Disc Anatomy 2 Ainsworth Institute
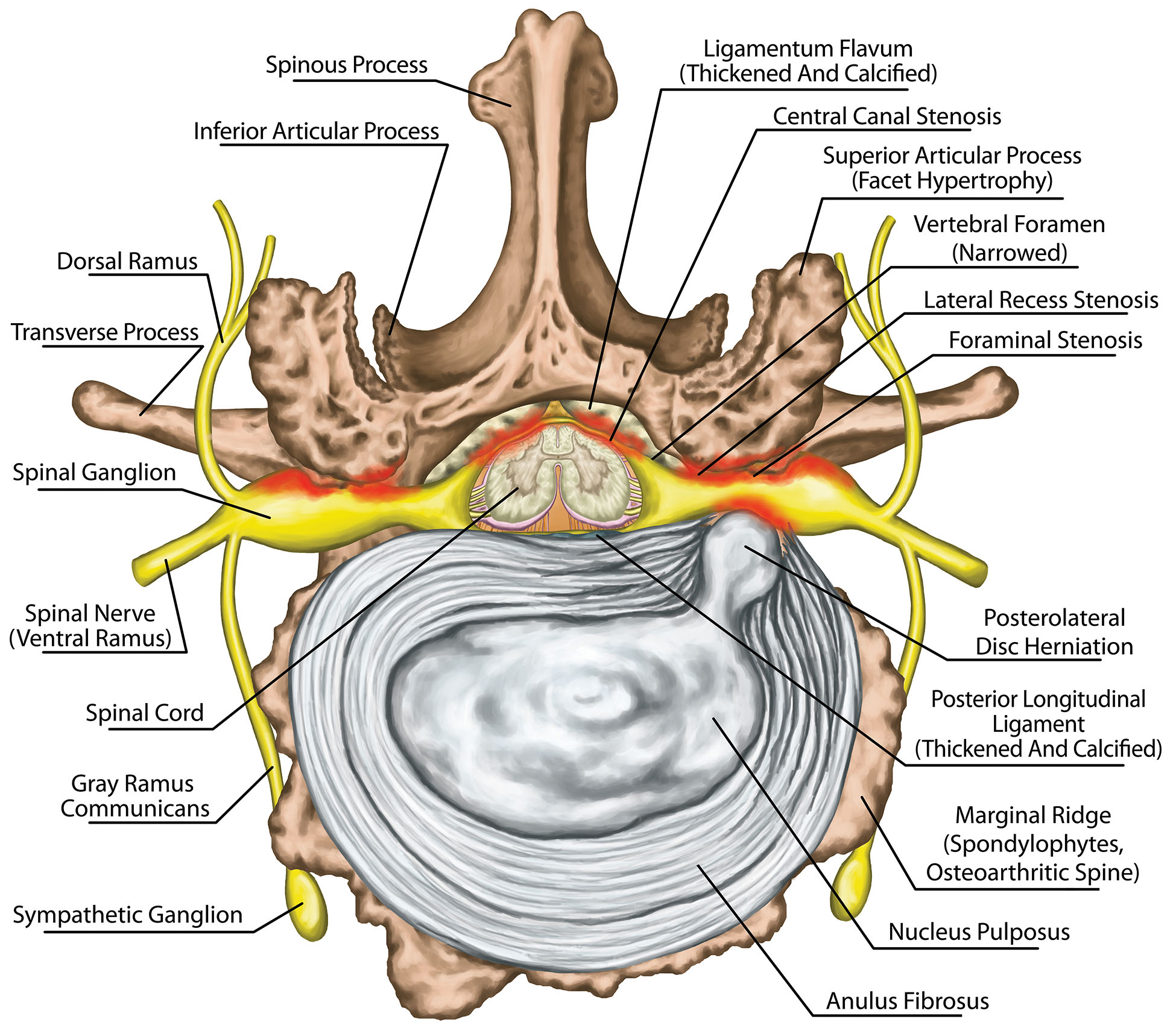
Disc Anatomy 2 Ainsworth Institute Intervertebral discs. between each vertebral body is a cushion called an intervertebral disc. these discs contribute a significant proportion to the height of the spinal column around 25 30%. in addition to adding height, each disc plays a vital role absorbing the stress and shock the body incurs during movement and prevents the vertebrae from. The sacroiliac joint (sij) is the largest joint in the body and a common cause of lower back and buttock pain.[1] fifteen to twenty percent of all lower back pain cases originate in the sij.[2] sacroiliac joint pain, also known as sacroiliitis, can present in a variety of ways and is commonly confused with low back pain or a herniated bulging disc.
