Chapter 4 Cells Chapter 4 Cells The Cell Theory The Cel

Chapter 4 Cells Chapter 4 Cells The Cell Theory T In the 17th century, observations of microscopic life led to the development of the cell theory: the idea that the fundamental unit of life is the cell, that all organisms contain at least one cell, and that cells only come from other cells. figure chapter4.1 c h a p t e r 4. 1: microorganisms vary visually in their size and shape, as can be. Chapter 4 cells the cell theory. the cell is the basic unit of life. all living organisms are made up of one or more cells. new cells only arise from pre existing cells. cell size. largest cell type in humans = egg cell; most cells are extremely small and cannot be seen with the naked eye. why is it advantageous to have trillions of cells in.
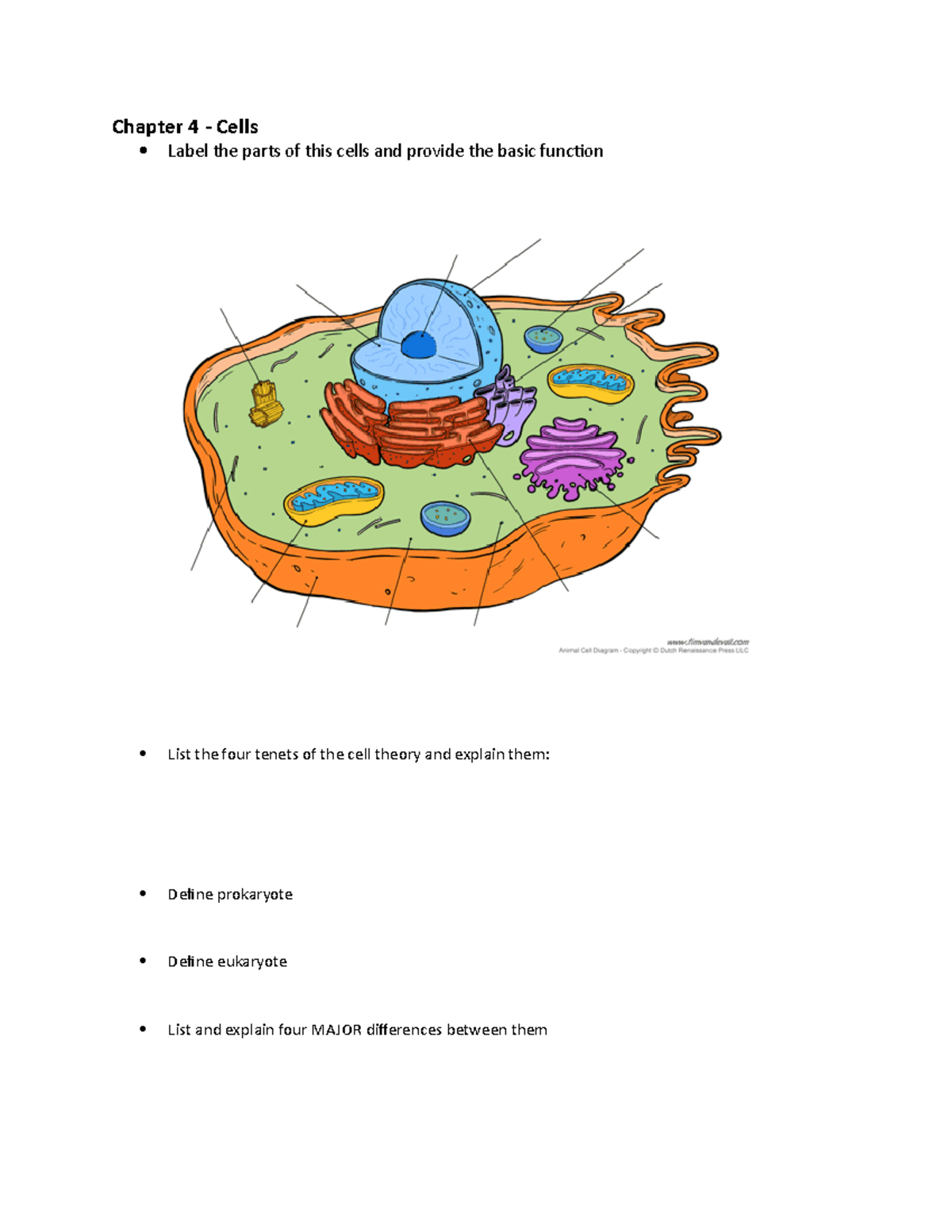
Chapter 4 Cells Outline Chapter 4 Cells Label The Parts Of This Cell theory. 1. all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, which hold the responsibility of metabolism and heredity. 2. cell are the smallest living things; the basic units of organization of organisms. 3. cells arise from division of previously existing cells. types of cell diffusion. 1. Terms in this set (79) study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the study of cells called?, explain cell theory., what are the three major categories of cell structure? and more. There are two kinds of channels that perform active transport in cells. sodium potassium pump. uses energy, in the form of atp, to pump three na out of the cell and to pump two k into the cell. nearly 1 3 of the energy expended by the body’s cells is given over to driving these pumps. proton pump. The cell wall. if you examine figure 4.8b, the diagram of a plant cell, you will see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls.

Chapter 4 Cells Ppt There are two kinds of channels that perform active transport in cells. sodium potassium pump. uses energy, in the form of atp, to pump three na out of the cell and to pump two k into the cell. nearly 1 3 of the energy expended by the body’s cells is given over to driving these pumps. proton pump. The cell wall. if you examine figure 4.8b, the diagram of a plant cell, you will see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. the cell wall is a rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support, and gives shape to the cell. fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls. Cells were first discovered in 1665 by robert hooke the accumulation of scientific evidence led to the cell theory, p. 57 all living things are composed of cells all cells form from previously existing cells cells are the smallest units capable of carrying out the processes of life: ex. respiration, digestion, reproduction, growth, ingestion, etc. All materials structures inside the plasma membrane. gy production protein synthesis) genetic inf. eukaryotic cells: dna contained in membrane bound nucleus. “true nucleus”. membrane bound)“before nucleus” obtai. nergy and nutrients from envir. cell function limits cell size. diffusion too slow in large cells.

Comments are closed.