Chest Bones And Muscles Diagram Labeled
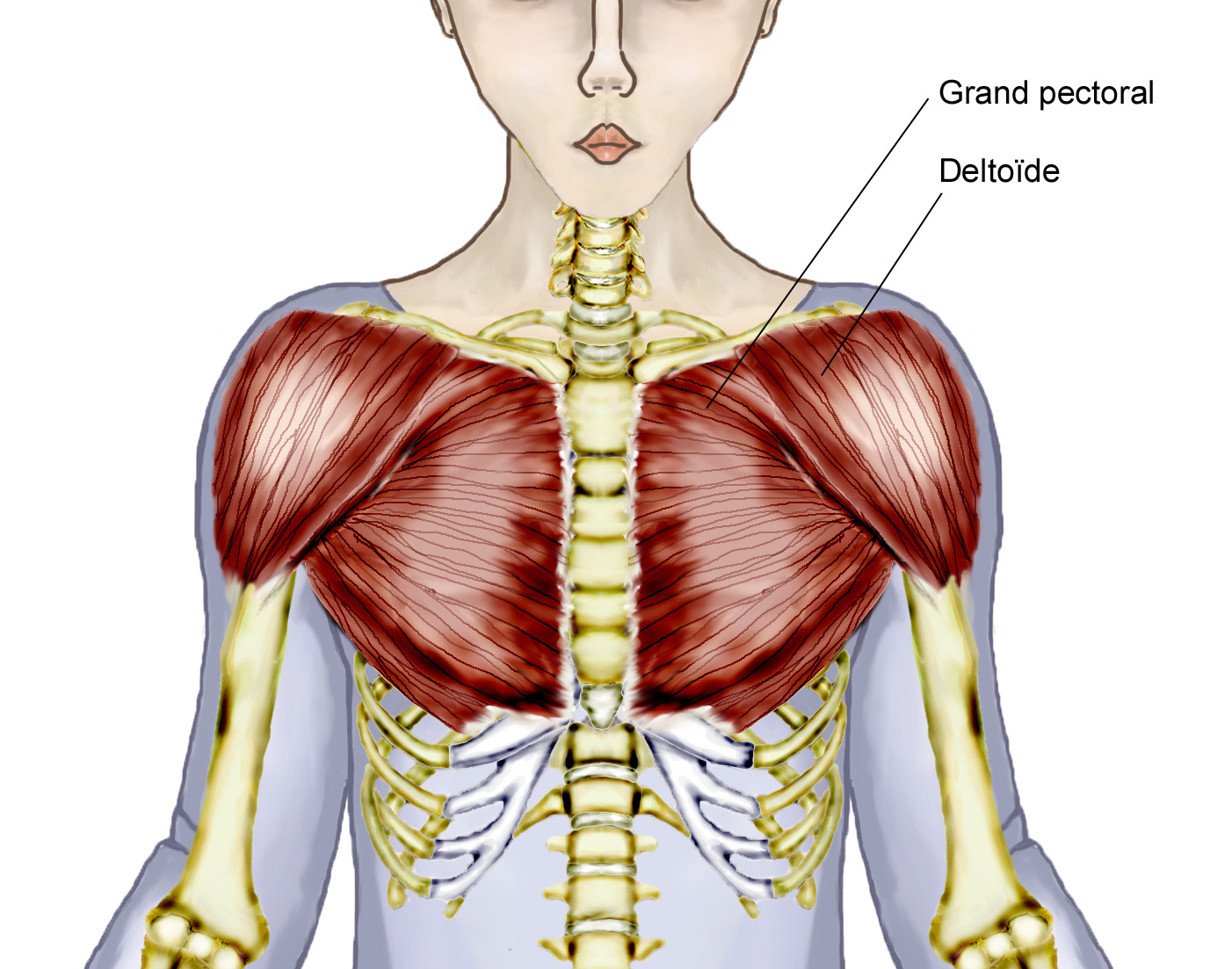
Overview Of Chest Muscles Teres major: this muscle helps rotate the upper arm. serratus anterior: located in the rib cage, this muscle keeps the shoulder blade against the chest wall and helps rotate the shoulder blade. Bones. the bones of the chest — namely the rib cage and spine — protect vital organs from injury, and also provide structural support for the body. the rib cage is one of the body’s best.

Chest Muscles Anatomy Labeled Neck And Chest Muscles Diagram Qui Sternum (1): also known as the breastbone, the sternum is a flat bone located in the middle of the chest. its primary function is protecting the heart. the bone has three parts – the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. the sternum is the attachment point for the costal cartilage, which connects it directly to the first seven pairs of ribs. Unlock your elbows and lower the bar down slowly until it touches your torso between your nipple line and your sternum. once you make contact (or descend as low as you’re comfortably able. The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. the thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture located inferiorly. Pectoralis major. the biggest chest muscle, extending from the shoulder region across the front of the chest, covering the ribs. origin: in two heads, from the clavicle and the costal cartilages of the 1st 6th ribs. insertion: bicipital groove and greater tubercle of the humerus.

