Changes In Supply And Demand Microeconomics

Causes Of Supply And Demand Changes In Microeconomics Lesson Study A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. Step 3. it is important to remember that in step 2, the only thing to change was the supply or demand. therefore, coming into step 3, the price is still equal to the initial equilibrium price. since either supply or demand changed, the market is in a state of disequilibrium. thus, there is either a surplus or shortage.

Changes In Supply And Demand Microeconomics A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. The law of supply and demand explains how changes in a product's market price relate to its supply and demand. demand for basic necessities is less responsive. microeconomics economic concepts. An increase in the number of sellers supplying a good or service shifts the supply curve to the right; a reduction in the number of sellers shifts the supply curve to the left. if for example, four new coffee producing stores enter the market, more will be supplied at each price. the market for cellular phone service has been affected by an. Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.
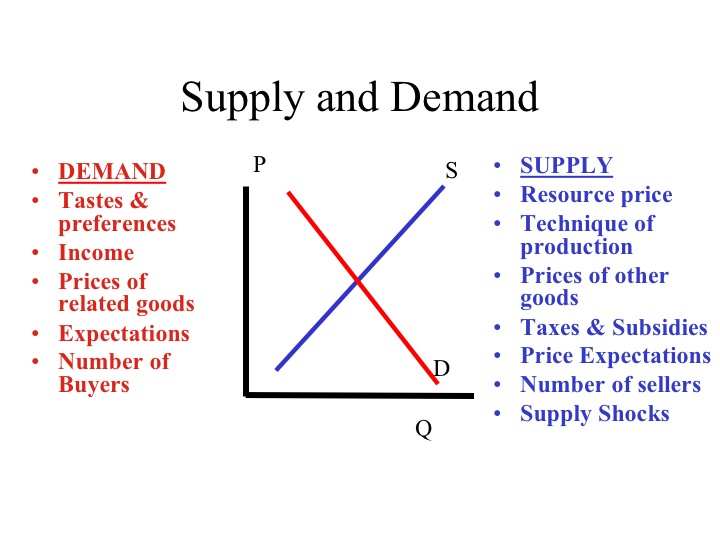
Econ 150 Microeconomics An increase in the number of sellers supplying a good or service shifts the supply curve to the right; a reduction in the number of sellers shifts the supply curve to the left. if for example, four new coffee producing stores enter the market, more will be supplied at each price. the market for cellular phone service has been affected by an. Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. Summing up factors that change supply. changes in the cost of inputs, natural disasters, new technologies, and the impact of government decisions all affect the cost of production. in turn, these factors affect how much firms are willing to supply at any given price. figure 3.15 summarizes factors that change the supply of goods and services. Introduction to demand and supply; 3.1 demand, supply, and equilibrium in markets for goods and services; 3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process; 3.4 price ceilings and price floors; 3.5 demand, supply, and efficiency; key terms; key concepts and summary; self.
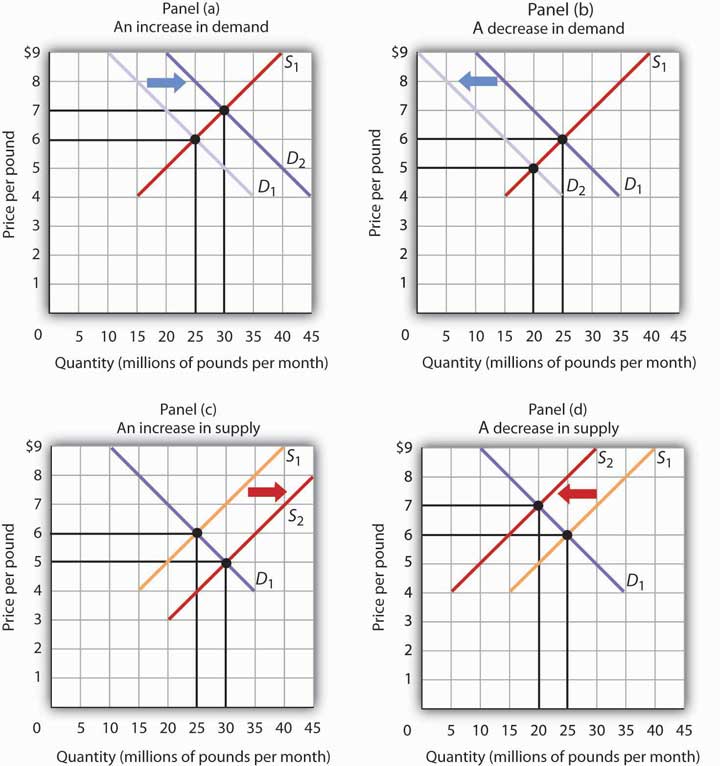
Demand Supply And Equilibrium вђ Microeconomics For Managers Summing up factors that change supply. changes in the cost of inputs, natural disasters, new technologies, and the impact of government decisions all affect the cost of production. in turn, these factors affect how much firms are willing to supply at any given price. figure 3.15 summarizes factors that change the supply of goods and services. Introduction to demand and supply; 3.1 demand, supply, and equilibrium in markets for goods and services; 3.2 shifts in demand and supply for goods and services; 3.3 changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process; 3.4 price ceilings and price floors; 3.5 demand, supply, and efficiency; key terms; key concepts and summary; self.

Comments are closed.