Diabetes And Self Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels

Diabetes And Self Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels Youtube The introduction of home blood glucose monitoring (bgm) in the late 1970s and regulatory clearance of the first meter for this purpose in 1980 revolutionized the self care of people with diabetes (pwd) (1 – 3). although often referred to as “self monitoring of blood (or plasma) glucose,” this form of glucose monitoring will be referred to. Monitoring also helps your health care team make decisions about your diabetes care plan. your doctor will tell you when and how often to check your blood sugar levels. most blood sugar meters (also known as glucometers) save your results for you and your health care team to review. some meters may use an app on your phone to track your levels.

Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose Apollo Sugar A blood sugar meter is used to test blood sugar. the meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood. most often, the blood comes from the side of the fingertip. then the blood is placed on a disposable test strip. with certain cgms, you still may need a blood sugar meter to set your cgm device daily. Researchers believe that blood glucose monitoring may prove helpful even in the short term, particularly for people who struggle to manage their levels. structured self monitoring of blood glucose can be useful to help people understand the impact of food and activity on their blood glucose levels and could be used for a short period as part of. Blood sugar monitoring during the day. certain times of the day are most helpful to check your blood sugar to assess your overall diabetes treatment plan, especially if you take insulin. these times include: when you wake up: your blood sugar level at this time is known as fasting glucose. it can help assess how your blood sugar levels are. Continuous glucose monitoring (cgm) is a way to monitor your glucose levels every 5 to 15 minutes, 24 hours a day. because of reliability issues, warm up periods, and the need to calibrate some of the devices, cgm does not eliminate the need for at least occasional fingersticks.
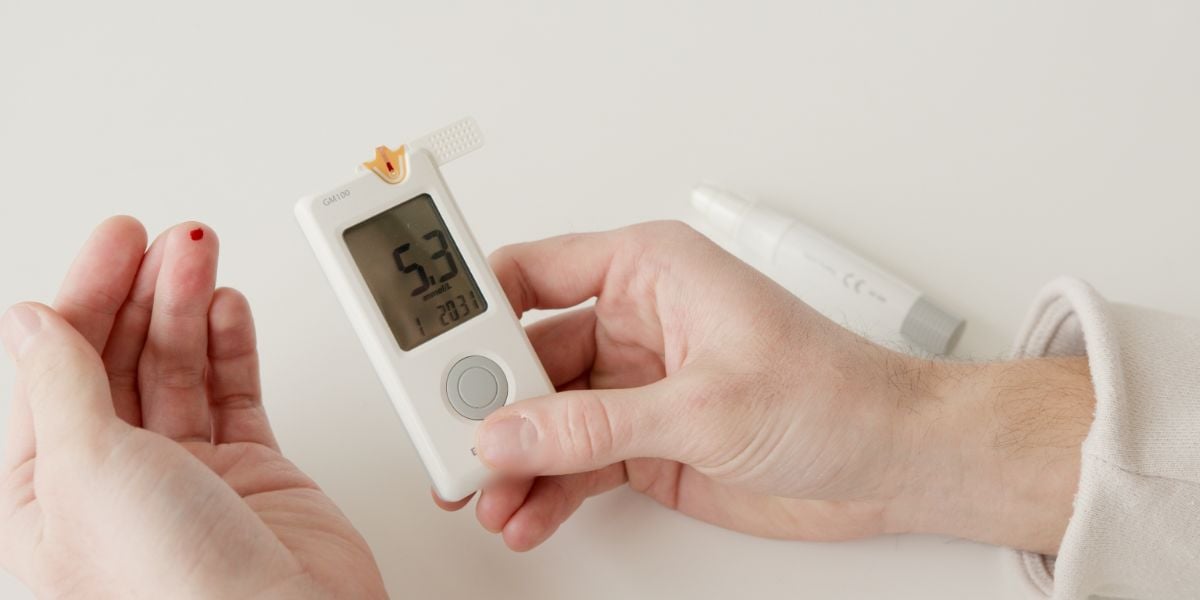
Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose Smbg Blood sugar monitoring during the day. certain times of the day are most helpful to check your blood sugar to assess your overall diabetes treatment plan, especially if you take insulin. these times include: when you wake up: your blood sugar level at this time is known as fasting glucose. it can help assess how your blood sugar levels are. Continuous glucose monitoring (cgm) is a way to monitor your glucose levels every 5 to 15 minutes, 24 hours a day. because of reliability issues, warm up periods, and the need to calibrate some of the devices, cgm does not eliminate the need for at least occasional fingersticks. Check your blood sugar level before bed. alcohol can lower blood sugar levels long after you've had your last drink. so check your blood sugar level before you go to sleep. if your blood sugar isn't between 100 mg dl and 140 mg dl (5.6 mm l and 7.8 mmol l), have a snack before bed. the snack can counter a drop in your blood sugar. After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter. use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood. touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result. your blood glucose level will appear on the meter's display. note: all meters are slightly different, so always refer.
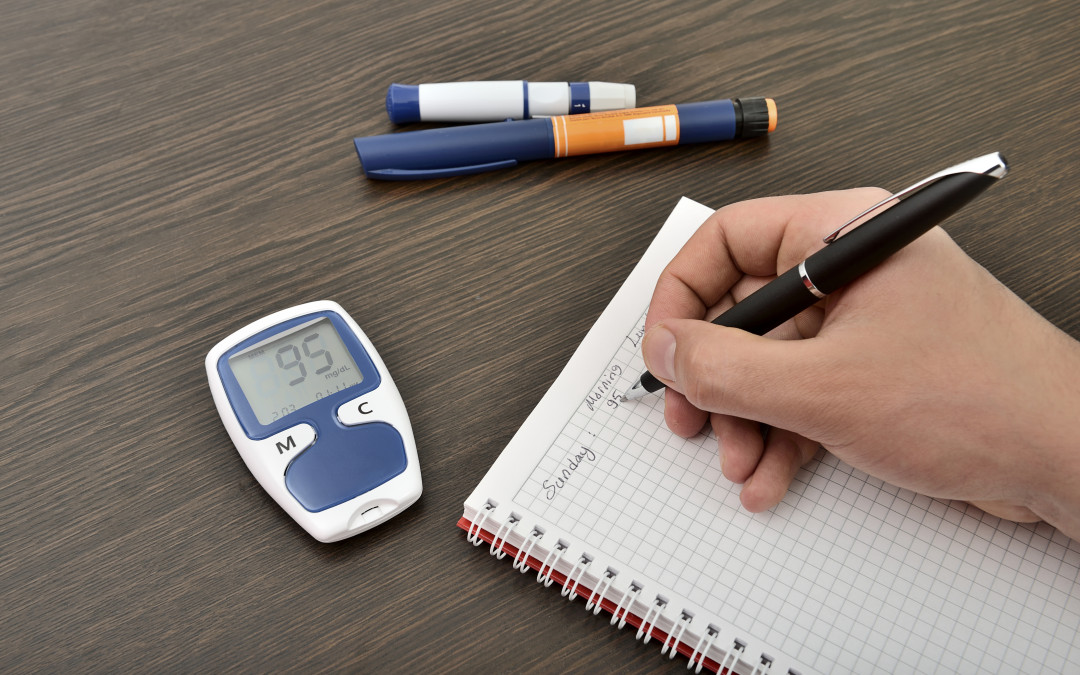

