Contrast Iv Contrast Pearls Educational Tools Ct Scanning Ct
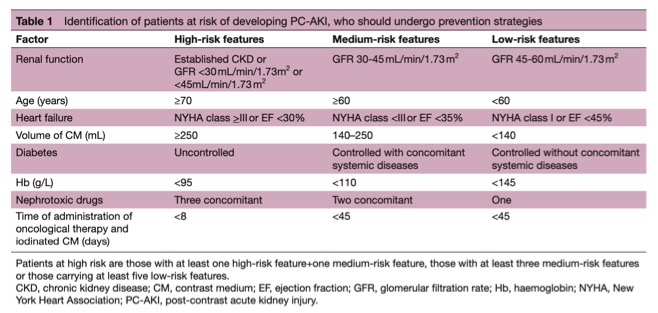
Contrast Iv Contrast Pearls Educational Tools Ct Scanning Ct Administration of iv contrast for the first ct ap was associated with increased detection of urgent findings compared with non contrast ct (p = 0.004) and a contrast enhanced ct ap following an initial non contrast ct ap examination better characterized both urgent (p = 0.002) and non urgent findings (p < 0.001). Modifying peripheral iv catheters with side holes and side slits results in favorable changes in fluid dynamic properties during the injection of iodinated contrast material weber pw et al. ajr 2009; 193:970 977.
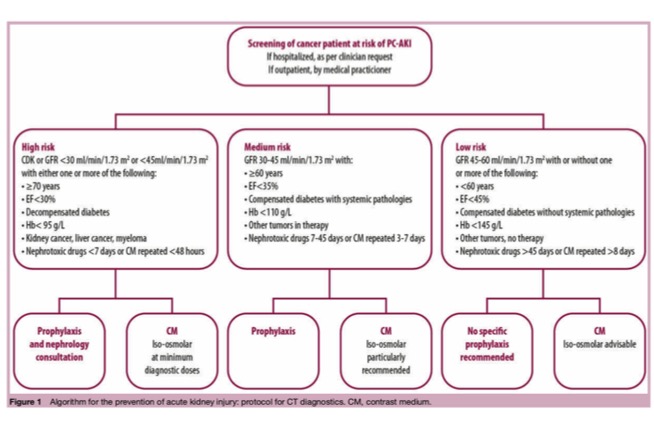
Contrast Iv Contrast Pearls Educational Tools Ct Scanning Ct Rate of contrast material extravasations and allergic like reactions: effect of extrinsic warming of low osmolality iodinated ct contrast material to 37° c davenport ms et al. radiology 2012; 262:475 484. The concept of contrast is the foundation upon which imaging rests. contrast is simply the ability to distinguish two objects. in medical imaging, it allows adjacent substances or tissue to be distinguishable and visualized. contrast allowed marie curie to identify her bones from the outline of her hand. [1] the ability to distinguish target tissue from the surrounding structures is how. There are 2 different ways to get contrast: oral contrast is contrast you take by mouth. intravenous (iv) contrast goes into your veins. this can be an iv in your arm, or a central venous catheter (cvc), such as an implanted port. contrast will leave your body through your urine (pee) within 24 hours (1 day). Intravenous contrast. all modern iv contrast agents are iodine based. the iodine causes increased absorption and scattering of the incoming radiation, which serves to increase the attenuation or “brightness” of the tissue or organ. 1 importantly, the iv contrast used in ct is distinct from the gadolinium based iv contrast used in magnetic resonance imaging, meaning that there is no cross.