Chest Muscles Diagram Quizlet The thoracic, or chest wall, consists of a skeletal framework, fascia, muscles, and neurovasculature – all connected together to form a strong and protective yet flexible cage. the thorax has two major openings: the superior thoracic aperture found superiorly and the inferior thoracic aperture located inferiorly. Pectoralis major. the biggest chest muscle, extending from the shoulder region across the front of the chest, covering the ribs. origin: in two heads, from the clavicle and the costal cartilages of the 1st 6th ribs. insertion: bicipital groove and greater tubercle of the humerus. The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, is a long, narrow flat bone that serves as the keystone of the rib cage and stabilizes the thoracic skeleton. several muscles that move the arms, head, and neck have their origins on the sternum. it also protects several vital organs of the chest, such as the heart, aorta, vena cava, and thymus. Bones of the chest. sternum (1): also referred to as the breastbone, the sternum is a flat bone situated in the center of the thorax. its primary role is to shield the heart. the bone comprises three parts – the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. the sternum serves as the point of attachment for the costal cartilage, which directly.
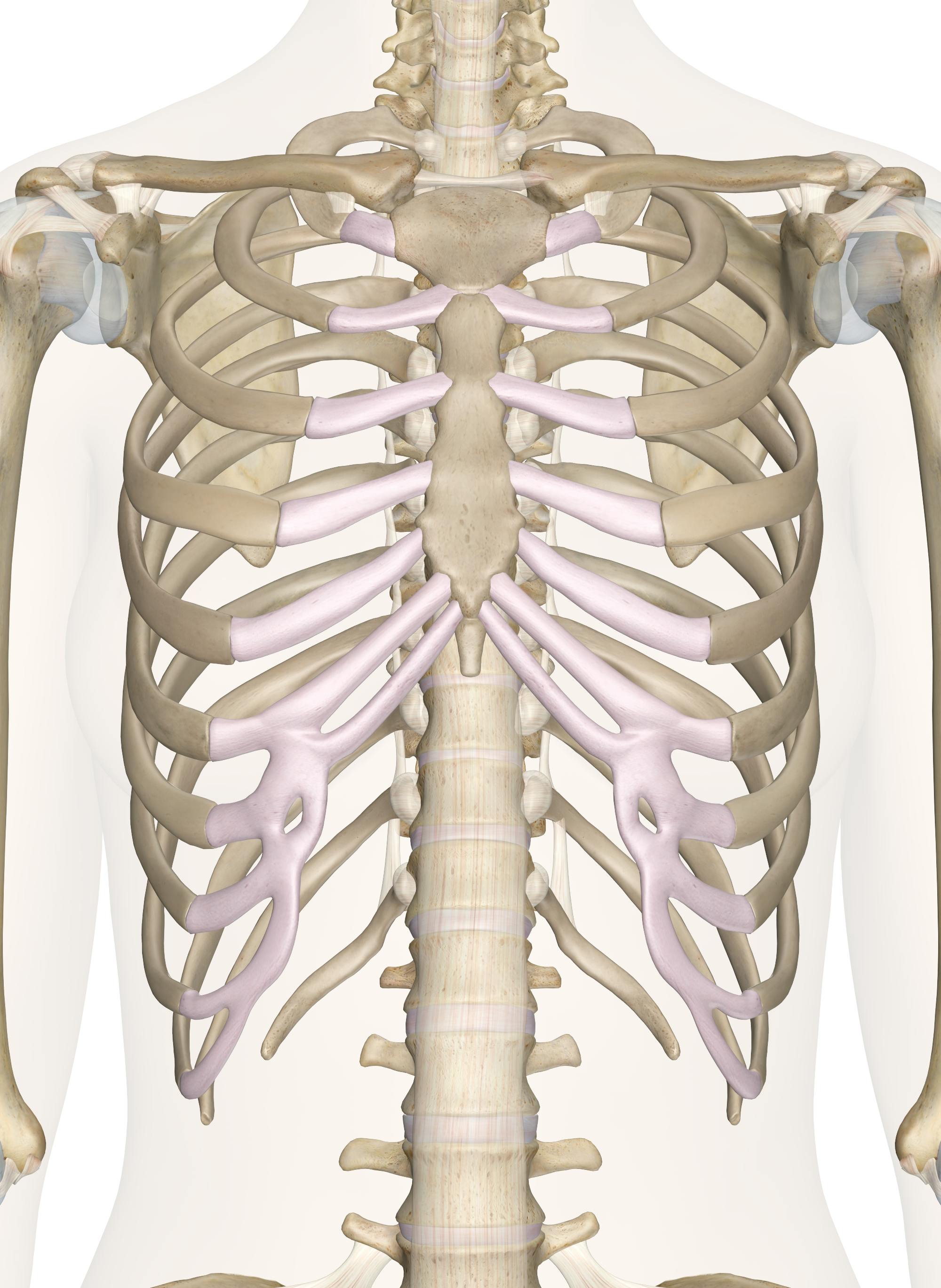
Chest Bone Diagram The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, is a long, narrow flat bone that serves as the keystone of the rib cage and stabilizes the thoracic skeleton. several muscles that move the arms, head, and neck have their origins on the sternum. it also protects several vital organs of the chest, such as the heart, aorta, vena cava, and thymus. Bones of the chest. sternum (1): also referred to as the breastbone, the sternum is a flat bone situated in the center of the thorax. its primary role is to shield the heart. the bone comprises three parts – the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. the sternum serves as the point of attachment for the costal cartilage, which directly.

Chest Muscles Diagram Quizlet

Comments are closed.