Deadweight Loss Definition Inomics El Sitio Para Economistas
Deadweight Loss Definition Inomics El Sitio Para Economistas Proyectar esta idea en mercados completos en tiempos festivos del año cuando se intercambian regalos (no monetarios), podría resultar en pérdidas irrecuperables de eficiencia en la economía. consulta el provocativo artículo de joel waldfogel, “the deadweight loss of christmas” (american economic review, 1993) para más información. Deadweight loss is created whenever governments intervene in markets. for example, the market for cigarettes produces a negative externality, as it forces non smokers to deal with secondhand smoke. further, the health problems caused by smoking increase healthcare costs.
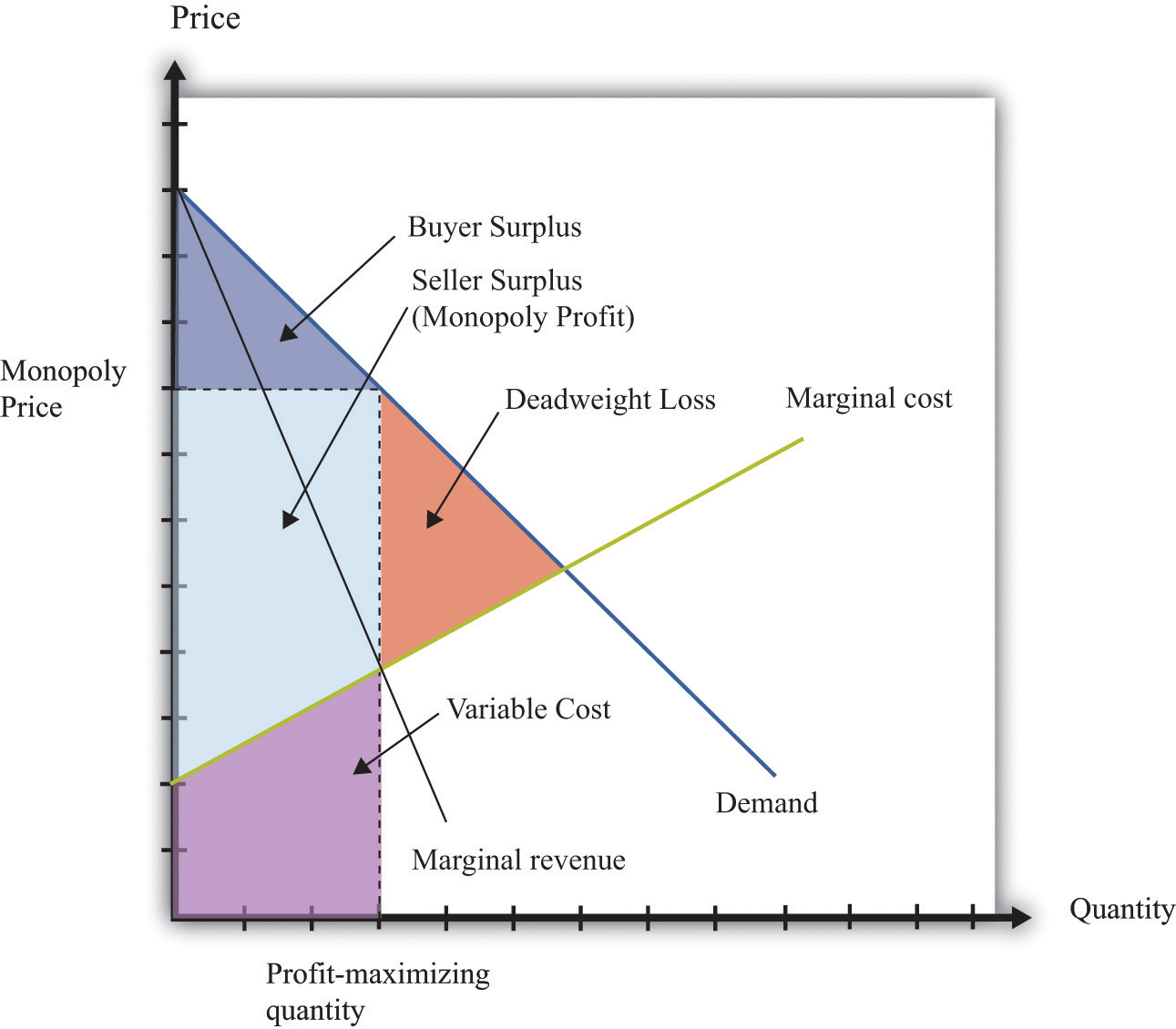
Efficiency And Deadweight Loss Deadweight loss. in economics, deadweight loss is the loss of societal economic welfare due to production consumption of a good at a quantity where marginal benefit (to society) does not equal marginal cost (to society) – in other words, there are either goods being produced despite the cost of doing so being larger than the benefit, or. Deadweight loss and tax revenue. the amount of money collected in taxes is proportional to the tax applied to the total cost of a product or service. figure 4: tax rate affects the size of deadweight loss. the first graphic above shows that the highest tax income is collected with a modest tax rate. A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market. deadweight loss can also be referred to as “excess burden.”. a deadweight loss arises at times when supply and demand –the two most fundamental forces driving the economy–are not balanced. In this case the deadweight loss is $4,000. breakdown: • p 1 = producer’s cost of a comic book = $5. • p 2 = producer’s price to sell a comic book = $9. • p 3 = price a consumer pays = $11. • p 4 = price a consumer is willing to pay = $15. • units sold = 600.
