Coronary Artery Disease Northwestern Medicine

Taking Action Against Coronary Artery Disease Northwestern Medicine Northwestern medicine focuses on treating patients before they develop a sometimes fatal heart attack, using advanced treatment options. if you have coronary artery disease that requires coronary angioplasty or bypass surgery, know that northwestern medicine consistently ranks among the top hospitals in the nation for exceptional interventional. Physicians can treat the side effects of coronary artery disease with: antiplatelet medications to decrease the ability of platelets in the blood to stick together and cause clots. anticoagulants (blood thinners) that decrease the blood’s ability to clot. antihyperlipidemics to lower lipids (fats) in the blood, such as statins and bile acid.

10 Things You May Not Know About Heart Disease Northwestern Medicine Northwestern medicine bluhm cardiovascular institute provides comprehensive care for patients with a coronary artery chronic total occlusion (cto). this is the most severe form of coronary artery disease (cad). we are here to help. 1850 gateway drive. sycamore, il 60178. 815.748.2975 (tty: 711) find your northwestern medicine location. if you are a current patient with northwestern medicine: to schedule a coronary calcium scan at any of our nm locations: log onto the mynm website or the mynm app (available from the app store or google play) click “menu” (on the mynm. Coronary artery disease (cad) is the most common type of heart disease. it is the leading cause of death in the united states in both men and women. determine your risk for developing cad using this assessment tool. Some factors that affect whether a person develops coronary artery disease cannot be modified. they include. advancing age. male sex. family history of early coronary artery disease (that is, having a close relative who developed the disease before age 55 years in the case of a male relative or 65 years in the case of a female relative).
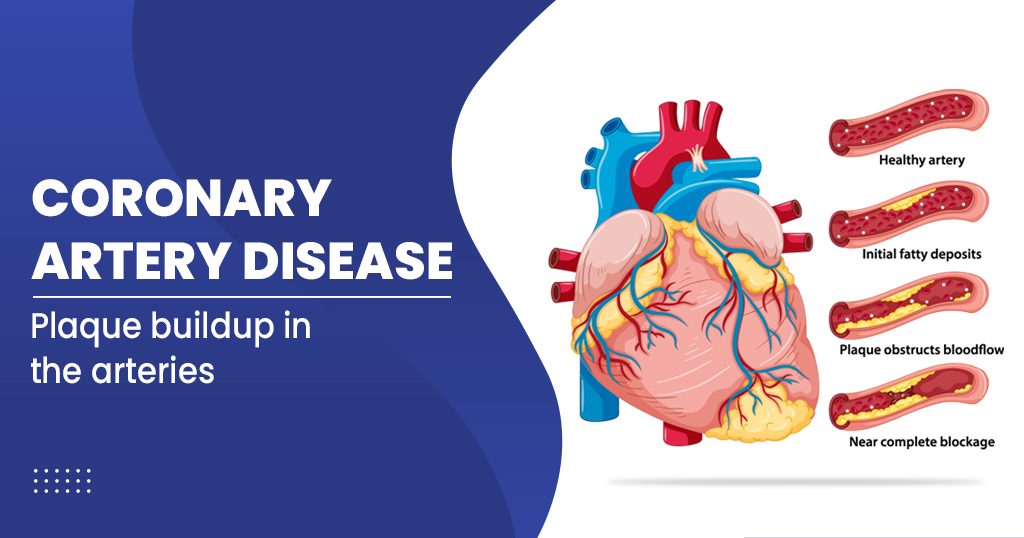
Coronary Artery Disease Coronary artery disease (cad) is the most common type of heart disease. it is the leading cause of death in the united states in both men and women. determine your risk for developing cad using this assessment tool. Some factors that affect whether a person develops coronary artery disease cannot be modified. they include. advancing age. male sex. family history of early coronary artery disease (that is, having a close relative who developed the disease before age 55 years in the case of a male relative or 65 years in the case of a female relative). Coronary artery disease that narrows one or more of these arteries can block blood flow, causing chest pain (angina) or an acute coronary syndrome (see also overview of coronary artery disease). in an acute coronary syndrome, sudden blockage in a coronary artery greatly reduces or cuts off the blood supply to an area of the heart muscle. Risk factors for coronary artery disease are the same as risk factors for atherosclerosis: older age. male sex. family history of early coronary artery disease (death from coronary artery disease in a first degree relative prior to age 55 in males or age 65 in females) high blood levels of low density lipoprotein (ldl) cholesterol (see.