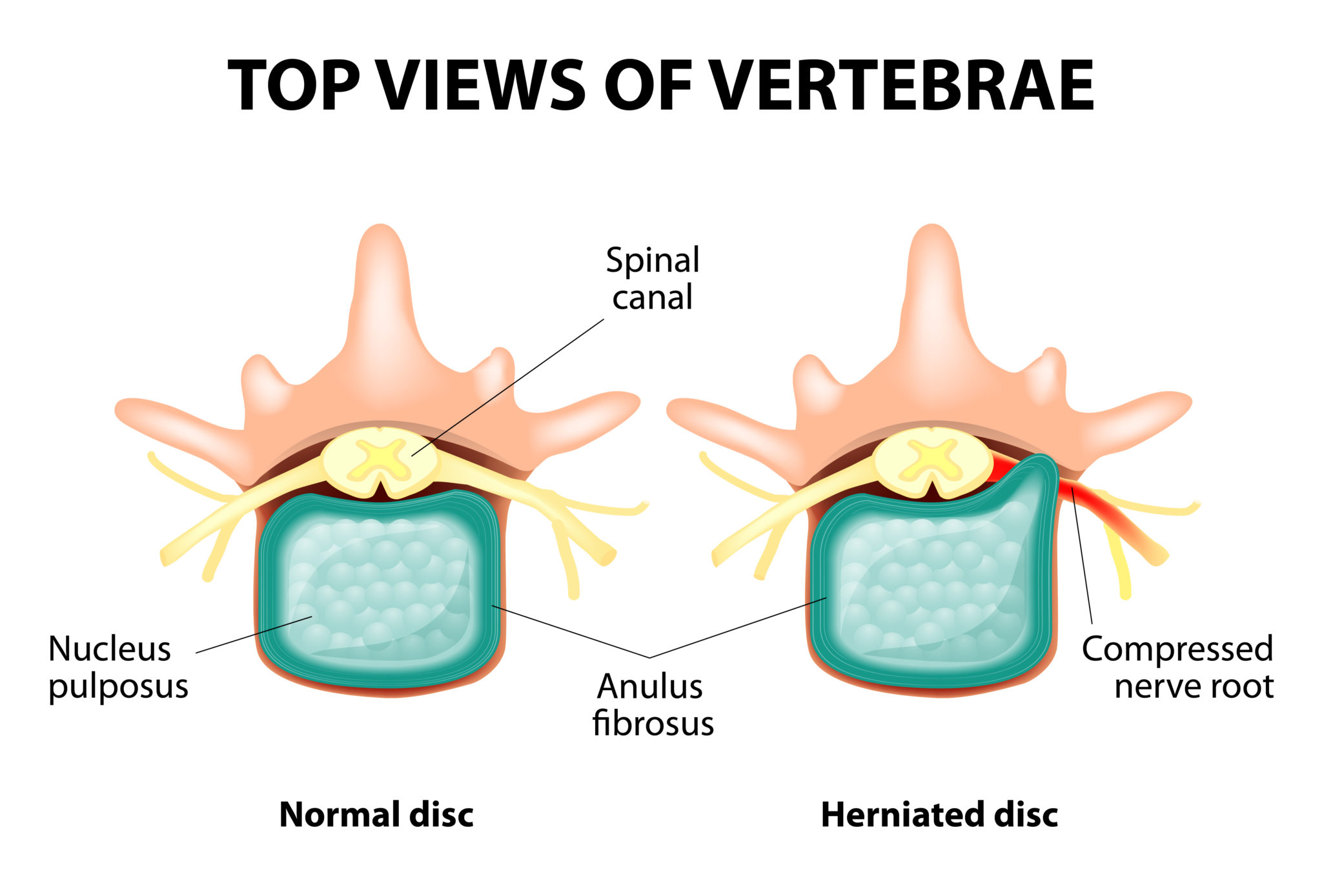
Intervertebral Discs Ainsworth Institute The central nervous system, also known as the cns, consists of the brain and the spinal cord. the primary role of the central nervous system is twofold: 1) integrate and coordinate incoming and outgoing neural signals and 2) control higher mental functions such as thinking and leaning. read more about the central nervous system read more. The notochord is an embryonic structure common to all vertebrates. it is a structure around which axial development is oriented. while vertebrae develop around the notochord from the sclerotome (paired, condensed regions of mesenchymal cells), the intervertebral discs form, in part, from the notochord itself. Functions. the intervertebral disc forms the fibrocartilaginous joint which allows slight movement of the vertebral column, and acts as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together. the discs act as fibrocartilaginous cushions, serving as the spine’s shock absorbing system. this cushions the effect of shock and stress produced when an individual. Understanding spinal anatomy: intervertebral discs. between each vertebral body is a cushion called an intervertebral disc. each disc absorbs the stress and shock the body incurs during movement and prevents the vertebrae from grinding against one another. the intervertebral discs are the largest structures in the body without a vascular supply.
