Copper Chaperone Ccs Delivers Cu I To Cu Zn Sod Sod1 Chemistry
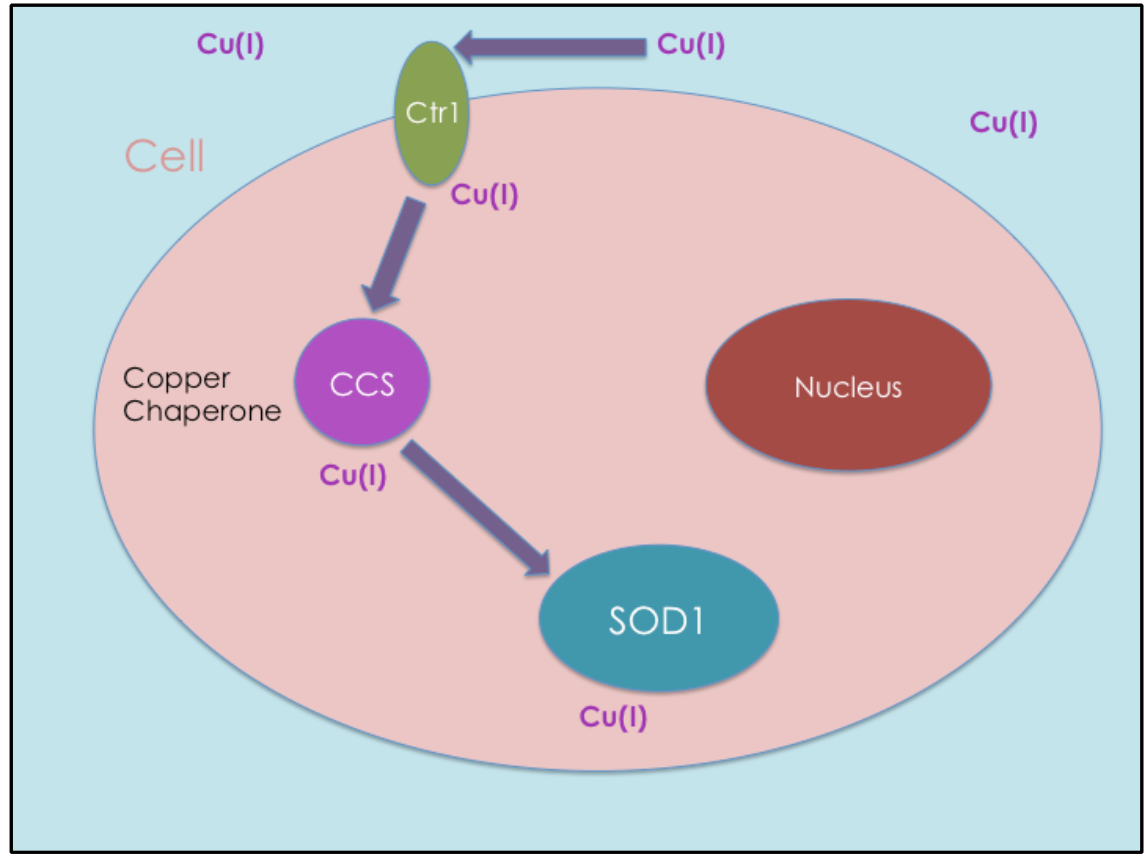
Copper Chaperone Ccs Delivers Cu I To Cu Zn Sod Sod1 Chemistry Cu, zn superoxide dismutase (sod1) and copper chaperone for sod1 (ccs1) in 1969, mccord and fridovich discovered an enzyme, termed erythrocuprein, which has since been renamed sod1 [ 5 ]. it is a ubiquitously expressed antioxidant enzyme that protects the cell from the buildup of radical oxygen species through the disproportionation of. One chaperone is copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase 1 (ccs). human copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase (hccs) is a metalloprotein that delivers copper (i) to sod1 inside human cells (see figure 3). it is made up of 274 amino acids and weighs 54 kda. 5 inside cells, copper is primarily found in its 1 oxidation state since the.
