Cell Division Meiosis Reductional And Equational Division

Reduction Division Meiosis Meiosis 1 is a reductional phase where ploidy number is reduced in the cell. the initial cell in meiosis 1 is diploid, and the product is two haploid daughter cells. meiosis 2 is an equational. During meiosis ii, the two cells once again cycle through four phases of division. meiosis ii is sometimes referred to as an equational division because it does not reduce chromosome number in the.
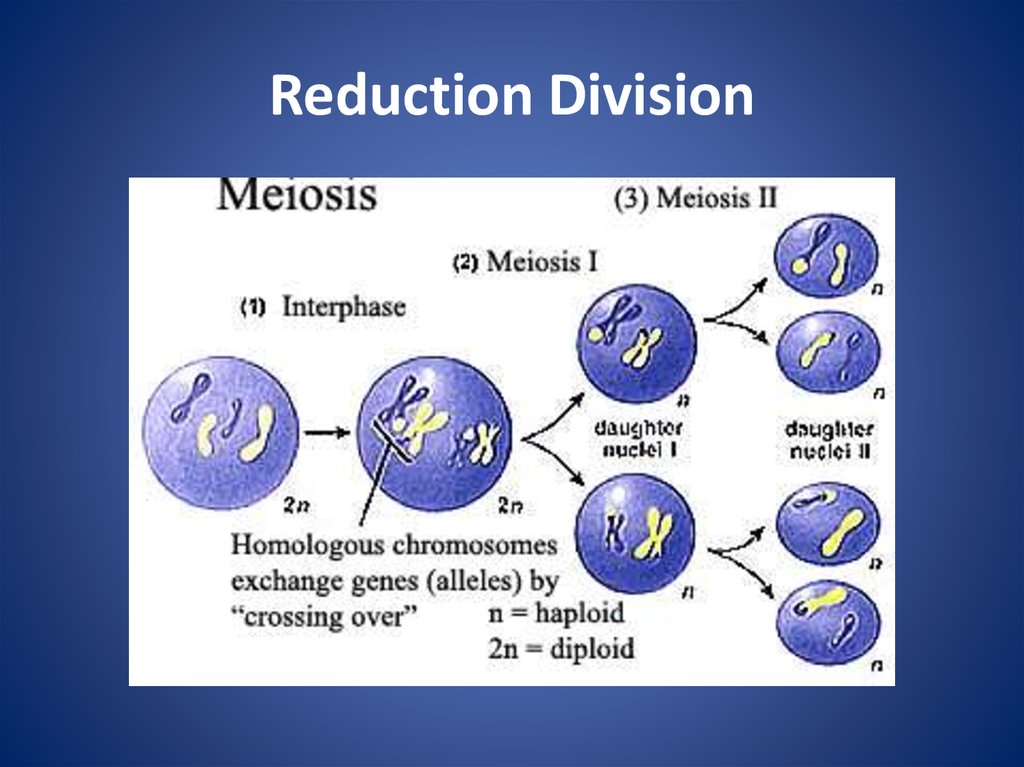
Cell Division Meiosis Online Presentation Equational division, also known as mitosis, is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. reduction division, also known as meiosis, is the process by which a cell divides into four non identical daughter cells. while both types of division are essential for different biological processes, they have distinct. Describe and draw the key events and stages of meiosis that lead to haploid gametes. recall that homologous chromosomes separate during meiosis i (a reductional division) and that sister chromatids separate during meiosis ii (an equational division). compare mitosis and meiosis. compare the processes of oogenesis and spermatogenesis in humans. Meiosis i: reductional division. before meiosis, gametic stem cells replicate through mitosis. at the very beginning of meiosis, the last g 1 phase of the diploid stem cells is followed by chromosome replication during s phase and g 2, ending the last somatic interphase. thus, each cell enters meiosis with two copies of the diploid genome (2n, 2c). Meiosis is a cell division in which four haploid cells are formed from a single diploid cell. it usually occurs in reproductive organs or gonads of the organisms. meiosis is also known as reductional cell division because four daughter cells produced contain half the number of chromosomes than that of their parent cell. meiosis has two nuclear.
