Covalent Bond Definition Properties Examples Facts 40 Off

Covalent Bond Examples Covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. the binding arises from the electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons. a covalent bond forms when the bonded atoms have a lower total energy than that of widely separated atoms. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds are types of atomic bonds. these bonds are different in their properties and structure. covalent bonds include pairs of electrons by two atoms binding them in a fixed orientation, while a bond between two ions is called an ionic bond. covalent vs ionic bonds. covalent bonding occurs between two non metallic atoms.

Covalent Bond Definition Properties Examples Facts 40 O Usually, sharing electrons gives each atom a full valence shell and makes the resulting compound more stable than its constituent atoms are on their own. covalent bonds usually form between nonmetals. examples of covalent compounds include hydrogen (h 2), oxygen (o 2), carbon monoxide (co), ammonia (nh 3), water (h 2 o), and all organic compounds. An example of double covalent bonds is the bonding between carbon and oxygen atoms in co2. 3. triple covalent bond. a triple covalent bond is formed by the sharing of three pairs of electrons between the participating atoms. a triple covalent bond is indicated by (≡). Based on the number of shared electron pairs, there are three types of covalent bonds [1 6]: 1. single covalent bond. when one pair of electrons, or two electrons, are shared between the atoms, it is known as a single covalent bond or merely a single bond. examples: h 2, cl 2, br 2, i 2, hcl, nh 3, ch 4, and c 2 h 6. 2. Anne marie helmenstine, ph.d. updated on july 03, 2019. a covalent bond in chemistry is a chemical link between two atoms or ions in which the electron pairs are shared between them. a covalent bond may also be termed a molecular bond. covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms with identical or relatively close electronegativity values.
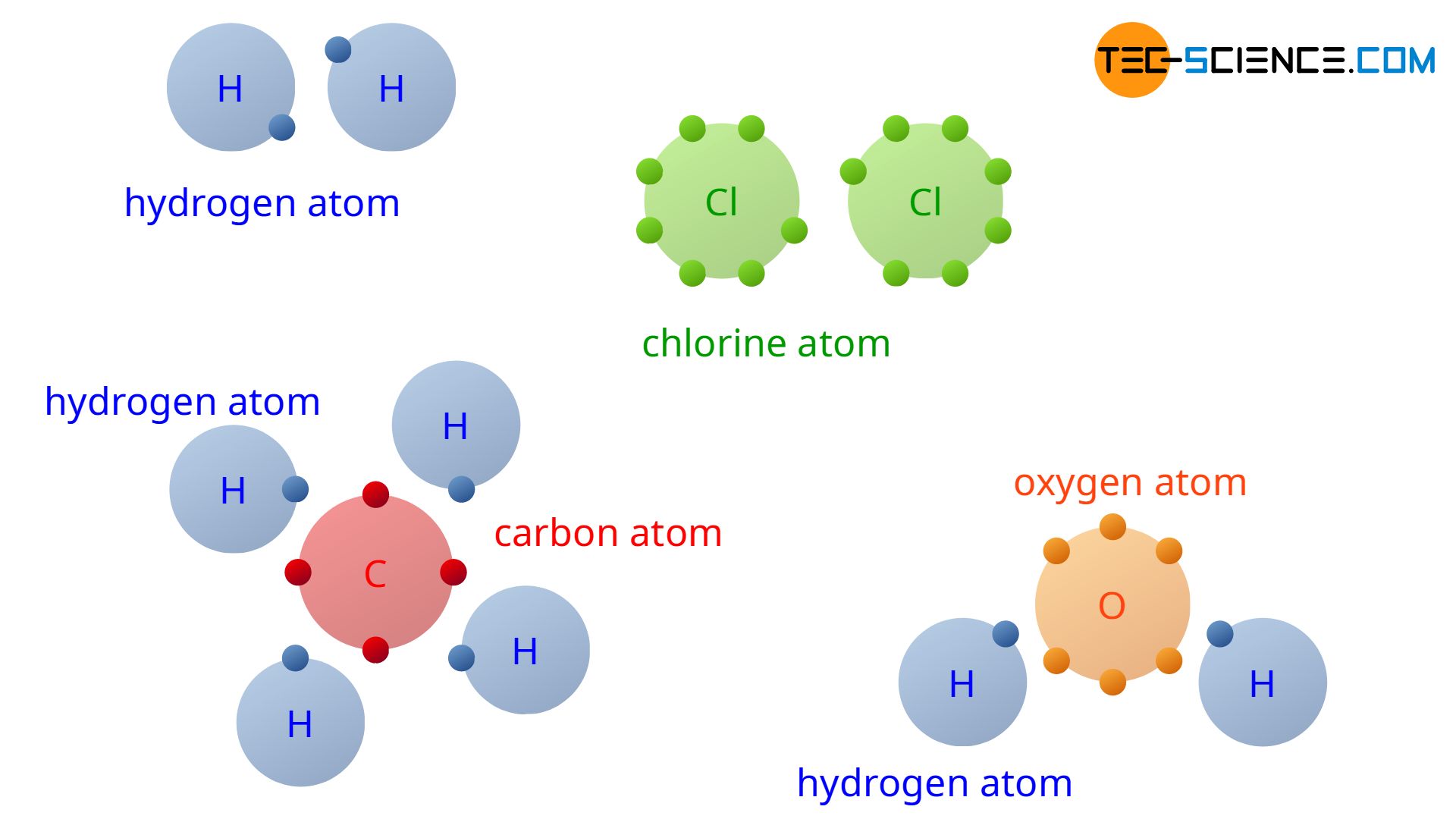
