Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Nursing Dka Pathophysiology Treatment
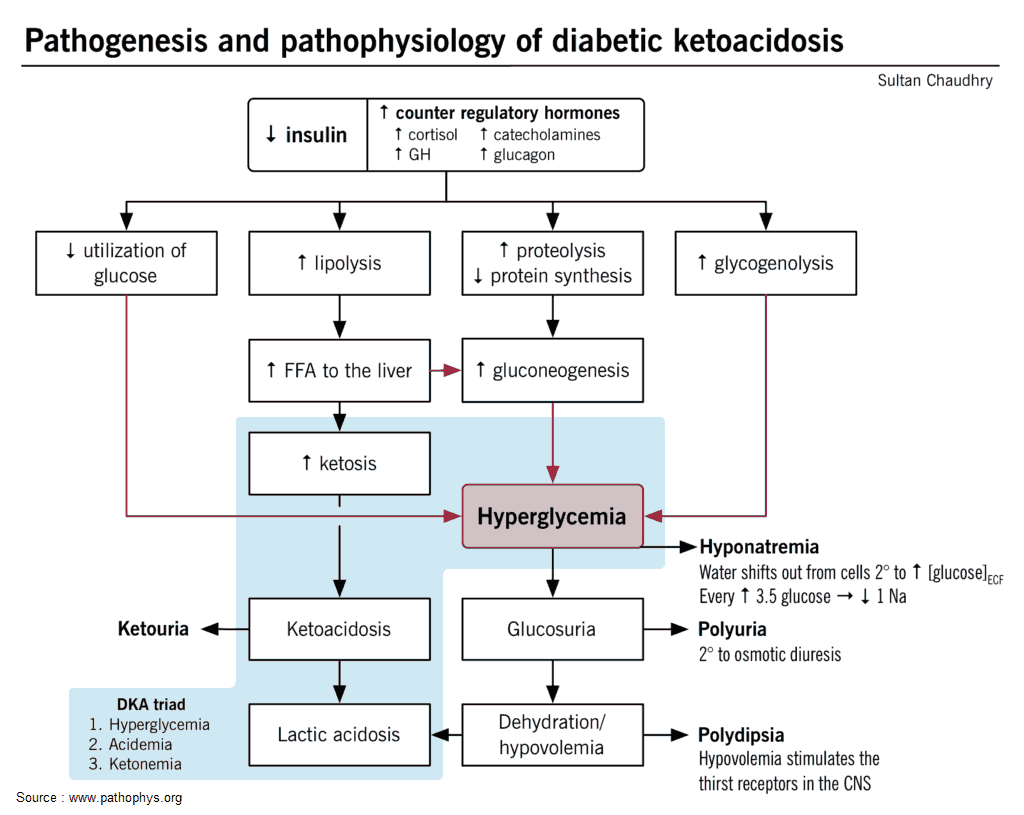
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Ketoacidosis Diabetic ођ Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with pathologically high serum and urine concentrations of ketone bodies, namely acetone, acetoacetate, and beta hydroxybutyrate. during catabolic states, fatty acids are metabolized to ketone bodies, which can be readily utilized for fuel by individual cells in the body. of the three major ketone bodies, acetoacetic acid is the only true ketoacid. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) is characterized by hyperglycemia, acidosis, and ketonemia. it is a life threatening complication of diabetes and typically seen in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, though it may also occur in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. in most cases, the trigger is new onset diabetes, an infection, or a lack of compliance with treatment.

Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Nursing Process Adpie Osmosis Video Diabetic ketoacidosis treatment and nursing interventions: there are 3 main nursing interventions for dka: fluids, insulin, and of course, continuing to assess your patient! the fluids you give to your patient will depend on their particular situation and what the doctor has ordered, but they may include normal saline, lactated ringers, 0.45%. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with significant fluid and electrolyte loss. dka occurs mostly in type 1 diabetes mellitus. it causes nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and can progress to. In this article, we provide a narrative review of management of dka in adults along with discussion of the various professional guidelines and propose evidence based recommendations on the topic. we conducted a literature search through pubmed and google scholar using the following search terms: “diabetic ketoacidosis,” “dka. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) occurs with severe hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis. this occurs because the blood sugar is so elevated and there is not enough insulin to take the sugar to the cell. the cell needs energy. since the cell can not get the energy from the sugar (because no insulin) it uses fatty acids for energy.
