Cross Bridge Cycle Pearson Channels
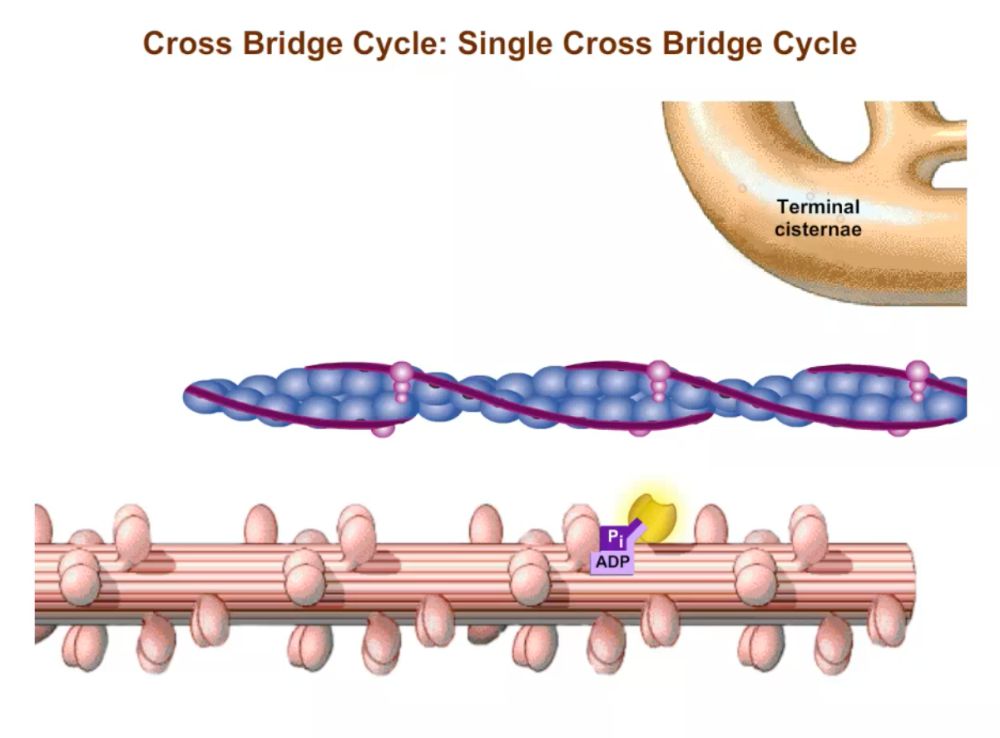
Cross Bridge Cycle Pearson Channels When a binding site on actin is exposed, an energized myosin head can bind to it, forming a cross bridge. the binding of myosin to actin brings about a change in the conformation of the myosin head, resulting in the release of adp and inorganic phosphate. at the same time, the myosin head flexes, pulling the thin filament inward toward the. C. cross bridge cycle.

Cross Bridge Cycle Channels For Pearson So the cross bridge cycle, we're going to say, is the interaction of the myosin head and the actin in a way that leads to the sarcomere shortening. and that's our goal. if we want a muscle to contract, we need that fundamental unit of muscle contraction, the sarcomere, to get shorter. so we have this cross bridge cycle broken up into 4 steps here. Cross bridge cycle: step 2. the power stroke: adp released and activated myosin head pivotes; slides thin myofilament toward center of sarcomere. cross bridge cycle: step 3. cross bridge detachment: link between mysoin head and actin weakens when another atp ataches to myosin head; myosin head detaches. cross bridge cycle: step 4. This shortens the sarcomeres in the muscle fiber and causes the whole skeletal muscle to contract. the cross bridge cycle ends when ca2 are actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. the cycle repeats as long as the binding sites on actin remain exposed, and both ca2 and atp are available. (usmle topics) molecular basis of the sliding filament theory (skeletal muscle contraction) the cross bridge cycle. purchase a license to download a non wa.

Comments are closed.