Classification Of Kingdom Fungi Study Biology Microbiology Study

Classification Of Kingdom Fungi Study Biology Microbiology Study The classification of fungi is designed mainly for practical application but it also bears some relation to phylogenetic considerations. the division of mycota, or fungi and moulds, includes the true slime moulds (myxomycetes), the lower fungi (phycomycetes), and the higher fungi (eumycetes). the fungi can be classified according to the various parameters including; o classification based on. 3 fascinating facts about fungi kingdom throughout the study of microbiology, the kingdom fungi has fascinated scientists and laymen alike, its unique characteristics and function making it a cornerstone of life. some of the awe inspiring features and profound implications of the fungi kingdom are: 1.

Mycology Classification Of Fungi Structure Advantages Disadvantages Kingdom fungi are classified based on different modes. the different classification of fungi is as follows: based on mode of nutrition. on the basis of nutrition, kingdom fungi can be classified into 3 groups. saprophytic – the fungi obtain their nutrition by feeding on dead organic substances. examples: rhizopus, penicillium and aspergillus. Kingdom fungi, one of the most diverse and ancient branches of the tree of life, includes an estimated 2–5 million species that play vital roles in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (). 1–3 fungi exhibit a wide variety of feeding lifestyles, morphologies, developmental patterns, and ecologies and are thought to have coevolved with plants. 1, 4 a robustly resolved phylogeny of fungi is. Fungi, though, only merit a brief mention in high school text books, and very rarely occupy a central position in university‐level biology degrees, generally falling between the fields of botany and microbiology (editorial, 2017; freimoser, 2017). yet fungi are literally everywhere, shaping the world as we know it. The kingdom fungi forms a highly diverse lineage of eukaryotes that shares a common ancestor with animals. both comprise heterotrophic organisms, but fungi form (chitinous) cell walls and are.
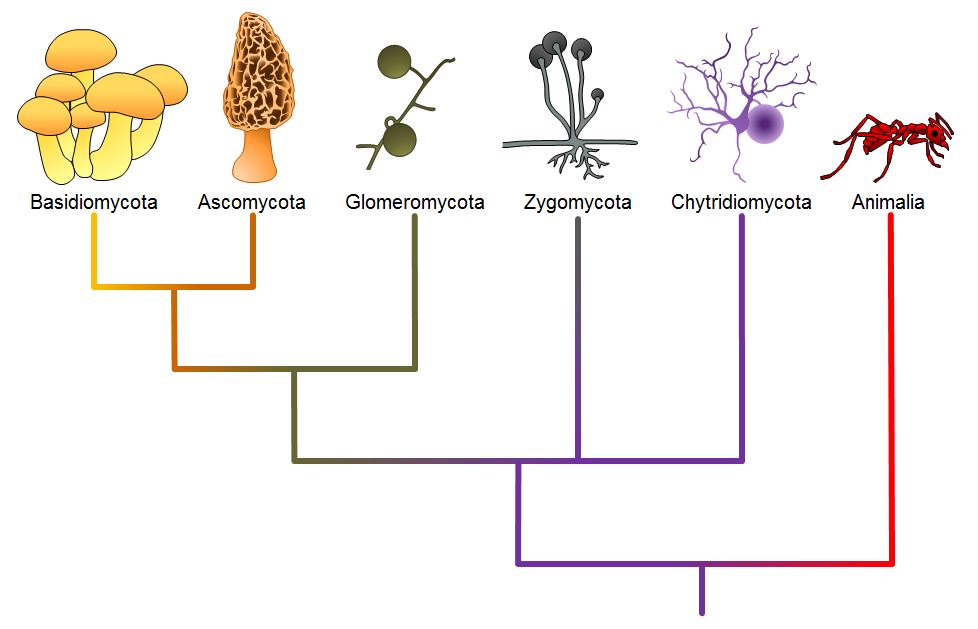
Classifications Of Fungi вђ Introductory Biology Evolutionary And Fungi, though, only merit a brief mention in high school text books, and very rarely occupy a central position in university‐level biology degrees, generally falling between the fields of botany and microbiology (editorial, 2017; freimoser, 2017). yet fungi are literally everywhere, shaping the world as we know it. The kingdom fungi forms a highly diverse lineage of eukaryotes that shares a common ancestor with animals. both comprise heterotrophic organisms, but fungi form (chitinous) cell walls and are. The kingdom fungi contains five major phyla that were established according to their mode of sexual reproduction or using molecular data. polyphyletic, unrelated fungi that reproduce without a sexual cycle, were once placed for convenience in a sixth group, the deuteromycota, called a “form phylum,” because superficially they appeared to be similar. Chapter 1. fungi: characteristics and classification. fungi are the interface organisms between life and death. paul stamets. we study fungi because they are fascinating organisms that play a key role in sustaining life on earth. fungi are the second most diverse eukaryotic organisms on earth, next only to insects.

Fungi Diagram Kingdom The kingdom fungi contains five major phyla that were established according to their mode of sexual reproduction or using molecular data. polyphyletic, unrelated fungi that reproduce without a sexual cycle, were once placed for convenience in a sixth group, the deuteromycota, called a “form phylum,” because superficially they appeared to be similar. Chapter 1. fungi: characteristics and classification. fungi are the interface organisms between life and death. paul stamets. we study fungi because they are fascinating organisms that play a key role in sustaining life on earth. fungi are the second most diverse eukaryotic organisms on earth, next only to insects.

Classification Of Fungi Phycomycetes Ascomycetes Basidiomycetes And

Comments are closed.