Educational Sessions Single Cell Analysis Of Circulating Tumor Cells

Educational Sessions Single Cell Analysis Of Circulating Tumor Cells Multimodal analysis of circulating tumour cells (ctcs) has the potential to provide remarkable insight for cancer development and metastasis. ctcs and ctc clusters investigation using single cell analysis, enables researchers to gain crucial information on metastatic mechanisms and the genomic alterations responsible for drug resistance, empowering treatment, and management of cancer. One technical solution to the challenge of heterogeneity is the high definition single cell analysis (hd sca) workflow that has been developed to take the entire population of nucleated circulating cells in a peripheral blood sample into account [16, 17]. it offers an enrichment free, high throughput approach for rare cell detection and multimodal single cell analysis following the principle.
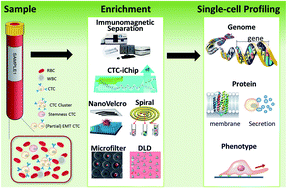
Enrichment And Single Cell Analysis Of Circulating Tumor Cells Abstract. circulating tumor cells (ctcs) are rare cells that can be found in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. they have been demonstrated to be useful prognostic markers in many cancer types. within the last decade various methods have been developed to detect rare cells within a liquid biopsy from a cancer patient. Metastasis is the hallmark of malignancies and the leading cause of cancer related deaths. 1 the metastatic process depends on the spread of tumor cells through the bloodstream to form distant tumors. 2 circulating tumor cells (ctcs) are those tumor cells that are present in the blood of cancer patients and considered to be the “seeds” of tumor metastasis. 3, 4 during the past decade, ctcs. These cells, named circulating tumor cells (ctcs), display the same spatial and temporal heterogeneity as the primary tumor. since ctcs are involved in tumor progression, they represent a privileged window to disclose mechanisms of metastases, while omic analyses at the single cell level allow dissection of the complex relationships between the tumor subpopulations and the surrounding normal. As the most promising “liquid biopsy”, analysis of circulating tumor cells (ctcs) provides noninvasive access to obtain biological information of solid tumors. it not only advances the understanding of the mechanisms underlying tumor metastasis, relapse, and chemoresistance, but also promotes the development of precision medicine.

Single Cell Analysis Of Circulating Tumour Cells Enabling Technologies These cells, named circulating tumor cells (ctcs), display the same spatial and temporal heterogeneity as the primary tumor. since ctcs are involved in tumor progression, they represent a privileged window to disclose mechanisms of metastases, while omic analyses at the single cell level allow dissection of the complex relationships between the tumor subpopulations and the surrounding normal. As the most promising “liquid biopsy”, analysis of circulating tumor cells (ctcs) provides noninvasive access to obtain biological information of solid tumors. it not only advances the understanding of the mechanisms underlying tumor metastasis, relapse, and chemoresistance, but also promotes the development of precision medicine. Circulating tumor cells (ctcs) have a great potential for noninvasive diagnosis and real time monitoring of cancer. a comprehensive evaluation of four whole genome amplification (wga) next generation sequencing workflows for genomic analysis of single ctcs, including pcr based (genomeplex and ampli1), multiple displacement amplification (repli g), and hybrid pcr and multiple displacement. Dissemination of cancer cells from the primary tumour into circulation (step 1) can involve either single cells or cell clusters containing multiple circulating tumour cells (ctcs) as well as.

Comments are closed.