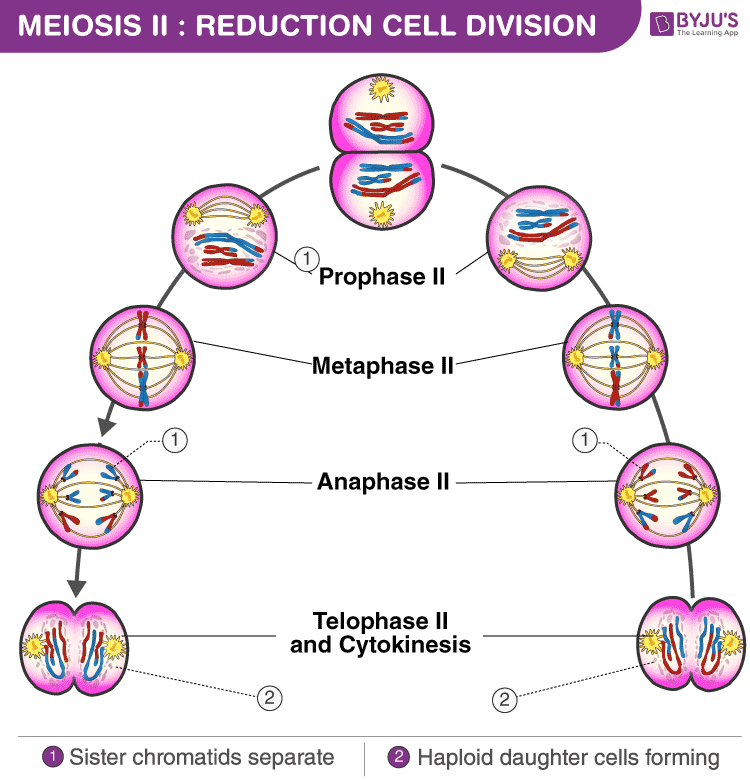
Meiosis Ii Stages And Significance Of Meiosis Ii Cell Division Meiosis i: reductional division. before meiosis, gametic stem cells replicate through mitosis. at the very beginning of meiosis, the last g 1 phase of the diploid stem cells is followed by chromosome replication during s phase and g 2, ending the last somatic interphase. thus, each cell enters meiosis with two copies of the diploid genome (2n, 2c). Meiosis is a cell division in which four haploid cells are formed from a single diploid cell. it usually occurs in reproductive organs or gonads of the organisms. meiosis is also known as reductional cell division because four daughter cells produced contain half the number of chromosomes than that of their parent cell. meiosis has two nuclear. Mitosis is the type of cell division that makes a multicellular organism from a fertilized egg, replaces old cells, regenerates organs, and is a means of asexual reproduction for many organisms. mitosis is divided into four stages. prophase: during prophase, chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane disappears, nucleolus disappears, and the. Meiosis employs many of the same mechanisms as mitosis. however, the starting nucleus is always diploid and the nuclei that result at the end of a meiotic cell division are haploid. to achieve this reduction in chromosome number, meiosis consists of one round of chromosome duplication and two rounds of nuclear division.