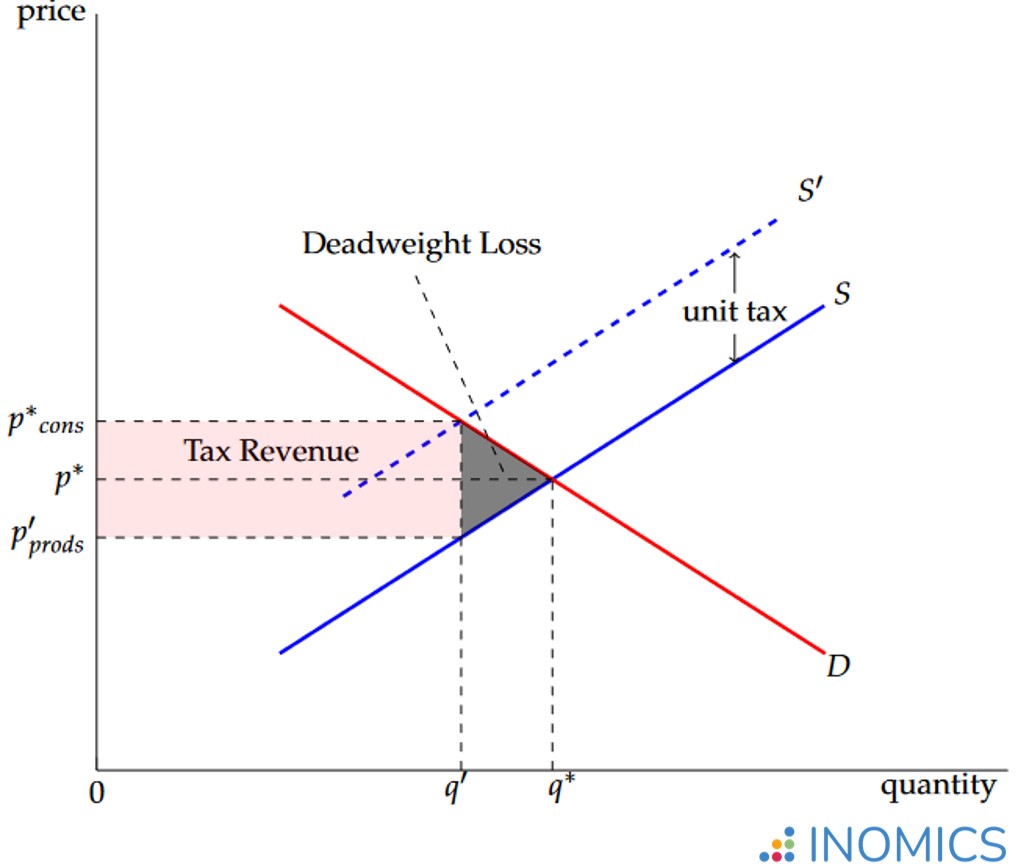
Deadweight Loss Inomics A deadweight loss is a cost to society as a whole that is generated by an economically inefficient allocation of resources within the market. deadweight loss can also be referred to as “excess burden.”. a deadweight loss arises at times when supply and demand –the two most fundamental forces driving the economy–are not balanced. In this case the deadweight loss is $4,000. breakdown: • p 1 = producer’s cost of a comic book = $5. • p 2 = producer’s price to sell a comic book = $9. • p 3 = price a consumer pays = $11. • p 4 = price a consumer is willing to pay = $15. • units sold = 600. A cost to society that is created by market inefficiency (which takes place when supply and demand are not in equilibrium) is called a deadweight loss. this term is mainly used in economics. the concept of deadweight loss can be applied to any deficiency that is caused by the inefficient allocation of resources. Deadweight loss is the economic cost borne by society. it is a market inefficiency caused by an imbalance between consumption and allocation of resources. the deadweight inefficiency of a product can never be negative; it can be zero. deadweight loss is zero when the demand is perfectly elastic or when the supply is perfectly inelastic.
