Classification Of Living Things Classnotes Ng

Classification Of Living Things Classnotes Ng Living things and non living things. classification of living things is the sorting or grouping of living things; according to their common or similar characteristics. the scientist who developed the first system of classification is called carolus linnaeus. all organisms cannot be classified as either plants or animals based on carolus. Biology sss 1 first term. week 2. classification of living things. performance objectives. student should be able to: classify organisms into the kingdoms monera and protista. give the characteristics of kingdom monera and protista. content. all living organisms are classified into groups based on very basic, shared characteristics.

Classification Of Living Things Chart By Usefulcharts Vrogue Co To be classified as a living thing, it must grow and develop, use energy, produce, adapt, and response to the environment. these are some of the example of human being, plants, bacteria, insects, animals, lichens, reptiles, mammals, trees, mosses, etc. non living things are things that do not have life and they do not have a characteristic of life. Objects that are living have life in them while non living things do not have life in them. living things can also be referred to as organisms. there are various qualities (characteristics) that will help or enable us to recognize living things (objects that have life in them). these characteristics are also called life processes. All living and non living things are made up of matter. it means everything you can see, touch, smell, breathe, or eat is made up of matter. matter can be classified as a living and non living matter. state of matter. the matter is classified into solid, liquid, and gas. matter can change from one state to another by addition or subtraction. 3. they have two body layers. 4. organs are absent. 5. possession of nematoblast called stinging cells. 6. asexual reproduction is by budding while sexual reproduction is by fussion of gametes. phylum platyhelminthes e.g the flat worms examples include liver fluke, tape worms, planarian.
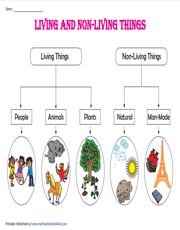
Living Things Classification Chart All living and non living things are made up of matter. it means everything you can see, touch, smell, breathe, or eat is made up of matter. matter can be classified as a living and non living matter. state of matter. the matter is classified into solid, liquid, and gas. matter can change from one state to another by addition or subtraction. 3. they have two body layers. 4. organs are absent. 5. possession of nematoblast called stinging cells. 6. asexual reproduction is by budding while sexual reproduction is by fussion of gametes. phylum platyhelminthes e.g the flat worms examples include liver fluke, tape worms, planarian. Week 1. recognising living things. performance objectives. student should be able to: give the characteristics of living things with examples. differentiate between plant and animals. understand the levels of organization of life and give examples. content. the earth in which we are living is made up of several things. The seven groups used in classification of living things in order of hierarchy are; kingdom → phylum (animal) or division (plant) → class → order → family → genus → species. the species is the basic (i.e. smallest) unit in biological classification. a species is a group of individuals which can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.

Classification Of Living Things Diagram Week 1. recognising living things. performance objectives. student should be able to: give the characteristics of living things with examples. differentiate between plant and animals. understand the levels of organization of life and give examples. content. the earth in which we are living is made up of several things. The seven groups used in classification of living things in order of hierarchy are; kingdom → phylum (animal) or division (plant) → class → order → family → genus → species. the species is the basic (i.e. smallest) unit in biological classification. a species is a group of individuals which can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
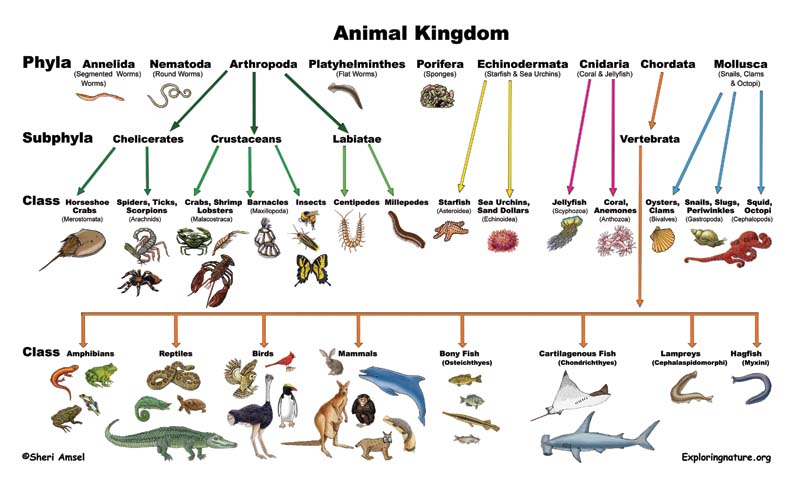
Classification Of Living Things

Comments are closed.