Cryogenic Distillation Process The Engineer S Perspective
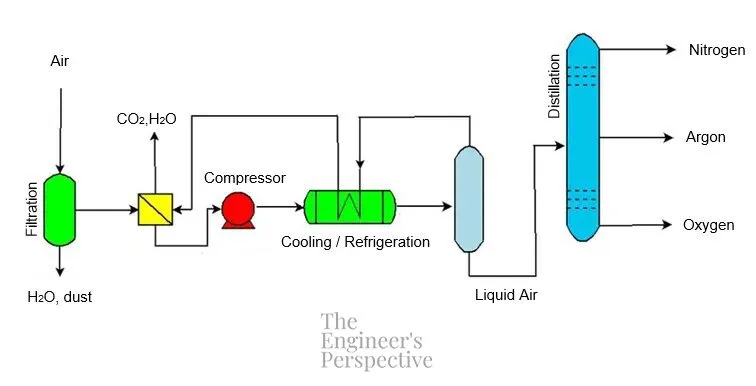
Cryogenic Distillation Process The Engineer S Perspective Through a process called liquefaction, air condenses and becomes liquid at cryogenic temperature. distillation of air. by slowly warming up the liquid air, distillation separates air into its different component gases. nitrogen is separated first (boiling point 196°c), then argon (boiling point 186°c), and oxygen last (boiling point 183°c). Steam distillation principle. steam distillation, or steam stripping (depending on its application) is a distillation separation technique which utilizes steam as a carrier vapor to separate temperature sensitive volatile components in a solution at a much lower temperature than its boiling point.

Cryogenic Distillation Process The Engineer S Perspective 3.2.4 cryogenic distillation. the process of cryogenic distillation splits co 2 from a gas mixture by condensation [105]. fig. 7 d shows a simple drawing of the process. the gas mixture is compressed and in the heat exchanger cooled down. the cooled pressurized fluid mixture is then fed into the distillation column (tray or packed). Cryogenic distillation is used on gas gas mixtures whose components have boiling points at freezing temperatures. it is called as such because the process occurs at cryogenic temperatures ranging from 170°c to 190°c. gases are liquefied at these temperatures which makes it easier to purify. Biomethane can be liquified (also known as lbm) at a significantly lower cost by the anti sublimation process than by the cryogenic distillation process [17]. the environmental effect of biogas is an important aspect that should be considered. undertaking a life cycle assessment (lca) is useful for studying environmental impacts. The output syngas from the water gas shift reaction, a feed for the igcc plant, in addition to h 2, co, and co 2, as shown in table 2, consists of h 2 s, h 2 o, n 2, nh 3, ch 4, and ar. co 2 percent in this flow is approximately up to 39.85%, which is high enough; thus, a distillation cryogenic temperature process is a suitable method for this.

Cryogenic Distillation Process The Engineer S Perspective Biomethane can be liquified (also known as lbm) at a significantly lower cost by the anti sublimation process than by the cryogenic distillation process [17]. the environmental effect of biogas is an important aspect that should be considered. undertaking a life cycle assessment (lca) is useful for studying environmental impacts. The output syngas from the water gas shift reaction, a feed for the igcc plant, in addition to h 2, co, and co 2, as shown in table 2, consists of h 2 s, h 2 o, n 2, nh 3, ch 4, and ar. co 2 percent in this flow is approximately up to 39.85%, which is high enough; thus, a distillation cryogenic temperature process is a suitable method for this. The removal of h 2 s through the cryogenic process remains challenging, as it is a highly energy intensive process which requires a very low operating temperature, leading to dramatic increases in operating expenditure . hence, future work on the integration between cryogenic process and liquefied natural gas (lng) production is significantly. Natural gas demand has dramatically increased due to the emerging growth of the world economy and industry. presently, co2 and h2s content in gas fields accounts for up to 90% and 15%, respectively. apart from fulfilling the market demand, co2 and h2s removal from natural gas is critical due to their corrosive natures, the low heating value of natural gas and the greenhouse gas effect. to date.

Comments are closed.