Classification Of Gastritis Non Atrophic Helicobacter Grepmed

Etiological Classification Of Gastritis Download Table Classification of gastritis non atrophic: helicobacter pylori atrophic • autoimmune: autoimmunity • multifocal atrophic: h. pylori, environmental insults special forms • chemical: nsaids, bile?, other agents • radiation injury • lymphocytic: gluten (coeliac disease), h. pylori, idiopathic, drugs • non infectious granulomatous: crohn's disease, sarcoidosis, wegener's granulomatosis. Chronic gastritis is categorized into 2 forms—atrophic and non atrophic. the primary cause of chronic gastritis is a helicobacter pylori infection, which typically starts with a non atrophic morphology. the non atrophic form of chronic gastritis can progress to atrophic without treatment.

Ppt Gastritis Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 228190 This definition is derived from an international group of pathologists (atrophy club 2000) who established new diagnostic criteria for the two main phenotypes of the chronic gastritis (non atrophic and atrophic) and proposed a classification of atrophy, which includes a non metaplasic and a metaplasic category (tab. iii) 34 37. the first framework is characterized by the decrease or complete. Purpose of review the gastritis constellation includes heterogeneous clinicopathological entities, among which long standing, non self limiting gastritis, mainly due to helicobacter pylori infection, has been epidemiologically, biologically, and clinically linked to gastric cancer development (i.e. “inflammation associated cancer”). this review illustrates the updated criteria applied in. Important features to report. location site. 5 biopsy specimens are essential. 2 from antrum (2 3 cm from the pylorus, 1 each from the lesser and greater curvature), 2 from the body (8 cm from the cardia, 1 each from the lesser and greater curvature) and incisura angularis. biopsies from different sites should be separately identifiable. Endoscopic features for the diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection status based on the kyoto classification of gastritis. dig endosc 2020; 32 : 74 83 [pmid: 31309632 doi: 10.1111 den.13486 ] 17.