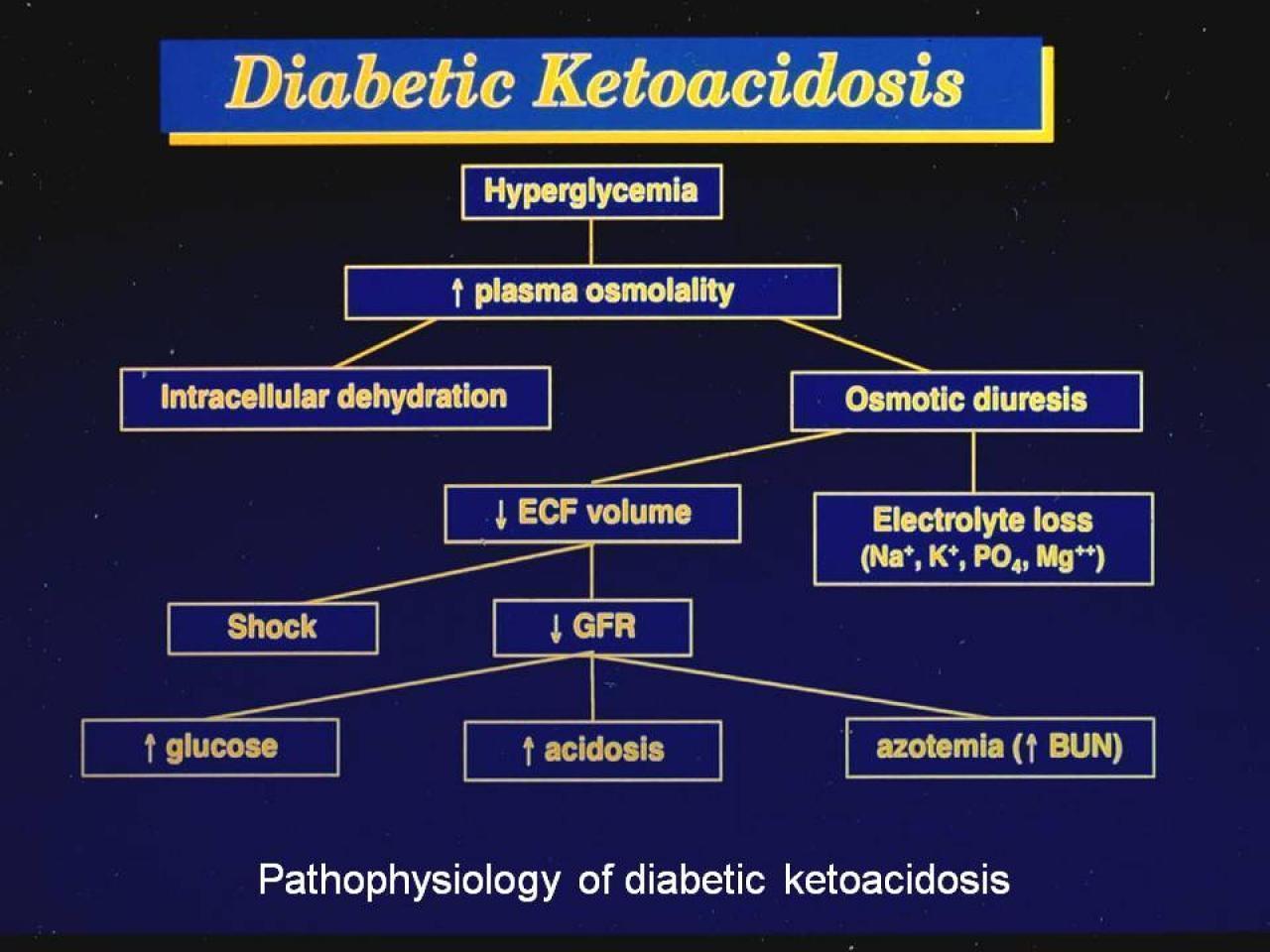
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Management Dka Causes Treatment Prevention In this article, we provide a narrative review of management of dka in adults along with discussion of the various professional guidelines and propose evidence based recommendations on the topic. we conducted a literature search through pubmed and google scholar using the following search terms: “diabetic ketoacidosis,” “dka. Diabetic ketoacidosis (dka) occurs with severe hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis. this occurs because the blood sugar is so elevated and there is not enough insulin to take the sugar to the cell. the cell needs energy. since the cell can not get the energy from the sugar (because no insulin) it uses fatty acids for energy. Diagnostic evaluation (more) minimum evaluation for a patient with dka: electrolytes including ca mg phos, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, ekg, pregnancy test as appropriate. if unclear whether patient has dka: beta hydroxybutyrate & lactate levels. if the cause of dka is unclear: blood cultures urine culture, chest x. Prevention of dka is the ultimate goal (80% of hospital admissions for dka occur in treated diabetics) [3,8]. it is necessary for clinicians to understand the pathophysiology and treatment of dka to care for this increasing diabetic population. we discuss the pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis, its management, and its complications.
