Comparison Between Overhead Power Lines And Underground Power
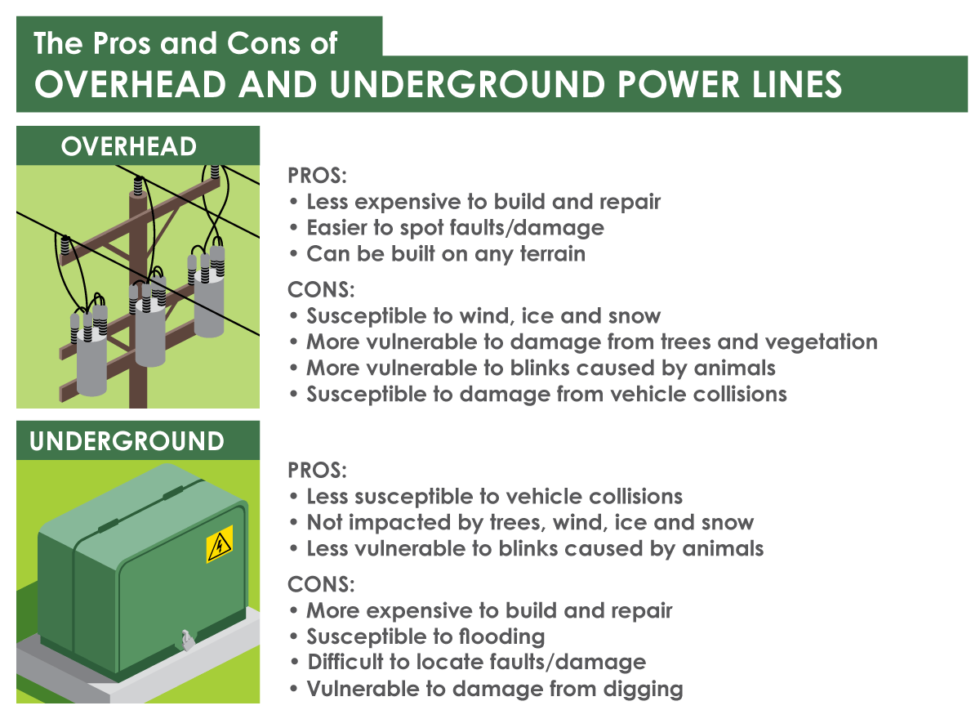
The Pros And Cons Of Overhead And Underground Power Lines Dawson Discover the pros and cons of overhead lines and underground cables for electric power transmission. this comprehensive comparison explores cost, maintenance, accidents, reliability, economy, installation, efficiency, and losses. understand the key factors influencing the choice between these methods and make informed decisions for your power engineering projects. Underground cable. 01. conductor. for the overhead (transmission and distribution) lines, the bare conductor is used. for underground (transmission and distribution) cable, the insulated conductor is used. 02. conductor. size. the size of the conductor is smaller as compared to the conductor of the overhead cables.

Comparison Between Overhead Power Lines And Underground Power Cables The underground cable requires a very high degree of insulation, hence it can not be operated above 132 kv. whereas, the overhead transmission lines have capable of transmitting power at 765 kv or even higher. the underground cable system is free from lighting and thunderstorm as compared to the overhead transmission system. the voltage drop is. Overhead power lines. the initial installation cost for overhead power lines is generally lower than for underground lines. however, you should factor in ongoing maintenance costs, as overhead lines are more susceptible to damage and may require frequent repairs. consider your budget and long term financial goals. Overhead distribution system. the overhead system is used for distribution. it is typically 5 to 10 times less expensive than the underground system. the spacing is usually provided between the conductors, at the supports & intermediate points. this spacing provides insulation which avoids an electric discharge between the conductors. Size of conductor. the size of conductor used in overhead lines is comparatively smaller. the size of conductor used in underground cables is relatively larger. voltage rating. overhead lines have higher voltage rating, near about 765 kv. undergrounds cables have comparatively lower voltage rating.

Comparison Between Overhead Lines And Underground Cables Youtube Overhead distribution system. the overhead system is used for distribution. it is typically 5 to 10 times less expensive than the underground system. the spacing is usually provided between the conductors, at the supports & intermediate points. this spacing provides insulation which avoids an electric discharge between the conductors. Size of conductor. the size of conductor used in overhead lines is comparatively smaller. the size of conductor used in underground cables is relatively larger. voltage rating. overhead lines have higher voltage rating, near about 765 kv. undergrounds cables have comparatively lower voltage rating. Electricity is transmitted and distributed using overhead power lines or underground power cables. in this video, 10 comparisons between these two are discus. Advantages. high power transmission. low installation and material cost. long distance transmissions. the fault or damage in overhead lines can easily locate. maintenance of the line is easier. extension or joining on overhead lines can be performed easily and also it facilitates easy replacing.

Comments are closed.