Complex Conjugates Theorem Youtube
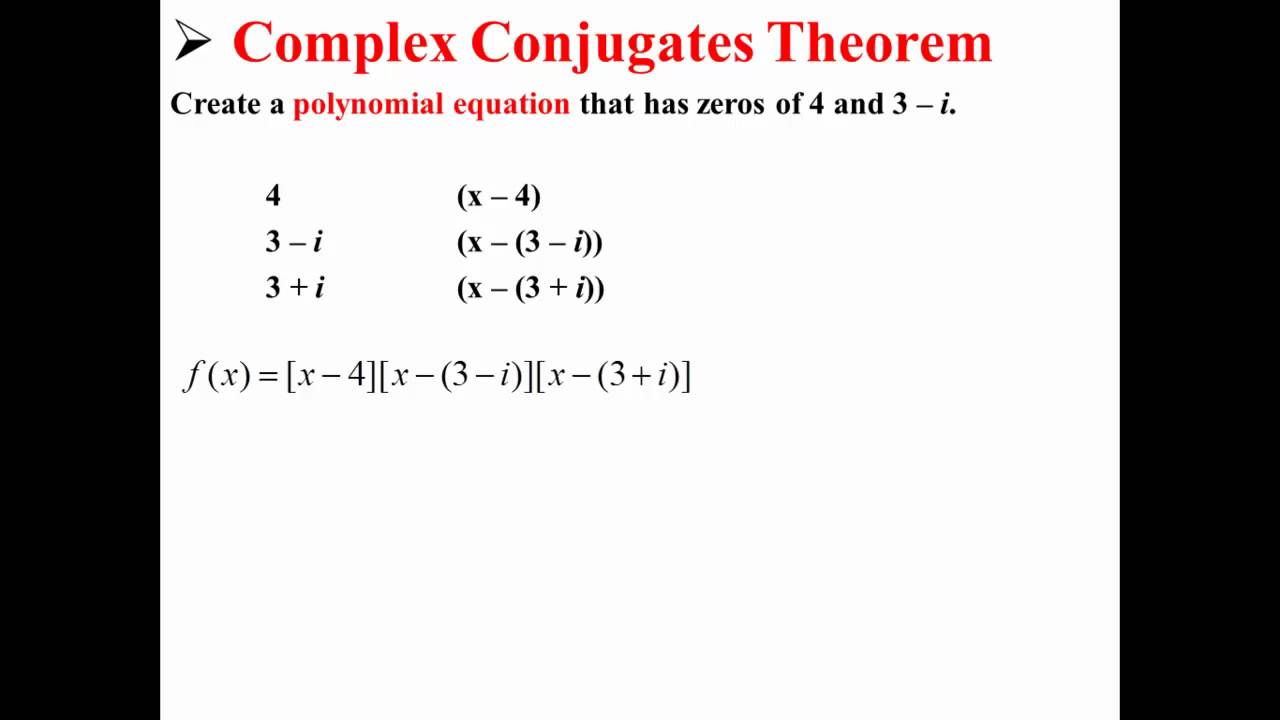
Complex Conjugates Theorem Youtube We learn the complex conjugate root theorem as well as work through an example, showing how it can be used to write a polynomial function as a product of its. The complex conjugate root theorem says that if z is a complex root of a polynomial then the conjugate of z is also a root. this video walks through the pro.

Complex Conjugates Theorem Youtube In getting through algebra, we never talked about complex numbers, but they are important so let's discuss them now! these are numbers with a real component. Complex conjugate root theorem. 展豪 張 contributed. complex conjugate root theorem states that for a real coefficient polynomial p (x) p (x), if a bi a bi (where i i is the imaginary unit) is a root of p (x) p (x), then so is a bi a− bi. to prove this, we need some lemma first. Complex conjugate root theorem. in mathematics, the complex conjugate root theorem states that if p is a polynomial in one variable with real coefficients, and a bi is a root of p with a and b real numbers, then its complex conjugate a − bi is also a root of p. [1] it follows from this (and the fundamental theorem of algebra) that, if the. In algebra, the complex conjugate root theorem states that if is a polynomial with real coefficients, then a complex number is a root of if and only if its complex conjugate is also a root. a common intermediate step in intermediate competitions is to recognize that when given a complex root of a real polynomial, its conjugate is also a root. proof.

The Complex Conjugates Theorem Youtube Complex conjugate root theorem. in mathematics, the complex conjugate root theorem states that if p is a polynomial in one variable with real coefficients, and a bi is a root of p with a and b real numbers, then its complex conjugate a − bi is also a root of p. [1] it follows from this (and the fundamental theorem of algebra) that, if the. In algebra, the complex conjugate root theorem states that if is a polynomial with real coefficients, then a complex number is a root of if and only if its complex conjugate is also a root. a common intermediate step in intermediate competitions is to recognize that when given a complex root of a real polynomial, its conjugate is also a root. proof. Complex conjugates have the same real part but opposite imaginary parts. the product of complex conjugates is always a real number. to find all zeros of a polynomial with real coefficients, once one complex root is found, its conjugate must also be included. The complex conjugate root theorem states that if f(x) is a polynomial with real coefficients and a ib is one of its roots, where a and b are real numbers, then the complex conjugate a ib is also a root of the polynomial f(x). to understand the theorem better, let us take an example of a polynomial with complex roots.

7 6 Complex Conjugates Theorem Youtube Complex conjugates have the same real part but opposite imaginary parts. the product of complex conjugates is always a real number. to find all zeros of a polynomial with real coefficients, once one complex root is found, its conjugate must also be included. The complex conjugate root theorem states that if f(x) is a polynomial with real coefficients and a ib is one of its roots, where a and b are real numbers, then the complex conjugate a ib is also a root of the polynomial f(x). to understand the theorem better, let us take an example of a polynomial with complex roots.

The Complex Conjugate Root Theorem Youtube

Comments are closed.