Cell Theory Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Cell Theory Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary A cell theory is a scientific theory stating that: all living things are made up of one or more cells. the cell is the structural and functional unit of all living things. cells come from pre existing cells through the process of division. all cells are the same in regard to chemical composition. Cell theory has three major hypotheses: first, all organisms are made of cells. second, cells are the fundamental building blocks used to create tissues, organs, and entire functioning organisms. the third, and probably most important part of the theory is that cells can only arise from other cells. thus, all organisms start as single cells.
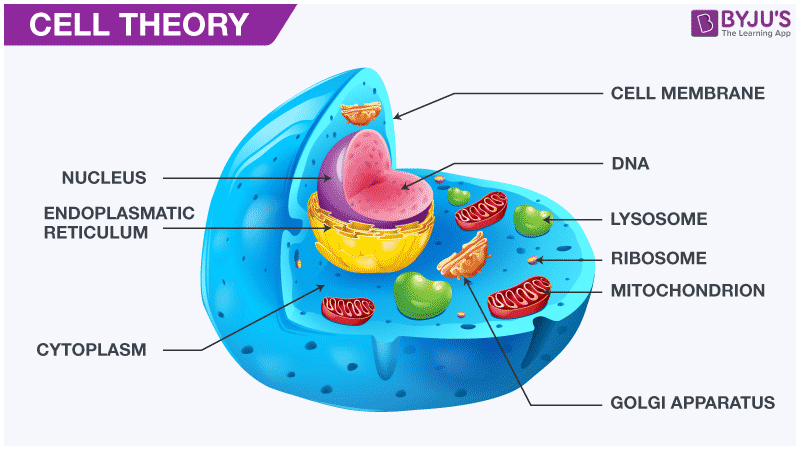
Cell Theory Definition Early Observations And Its Overview The cell is defined as the fundamental, functional unit of life. some organisms are comprised of only one cell whereas others have many cells that are organized into tissues, organs, and systems. the scientific study of the cell is called cell biology. this field deals with the cell structure and function in detail. There are countless different functions that cells must perform to obtain energy and reproduce. depending on the cell, examples of these functions can include photosynthesis, breaking down sugar, locomotion, copying its own dna, allowing certain substances to pass through the cell membrane while keeping others out, etc. Cell theory, fundamental scientific theory of biology according to which cells are held to be the basic units of all living tissues. first proposed by german scientists theodor schwann and matthias jakob schleiden in 1838, the theory that all plants and animals are made up of cells marked a great. Cell, in biology, the basic membrane bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. a single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. these cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become.

Cell Theory Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Cell theory, fundamental scientific theory of biology according to which cells are held to be the basic units of all living tissues. first proposed by german scientists theodor schwann and matthias jakob schleiden in 1838, the theory that all plants and animals are made up of cells marked a great. Cell, in biology, the basic membrane bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. a single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. these cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become. Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes, which are characterized by having a distinct, membrane bound nucleus. the term “ cell ” is a common word in biology, anatomy, medicine, and cell science. it is the basic unit of life. at the cellular level, cells may be classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. it is sometimes referred to as the “cell division cycle” for that reason. new cells are born through the division of their “parent” cell, producing two “daughter” cells from one single “parent” cell.

Three Parts Of Cell Theory Biology Dictionary Vrogue Co Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes, which are characterized by having a distinct, membrane bound nucleus. the term “ cell ” is a common word in biology, anatomy, medicine, and cell science. it is the basic unit of life. at the cellular level, cells may be classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells. The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. it is sometimes referred to as the “cell division cycle” for that reason. new cells are born through the division of their “parent” cell, producing two “daughter” cells from one single “parent” cell.

Comments are closed.