Coronary Artery Disease Of The Circumflex Artery Trial Exhibits Coronary artery disease that narrows one or more of these arteries can block blood flow, causing chest pain (angina) or an acute coronary syndrome (see also overview of coronary artery disease). in an acute coronary syndrome, sudden blockage in a coronary artery greatly reduces or cuts off the blood supply to an area of the heart muscle. Risk factors for coronary artery disease are the same as risk factors for atherosclerosis: older age. male sex. family history of early coronary artery disease (death from coronary artery disease in a first degree relative prior to age 55 in males or age 65 in females) high blood levels of low density lipoprotein (ldl) cholesterol (see.
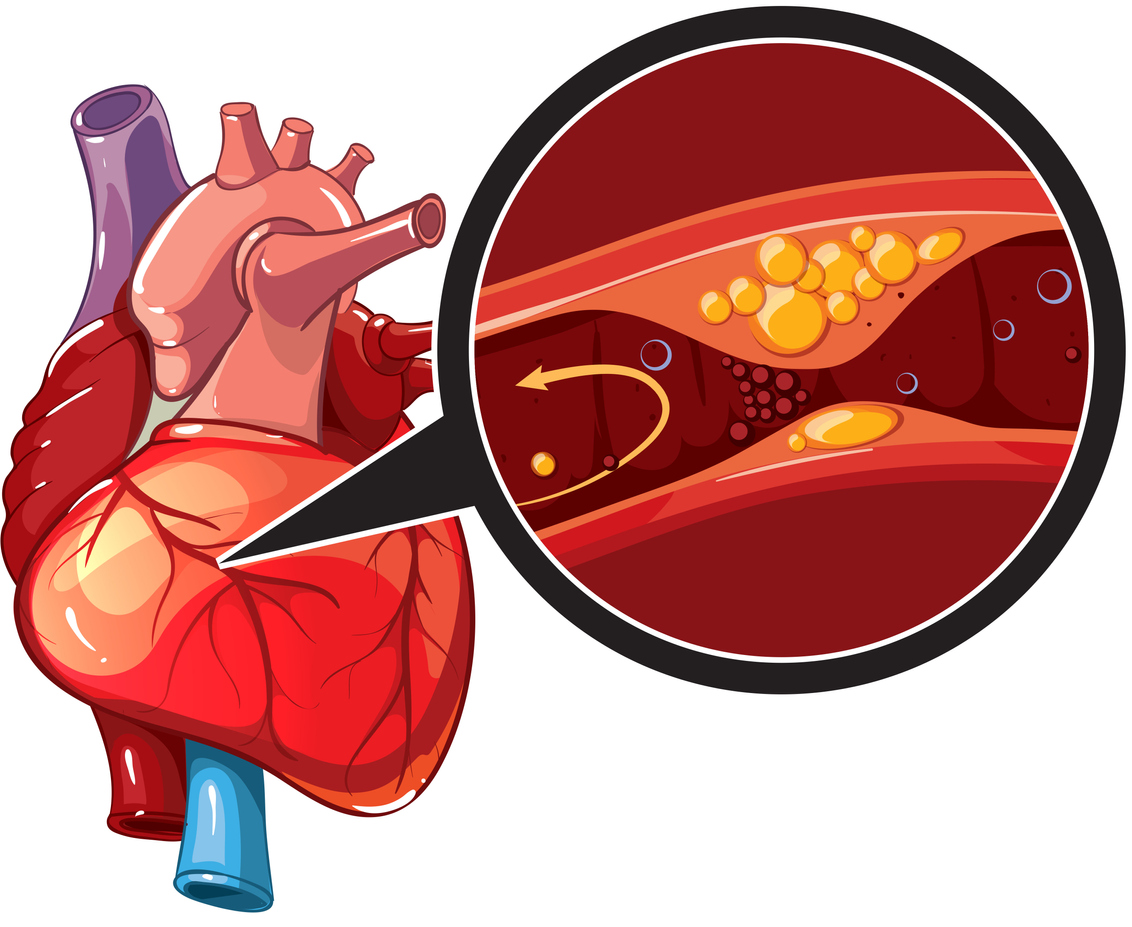
Coronary Artery Disease Treatment Causes Prevention

Comments are closed.