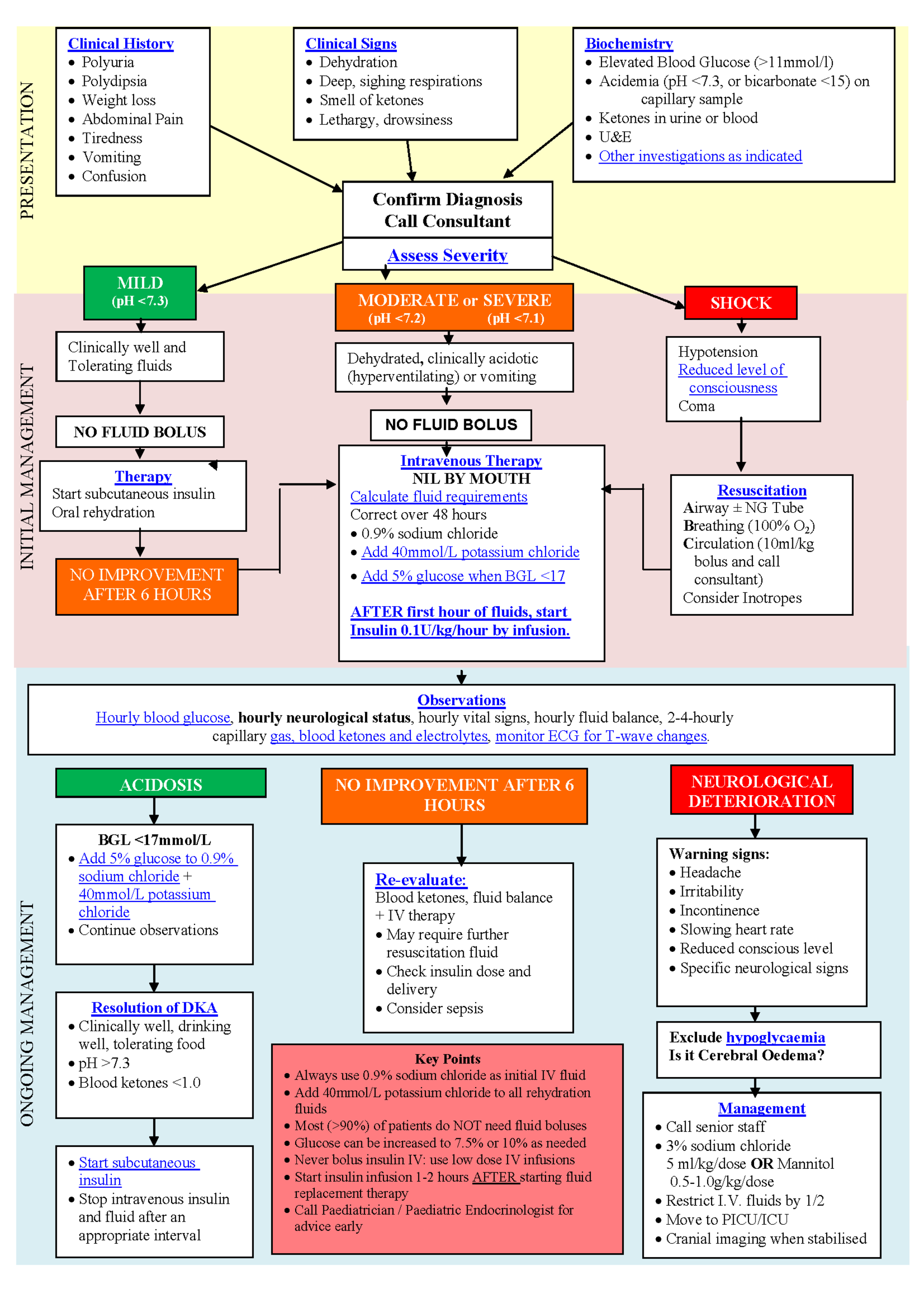
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Management Diagnostic evaluation (more) minimum evaluation for a patient with dka: electrolytes including ca mg phos, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, ekg, pregnancy test as appropriate. if unclear whether patient has dka: beta hydroxybutyrate & lactate levels. if the cause of dka is unclear: blood cultures urine culture, chest x. Prevention of dka is the ultimate goal (80% of hospital admissions for dka occur in treated diabetics) [3,8]. it is necessary for clinicians to understand the pathophysiology and treatment of dka to care for this increasing diabetic population. we discuss the pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis, its management, and its complications.

Comments are closed.