Self Monitoring Of Blood Glucose The Johns Hopkins Patient Guide To Check your blood sugar level before bed. alcohol can lower blood sugar levels long after you've had your last drink. so check your blood sugar level before you go to sleep. if your blood sugar isn't between 100 mg dl and 140 mg dl (5.6 mm l and 7.8 mmol l), have a snack before bed. the snack can counter a drop in your blood sugar. After washing your hands, insert a test strip into your meter. use your lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood. touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood and wait for the result. your blood glucose level will appear on the meter's display. note: all meters are slightly different, so always refer.
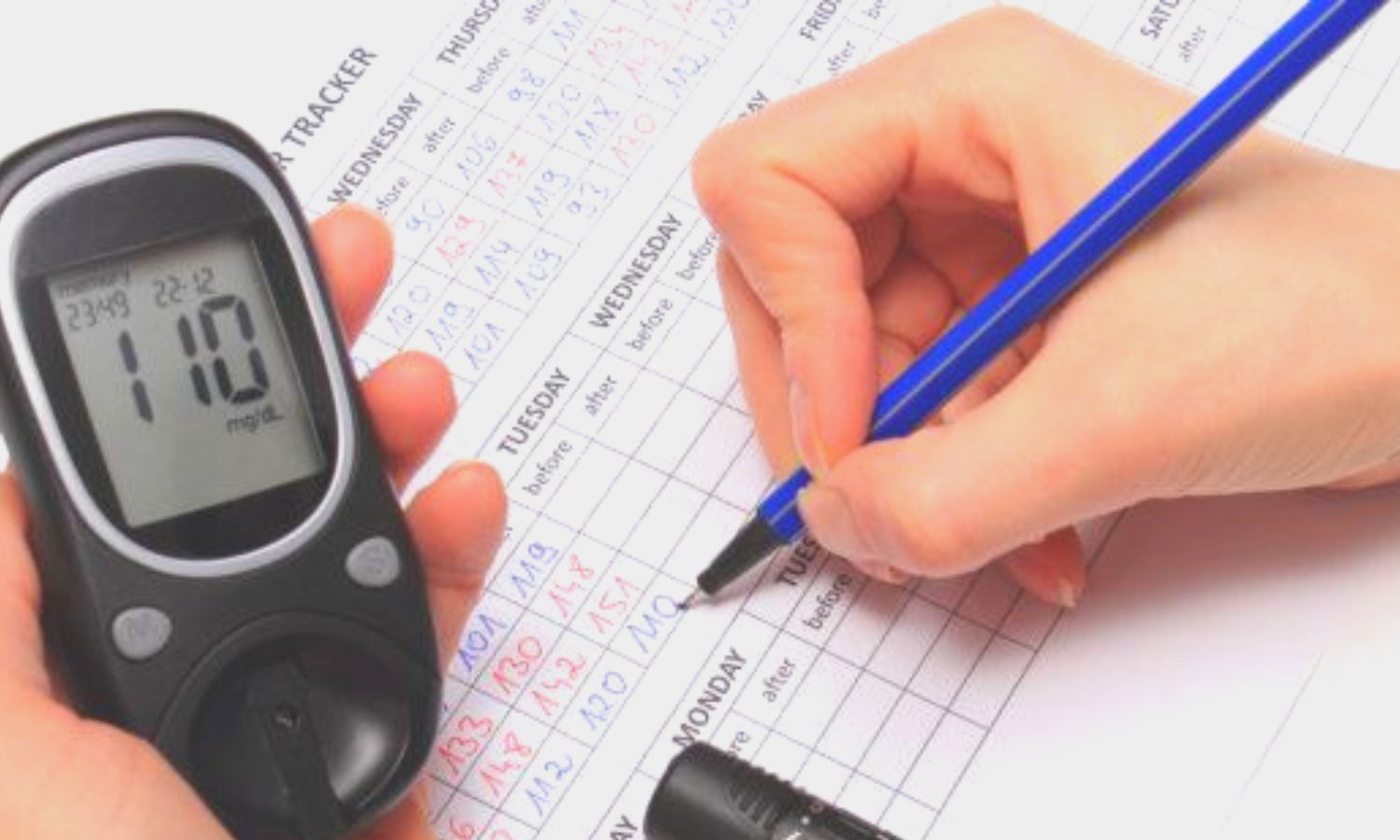

Self Monitoring Effectively Controls Blood Sugar In Non Insulin Treated

Comments are closed.