Covalent Bond Definition Properties Examples Facts 40 O Based on the number of shared electron pairs, there are three types of covalent bonds [1 6]: 1. single covalent bond. when one pair of electrons, or two electrons, are shared between the atoms, it is known as a single covalent bond or merely a single bond. examples: h 2, cl 2, br 2, i 2, hcl, nh 3, ch 4, and c 2 h 6. 2. Anne marie helmenstine, ph.d. updated on july 03, 2019. a covalent bond in chemistry is a chemical link between two atoms or ions in which the electron pairs are shared between them. a covalent bond may also be termed a molecular bond. covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms with identical or relatively close electronegativity values. – thus an alternative definition of a covalent bond would be: the attractive force between atoms is created by the sharing of an electron pair. – the compounds containing a covalent bond are called covalent compounds. conditions for the formation of covalent bond – the conditions favorable for the formation of an ionic bond are:. Most compounds with covalent bonds can be described using lewis structures and follow the octet rule. a covalent bond normally contains an energy of about ~80 kilocalories per mole (kcal mol). there are three types of covalent bonds: single, double, and triple. covalent bonds can also be classified as polar and nonpolar.
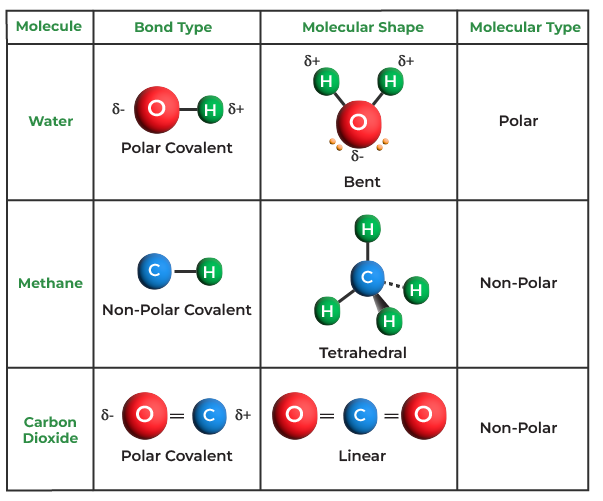
Covalent Bond Definition Types Properties And Example Vrogue Co – thus an alternative definition of a covalent bond would be: the attractive force between atoms is created by the sharing of an electron pair. – the compounds containing a covalent bond are called covalent compounds. conditions for the formation of covalent bond – the conditions favorable for the formation of an ionic bond are:. Most compounds with covalent bonds can be described using lewis structures and follow the octet rule. a covalent bond normally contains an energy of about ~80 kilocalories per mole (kcal mol). there are three types of covalent bonds: single, double, and triple. covalent bonds can also be classified as polar and nonpolar.

Covalent Bond Definition Types And Examples

Comments are closed.