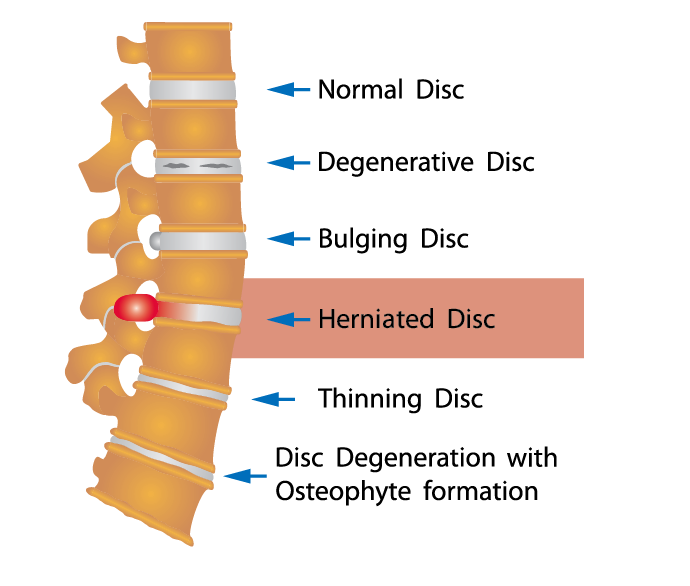
Herniated Disc Causes Symptoms Treatments Ainsworth Institute Functions. the intervertebral disc forms the fibrocartilaginous joint which allows slight movement of the vertebral column, and acts as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together. the discs act as fibrocartilaginous cushions, serving as the spine’s shock absorbing system. this cushions the effect of shock and stress produced when an individual. Understanding spinal anatomy: intervertebral discs. between each vertebral body is a cushion called an intervertebral disc. each disc absorbs the stress and shock the body incurs during movement and prevents the vertebrae from grinding against one another. the intervertebral discs are the largest structures in the body without a vascular supply. In atlas of implantable therapies for pain management, vol 2. new york: springer. 2015. 11 14. print; hunter c, lee e. chapter 4: preoperative evaluation for spinal cord stimulation. in atlas of implantable therapies for pain management, vol 2. new york: springer. 2015. 15 22. print. Disc anatomy 2 ainsworth institute. information about spine and intervetebral disc anatomy intervertebral disc anatomy, function, degeneration, herniation intervertebral foramen disc vertebral spinal canal ivd nerves basicmedical key fig. spinal lamina transverse spine vertebral column intervertebral discs bodies medicalrf.

Comments are closed.