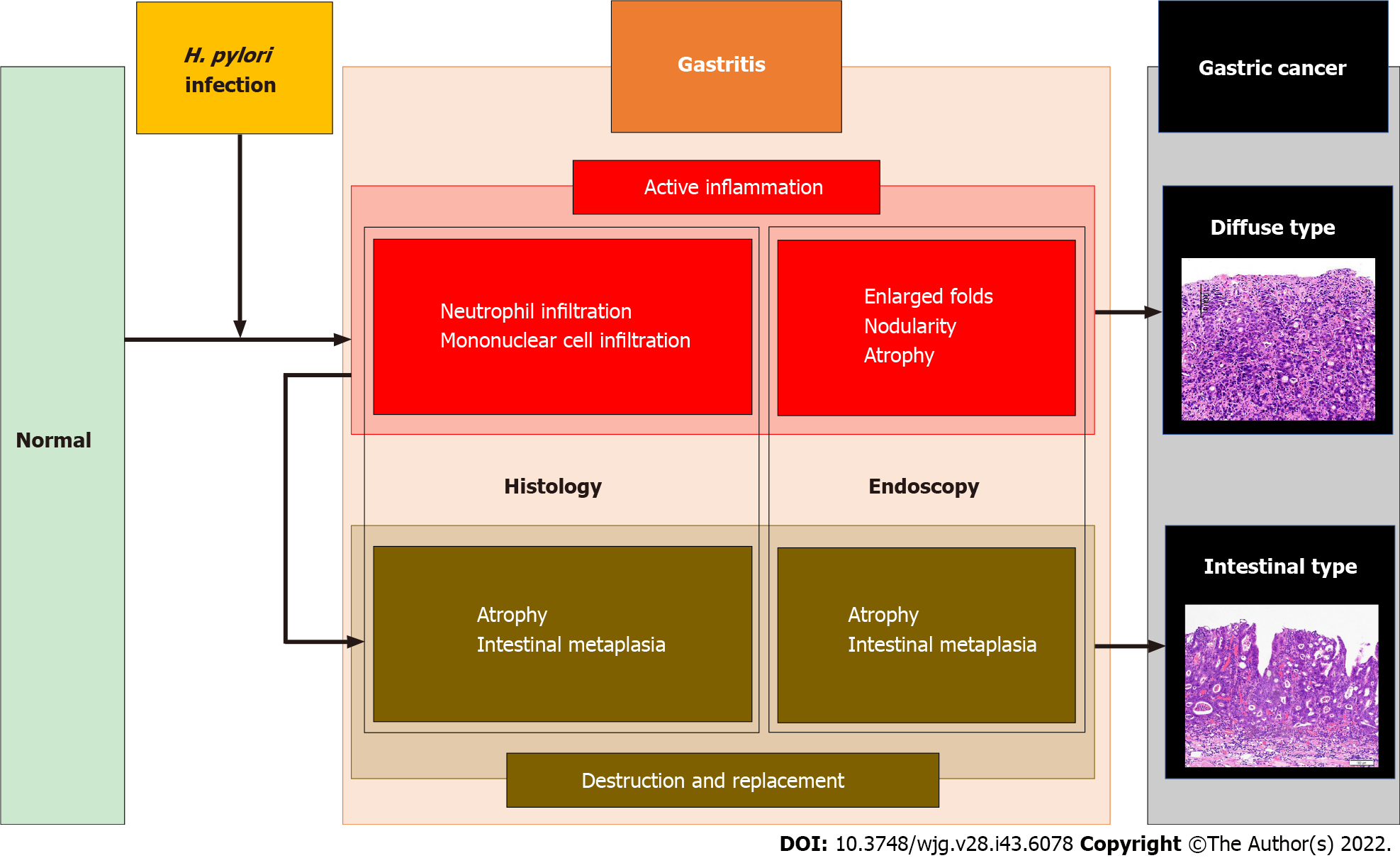
Kyoto Classification Of Gastritis Advances And Future Perspectives In Important features to report. location site. 5 biopsy specimens are essential. 2 from antrum (2 3 cm from the pylorus, 1 each from the lesser and greater curvature), 2 from the body (8 cm from the cardia, 1 each from the lesser and greater curvature) and incisura angularis. biopsies from different sites should be separately identifiable. Endoscopic features for the diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection status based on the kyoto classification of gastritis. dig endosc 2020; 32 : 74 83 [pmid: 31309632 doi: 10.1111 den.13486 ] 17. Infection, while the group of gastritis unassociated withh pylori can be differentiated into autoimmune, chemically induced reactive gastritis, ex h pylori gastritis, helicobacter heilmannii gas tritis, crohn’s gastritis and a number of special forms of gastritis. key words:autoimmune gastritis; crohn’s disease; gastritis; helicobacter pylori. Although the term "gastritis" is often used to describe endoscopic or radiologic characteristics of abnormal appearing gastric mucosa, a diagnosis of gastritis requires histopathologic evidence of inflammation. this topic will review the etiology, classification, and diagnosis of gastritis. specific causes of acute and chronic gastritis and.

Classification Of Gastritis Gastropanel Markers Versus Histology Infection, while the group of gastritis unassociated withh pylori can be differentiated into autoimmune, chemically induced reactive gastritis, ex h pylori gastritis, helicobacter heilmannii gas tritis, crohn’s gastritis and a number of special forms of gastritis. key words:autoimmune gastritis; crohn’s disease; gastritis; helicobacter pylori. Although the term "gastritis" is often used to describe endoscopic or radiologic characteristics of abnormal appearing gastric mucosa, a diagnosis of gastritis requires histopathologic evidence of inflammation. this topic will review the etiology, classification, and diagnosis of gastritis. specific causes of acute and chronic gastritis and.

Types Of Gastritis Illustration Stock Image F027 7422 Science

Comments are closed.