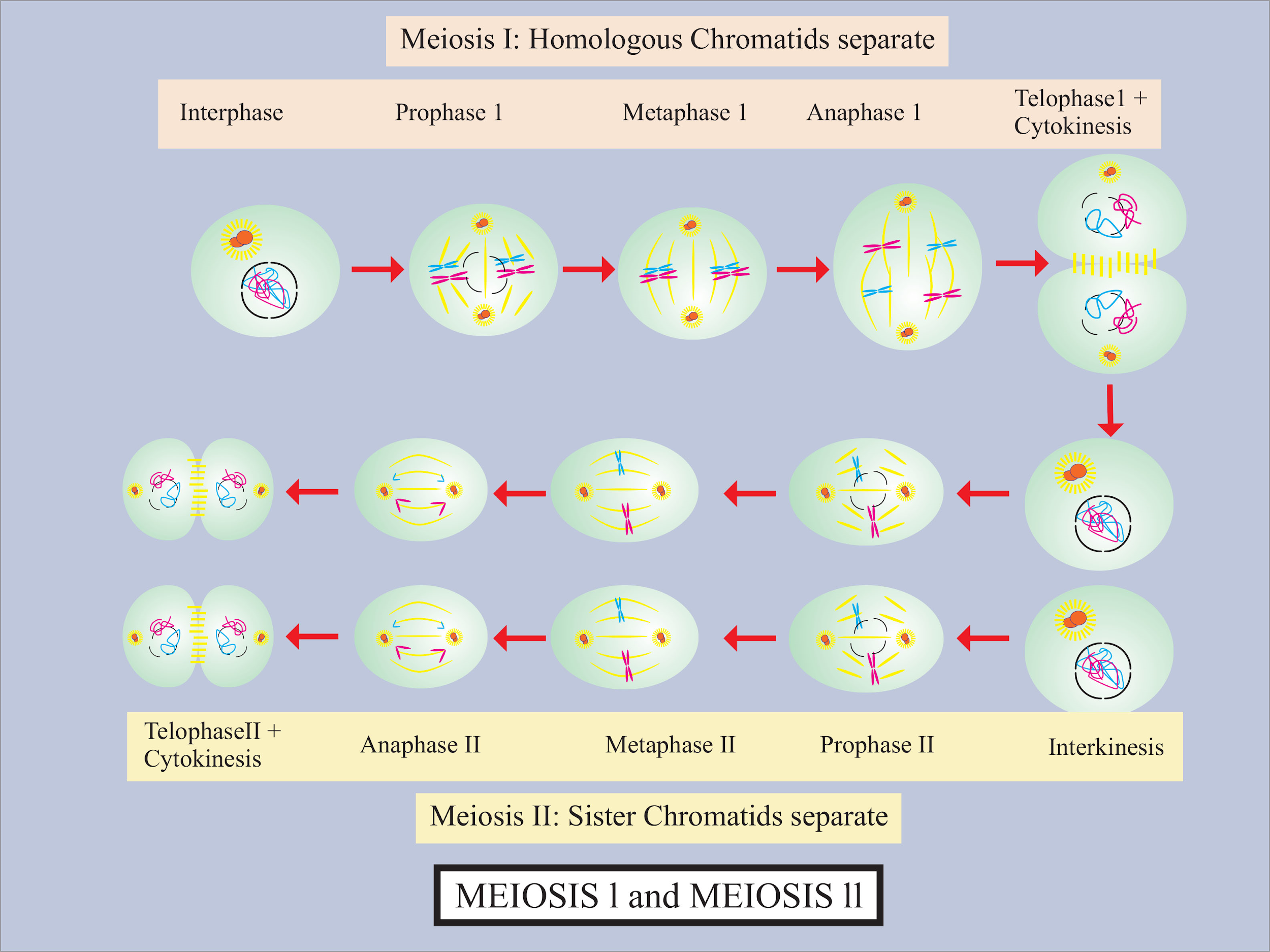
Visualizing Meiosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that makes a multicellular organism from a fertilized egg, replaces old cells, regenerates organs, and is a means of asexual reproduction for many organisms. mitosis is divided into four stages. prophase: during prophase, chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane disappears, nucleolus disappears, and the. Meiosis employs many of the same mechanisms as mitosis. however, the starting nucleus is always diploid and the nuclei that result at the end of a meiotic cell division are haploid. to achieve this reduction in chromosome number, meiosis consists of one round of chromosome duplication and two rounds of nuclear division.

Comments are closed.