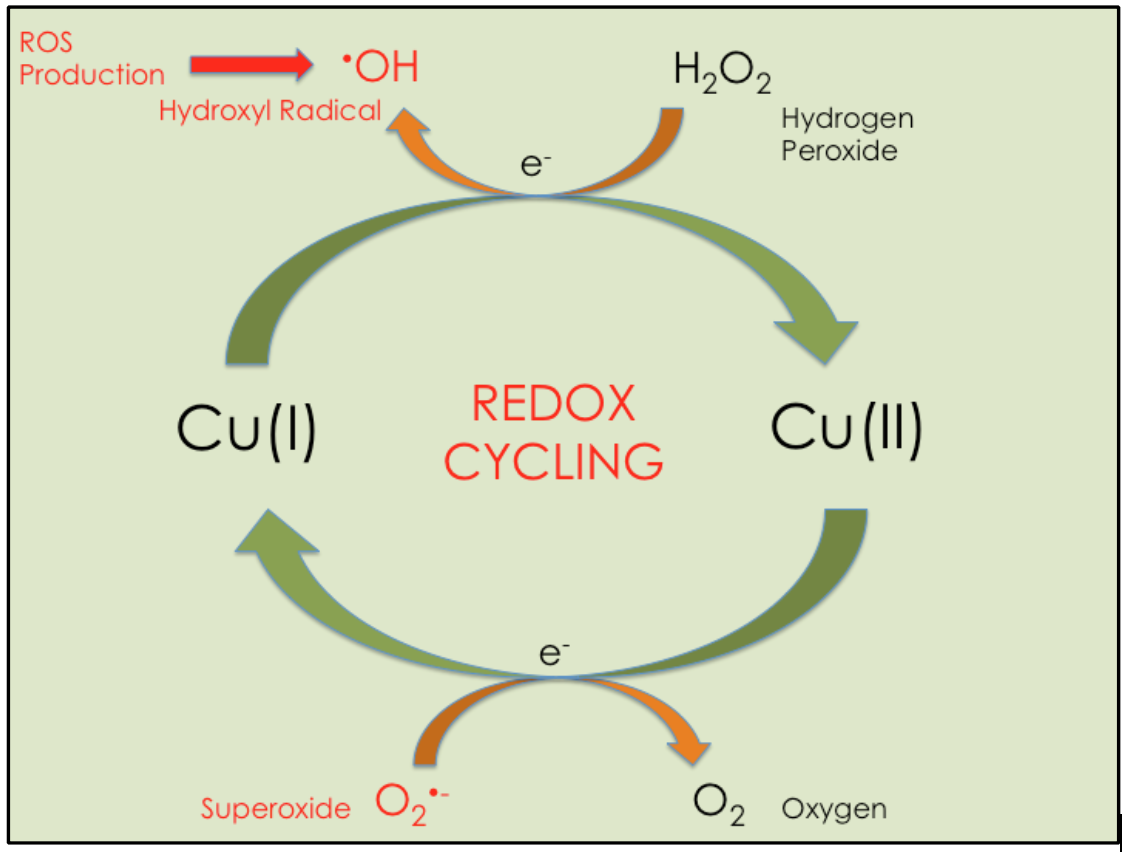
Copper Chaperone Ccs Delivers Cu I To Cu Zn Sod Sod1 Chemistry Cu, zn superoxide dismutase (sod1) protects the cell from the accumulation of radical oxygen species by way of the redox cycling activity of copper in its catalytic center. multiple posttranslational modification events, including copper incorporation, are reliant on the copper chaperone for sod1 (ccs). the high affinity copper uptake protein. Copper is distributed to distinct localizations in the cell through diverse pathways. we demonstrate here that the delivery of copper to copper zinc superoxide dismutase (sod1) is mediated through a soluble factor identified as saccharomyces cerevisiae lys7 and human ccs (copperchaperone for sod). this factor is specific for sod1 and does not deliver copper to proteins in the mitochondria. However, cu's chemical properties also make it toxic, requiring specific cellular mechanisms for cu uptake and handling, mediated by cu chaperones. ccs1, the budding yeast (s. cerevisiae) cu chaperone for cu zinc (zn) superoxide dismutase (sod1) activates by directly promoting both cu delivery and disulfide formation in sod1. the complete. The formation of this bond in newly synthesized sod1 is facilitated by ccs1 cu chaperone and is coupled to copper insertion 66,67. the process is initiated by a copper mediated (and ccs1.
