Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Nursing Dka Pathophysiology Treatment Management Nclex

Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Nursing Process Adpie Osmosis Video The onset of cerebral oedema is unpredictable; therefore the key to improving survival is early recognition and aggressive management DKA are high dependency patients and require 1:1 nursing All cases of recurrent DKA are preventable Written guidelines for sick day management and repeated discussions and review of these guidelines are essential Discussion of symptoms and
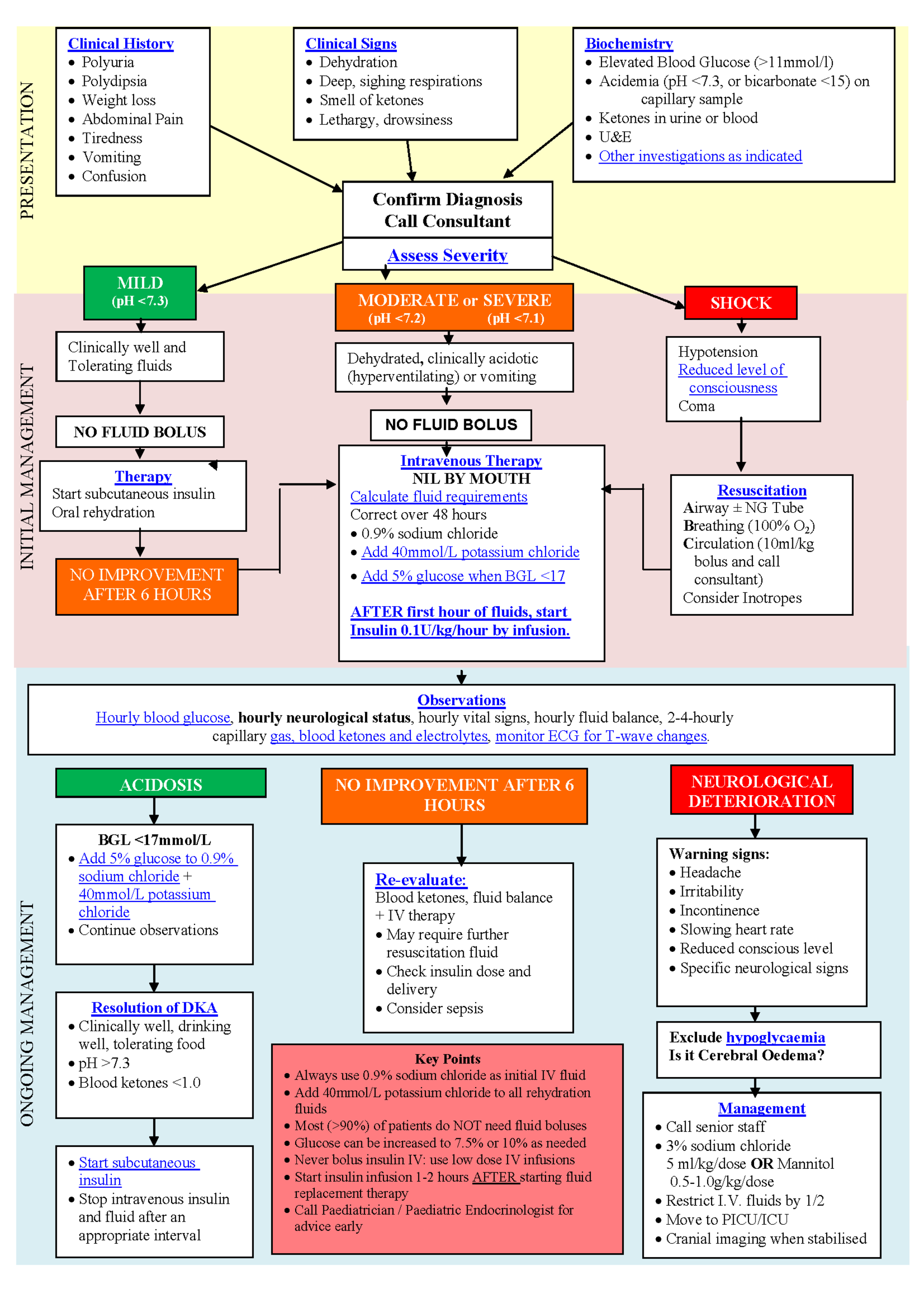
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka Management Maximum blood glucose, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, and sodium abnormalities predict adverse outcomes in diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA regarding level of nursing care, particularly in 12,13 In view of the unique coincidence of ketosis, hyperglycemia and hyperlipemia in diabetic ketoacidosis further evidence for interrelations was sought in 8 diabetic patients in ketoacidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a dangerous buildup of acids called ketones in your blood Ketones are produced when your body doesn’t have enough insulin to convert sugar into energy As a Diabetic ketoacidosis usually occurs in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus The formation of ketone bodies causes the blood to become more acidic The high levels of blood glucose in DKA causes

Comments are closed.