Ecology The Categories Of Consumers 2 Primary Consumer Consumers

Trophic Pyramid Definition Examples Britannica A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. trophic levels. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food through. The primary consumer plays an important role in the ecosystem by facilitating the flow of energy through the food chain. its main job is to consume plants, converting the energy stored in them into a form that can be used by other consumers in the ecosystem. primary consumers are vital in the trophic structure as they directly consume.

Ecology The Categories Of Consumers 2 Primary Consumer Consu Primary consumers feed exclusively on autotrophs. any organism that must eat in order to produce energy is both a heterotroph and a consumer. rather confusingly, primary consumers are located in the second trophic level of the ecosystem. a trophic level is the position any organism occupies within any food chain. These primary consumers are crucial as they transform the energy created by producers into a form that can be utilized by other members of the food chain. secondary consumers are typically small to medium sized carnivores or omnivores. this group preys on herbivorous animals, thereby deriving their energy and nutrients. A consumer in biology is an organism that obtains energy by eating other organisms due to its incapacity for creating energy on its own. a cow is an example of a consumer; it eats only plants, so. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain.
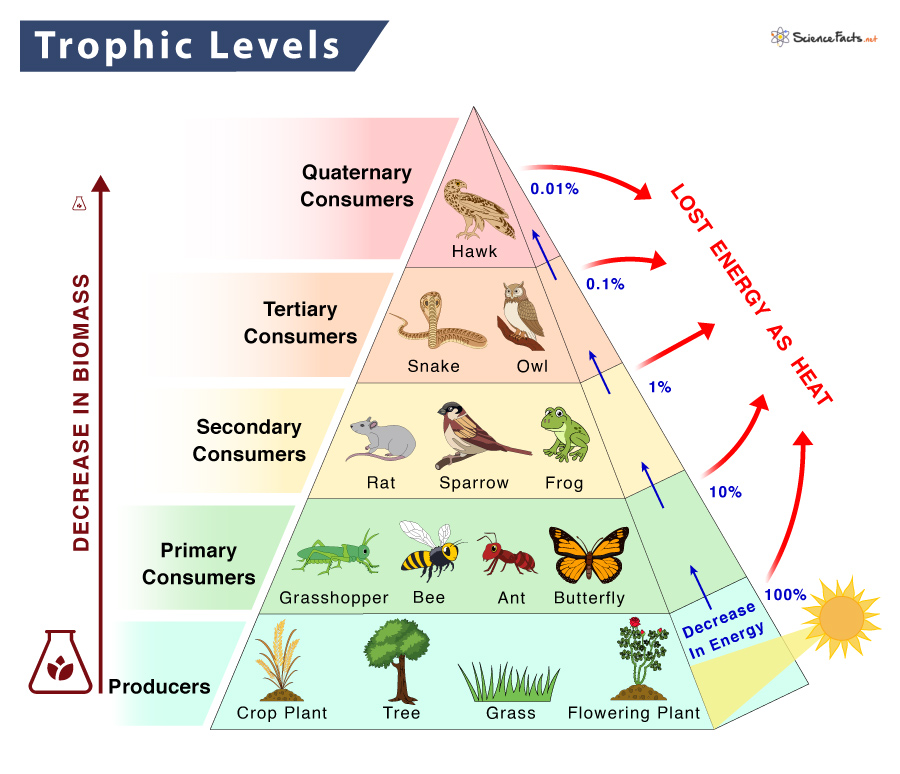
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram A consumer in biology is an organism that obtains energy by eating other organisms due to its incapacity for creating energy on its own. a cow is an example of a consumer; it eats only plants, so. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. Primary consumers can range from microscopic organisms like zooplankton to large creatures like elephants. here are some examples. 1. ruminants like giraffes and cows. primary herbivorous consumers such as cows, goats, zebras, giraffes are primary consumers. they consume plant material such as grass, branches, and roots. These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers.

Primary Consumers That Eat Plants Are Called At Barbara Copeland Blog Primary consumers can range from microscopic organisms like zooplankton to large creatures like elephants. here are some examples. 1. ruminants like giraffes and cows. primary herbivorous consumers such as cows, goats, zebras, giraffes are primary consumers. they consume plant material such as grass, branches, and roots. These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers.

Comments are closed.