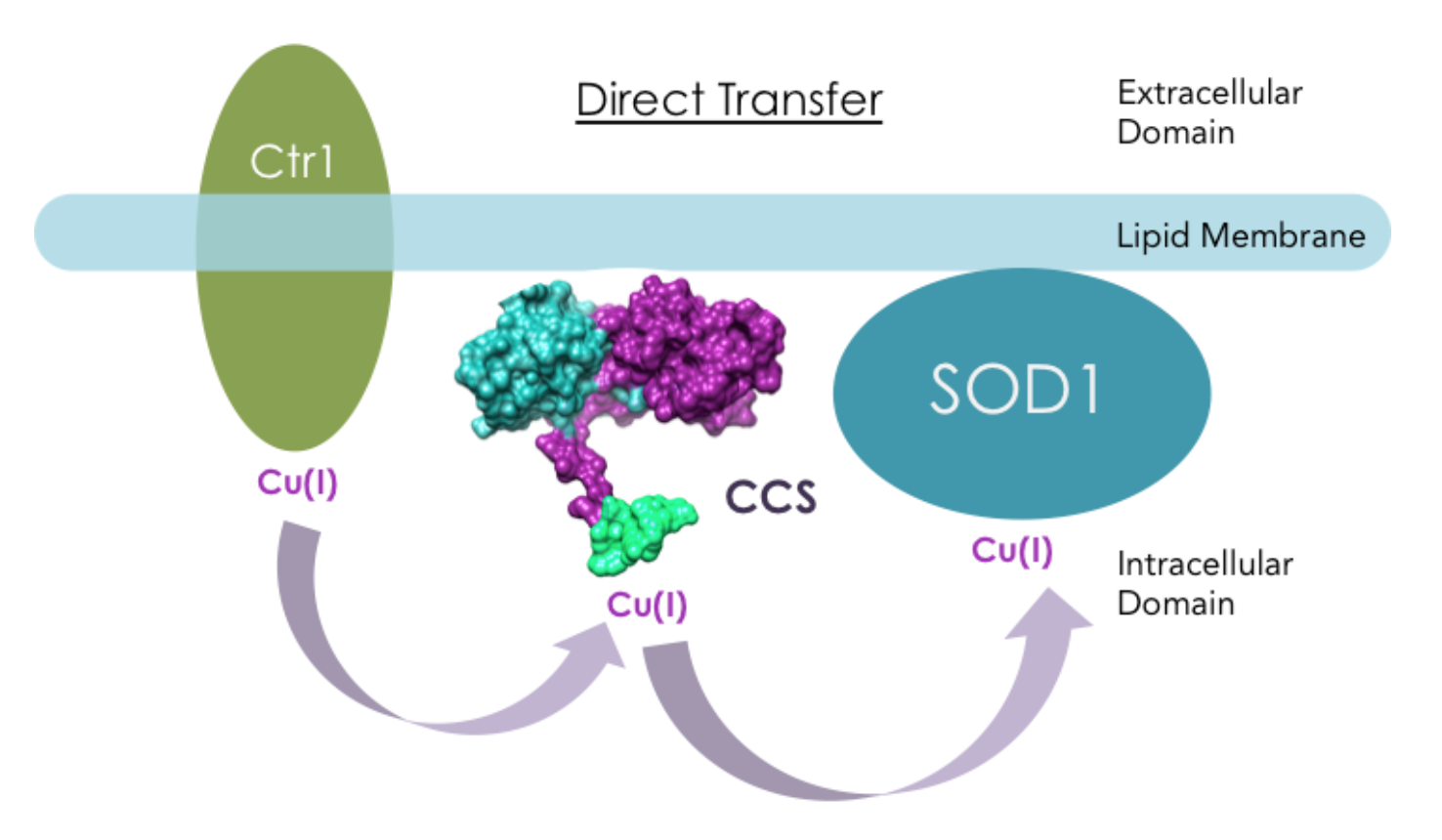
Copper Chaperone Ccs Delivers Cu I To Cu Zn Sod Sod1 Chemistry However, cu's chemical properties also make it toxic, requiring specific cellular mechanisms for cu uptake and handling, mediated by cu chaperones. ccs1, the budding yeast (s. cerevisiae) cu chaperone for cu zinc (zn) superoxide dismutase (sod1) activates by directly promoting both cu delivery and disulfide formation in sod1. the complete. The formation of this bond in newly synthesized sod1 is facilitated by ccs1 cu chaperone and is coupled to copper insertion 66,67. the process is initiated by a copper mediated (and ccs1. The cu chaperone for superoxide dismutase (ccs) delivers cu to cu zn sod in cytosol and mitochondria, cytochrome c oxidase cu chaperone (cox17) mediates cu transfer within the mitochondrial intermembrane space for metallation and assembly of cytochrome c oxidase (cox), and atox1 transfers cu to the cu atpases (atp7a and atp7b) for delivery to. Enzymes including cu,zn superoxide dismutase (sod1) via tran scriptional mechanisms; however, few examples of posttransla tional regulation are known. the copper chaperone for sod1 (ccs) is involved in physiological sod1 activation, and its primary func tion is thought to be delivery of copper to the enzyme. data.

Comments are closed.