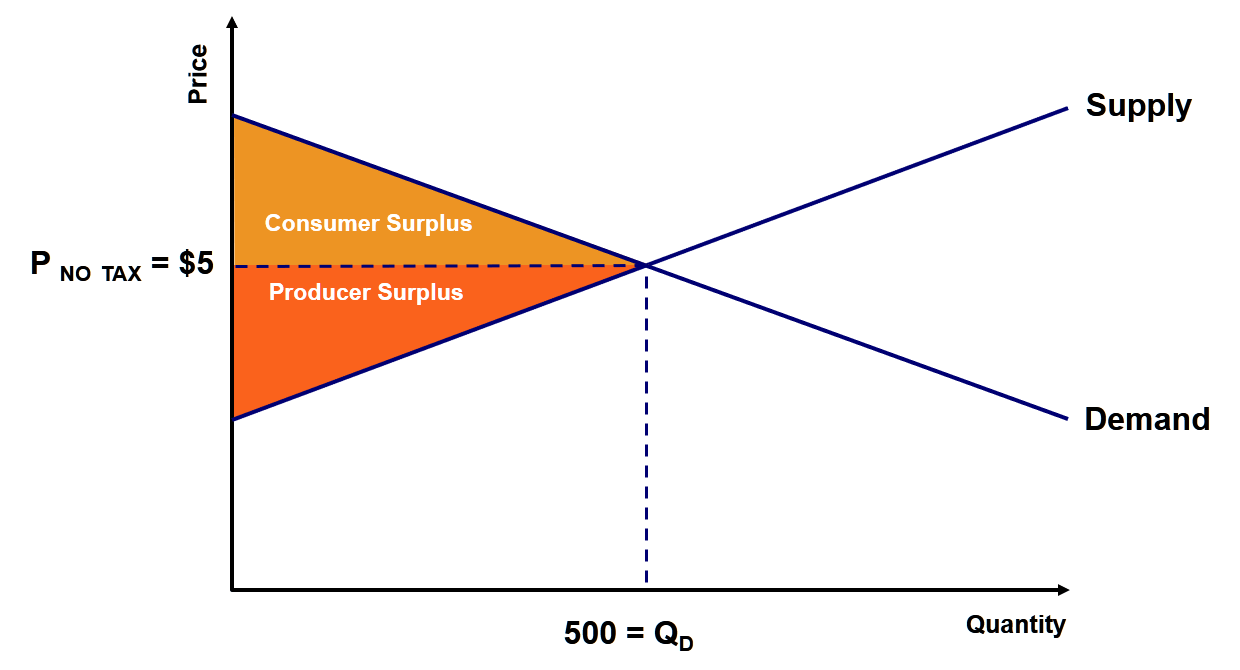
Deadweight Loss Examples How To Calculate Deadweight Loss A cost to society that is created by market inefficiency (which takes place when supply and demand are not in equilibrium) is called a deadweight loss. this term is mainly used in economics. the concept of deadweight loss can be applied to any deficiency that is caused by the inefficient allocation of resources. Deadweight loss is the economic cost borne by society. it is a market inefficiency caused by an imbalance between consumption and allocation of resources. the deadweight inefficiency of a product can never be negative; it can be zero. deadweight loss is zero when the demand is perfectly elastic or when the supply is perfectly inelastic.
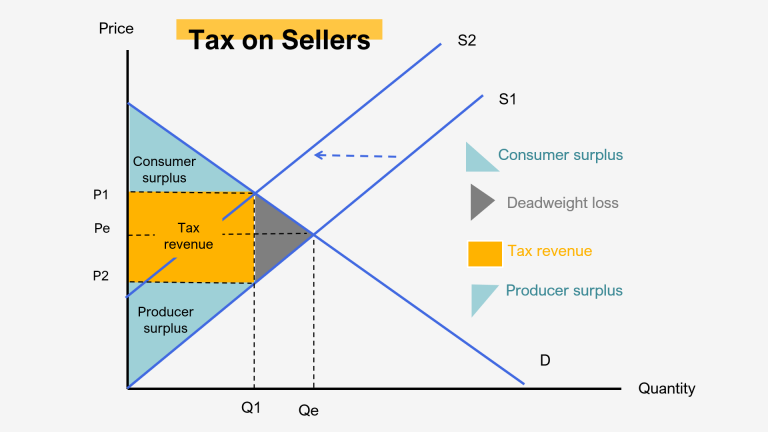
Deadweight Loss Pengertian Bentuk Penyebab Dan Contohnya

Comments are closed.