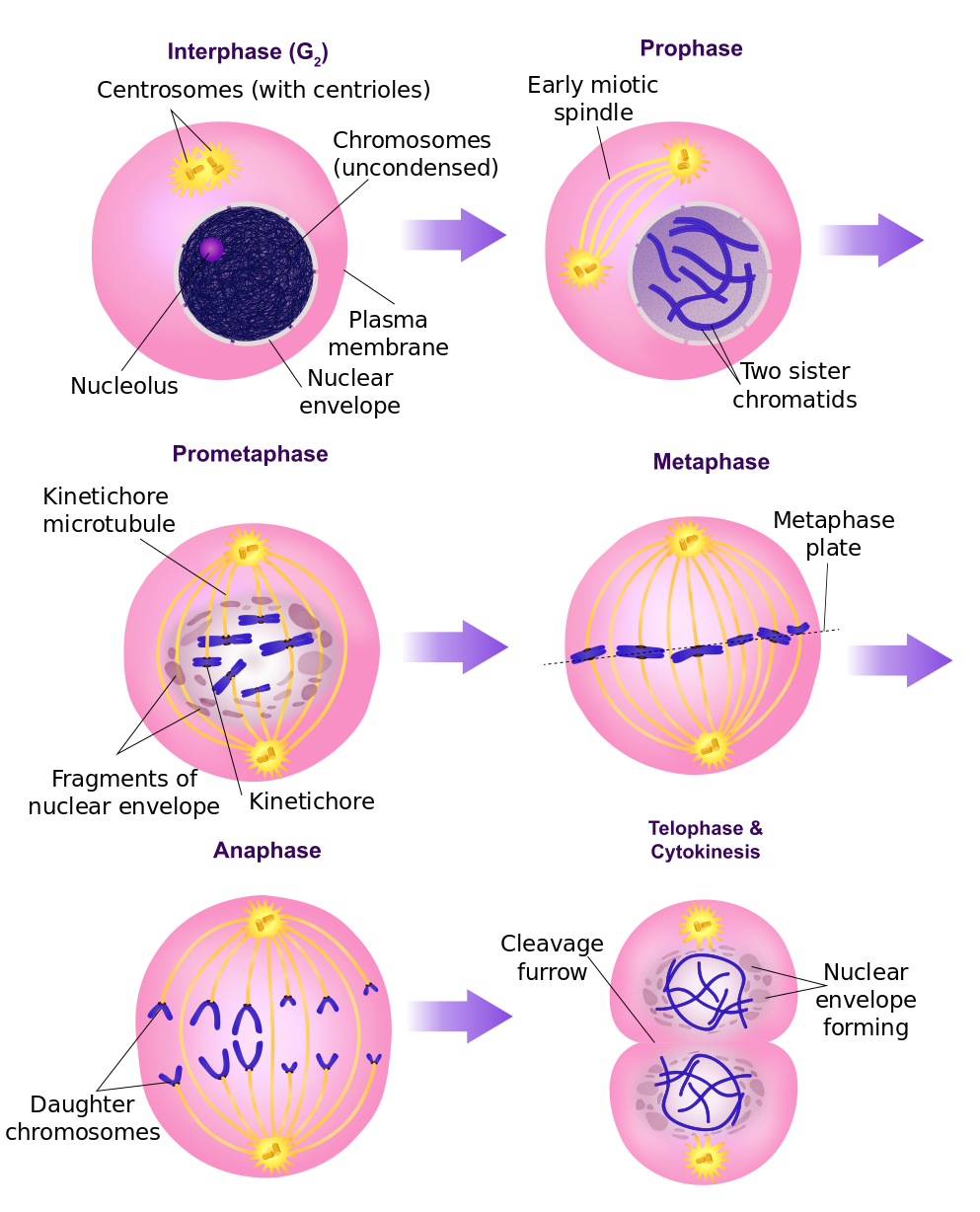
Stages Of Mitosis The cell cycle is a repeating series of events that include growth, dna synthesis, and cell division. the cell cycle in prokaryotes is quite simple: the cell grows, its dna replicates, and the cell divides. this form of division in prokaryotes is called asexual reproduction. in eukaryotes, the cell cycle is more complicated. The continuity of life from one cell to another has its foundation in the reproduction of cells by way of the cell cycle. the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events that describes the stages of a cell’s life from the division of a single parent cell to the production of two new daughter cells. the mechanisms involved in the cell cycle. Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or more daughter cells. it is an irreplaceable biological process in all living organisms; being the “means of growth, repair, and reproduction in multicellular organisms” and “the sole source of reproduction in unicellular organisms”. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. in eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. interphase is divided into g1, s, and g2 phases. mitosis consists of five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.

Comments are closed.