Diagnostic Approaches To Possible Pulmonary Embolism Aafp
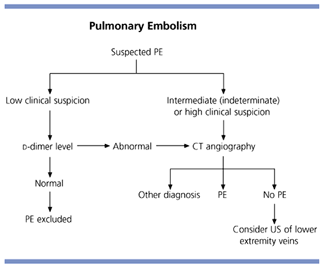
Diagnostic Approaches To Possible Pulmonary Embolism Aafp According to the prospective investigation of pulmonary embolism diagnosis (pioped) study, low , intermediate and high probability scan results had positive predictive values of 16 percent, 33. Deep venous thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism (pe) are the two most important manifestations of venous thromboembolism (vte), which is the third most common life threatening cardiovascular.
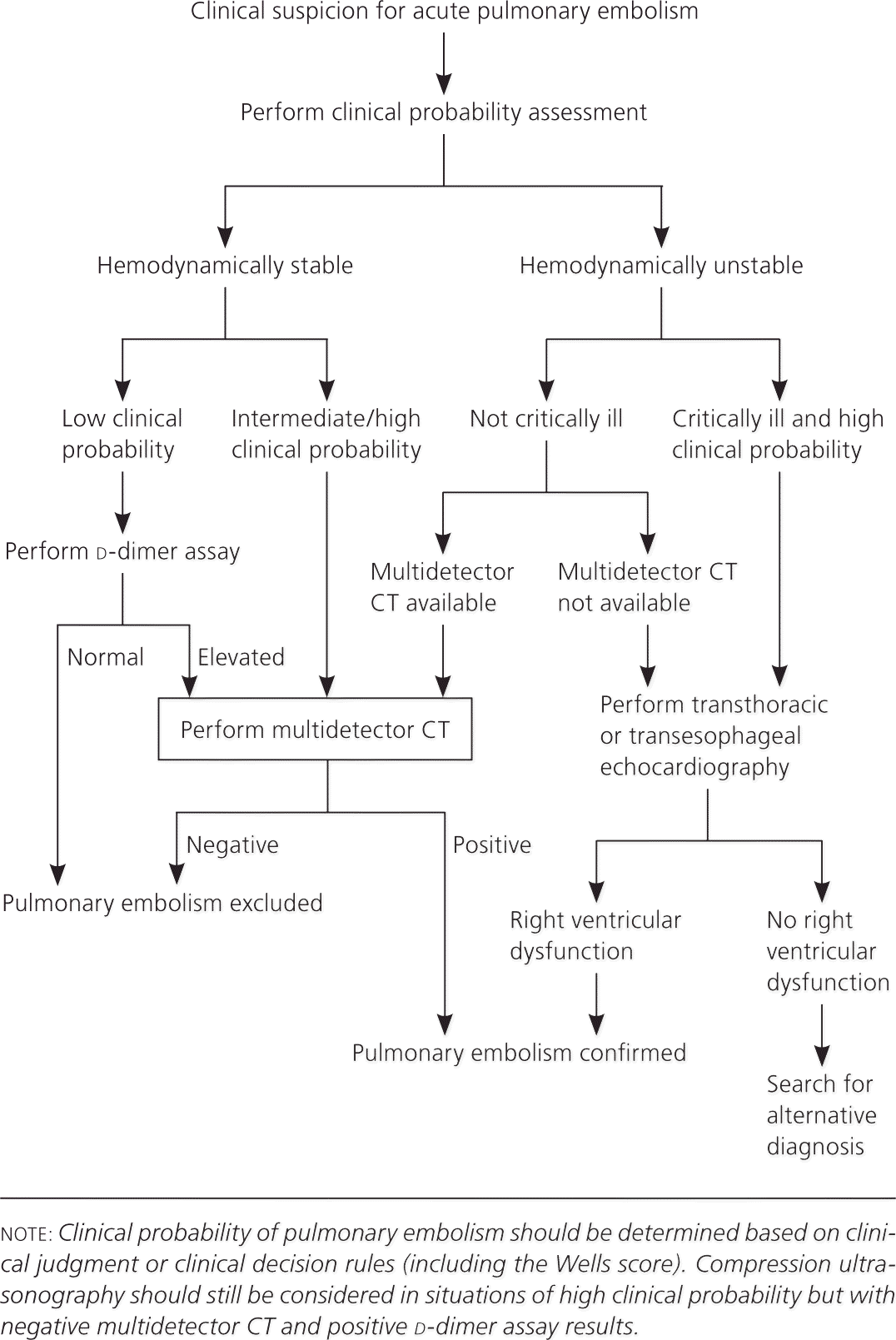
Diagnosis Of Deep Venous Thrombosis And Pulmonary Emb Vrogue Co Venous thromboembolism (vte) is a blood clotting condition that has two major manifestations: deep venous thrombosis (dvt) and pulmonary embolism. in the general u.s. population, the incidence of. A pulmonary embolism (pe) occurs when a blood clot obstructs the pulmonary artery or its branches. in deep vein thrombosis (dvt), a thrombus develops within the deep veins, most commonly in the lower extremities. pe usually occurs when a part of this thrombus breaks off and enters the pulmonary circulation. pe rarely occurs from the embolization of other materials into the pulmonary. Introduction. there are an estimated 900 000 cases of venous thromboembolism (vte) every year in the united states, 150 000 to 250 000 pulmonary embolism (pe) related hospitalizations and 60 000 to 100 000 deaths, making it the third most common cause of cardiovascular death. 1 once a pe is diagnosed, risk stratification is necessary to define appropriate management. Abstract. imaging plays an important role in the evaluation and management of acute pulmonary embolism (pe). computed tomography (ct) pulmonary angiography (ctpa) is the current standard of care and provides accurate diagnosis with rapid turnaround time. ct also provides information on other potential causes of acute chest pain.

Comments are closed.