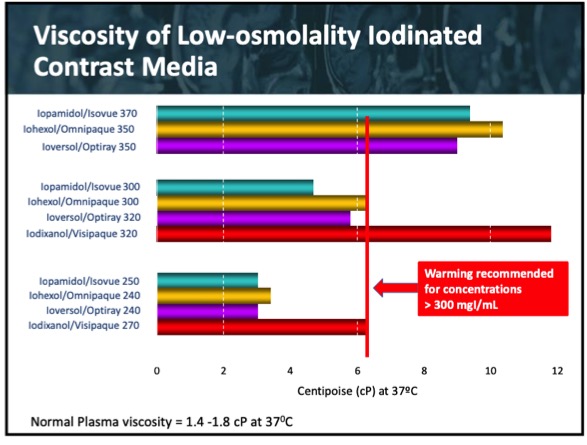
Best Practices In The Use Of Iodinated Contrast Media In The Clinical There are 2 different ways to get contrast: oral contrast is contrast you take by mouth. intravenous (iv) contrast goes into your veins. this can be an iv in your arm, or a central venous catheter (cvc), such as an implanted port. contrast will leave your body through your urine (pee) within 24 hours (1 day). Intravenous contrast. all modern iv contrast agents are iodine based. the iodine causes increased absorption and scattering of the incoming radiation, which serves to increase the attenuation or “brightness” of the tissue or organ. 1 importantly, the iv contrast used in ct is distinct from the gadolinium based iv contrast used in magnetic resonance imaging, meaning that there is no cross. An angiogram is a specific type of ct scan with contrast. in a ct angiogram the contrast is timed so that it will highlight either the arteries or veins (venogram) of interest. for instance, a ct angiogram of the chest to evaluate for pe will have the timing set so the contrast is present in the pulmonary arteries. Children 6 years and above: cetirizine 10 mg by mouth 1 hour prior to imaging study**. children 2 5 years: cetirizine 5 mg by mouth 1 hour prior to imaging study**. prior moderate, severe, or unknown severity contrast reaction premedication protocol. premedication with corticosteroid and antihistamine.
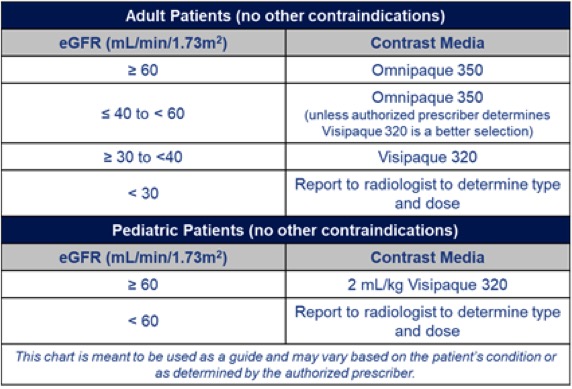
Adult Patients An angiogram is a specific type of ct scan with contrast. in a ct angiogram the contrast is timed so that it will highlight either the arteries or veins (venogram) of interest. for instance, a ct angiogram of the chest to evaluate for pe will have the timing set so the contrast is present in the pulmonary arteries. Children 6 years and above: cetirizine 10 mg by mouth 1 hour prior to imaging study**. children 2 5 years: cetirizine 5 mg by mouth 1 hour prior to imaging study**. prior moderate, severe, or unknown severity contrast reaction premedication protocol. premedication with corticosteroid and antihistamine.
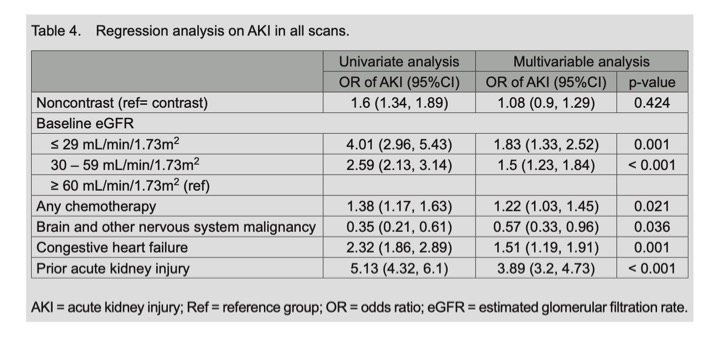
Contrast Iv Contrast Pearls Educational Tools Ct Scanning Ct

Comments are closed.