Energy In Ecosystems
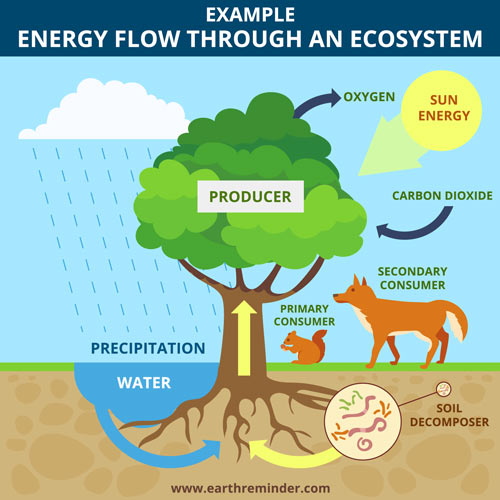
How Does Energy Flow Through An Ecosystem Earth Reminder Learn how energy from the sun is transferred through different trophic levels in ecosystems, from primary producers to secondary consumers. explore food chains, energy pyramids, and the 10 percent rule with examples and images. Learn how organisms acquire energy through photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, and consumption, and how energy is transferred and lost between trophic levels. explore the concepts of productivity, ecological efficiency, and ecological pyramids with examples and diagrams.

Energy Flow Biology Britannica Photoautotrophs are autotrophs that use energy from sunlight to make organic compounds by photosynthesis. photoautotrophs include plants, algae, and many bacteria, as shown in table 24.5.1 24.5. 1. they are the primary producers in the vast majority of ecosystems on earth. National 5; energy in ecosystems energy transfer in ecosystems. all organisms require energy. the feeding relationship in an ecosystem can be shown in a foodchain. learn about pyramids of biomass. An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their abiotic (non living) environment. ecosystems can be small, such as the tide pools found near the rocky shores of many oceans, or large, such as those found in the tropical rainforest of the amazon in brazil (figure 20.2). Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each.
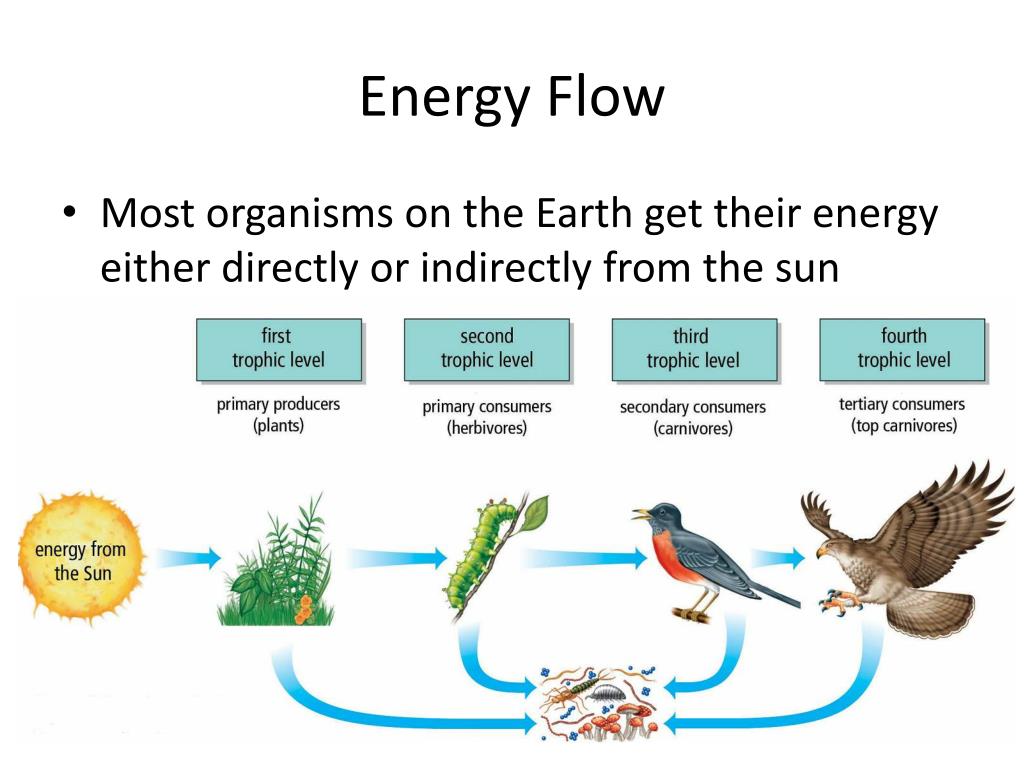
Ppt Energy Flow In An Ecosystem Powerpoint Presentation Free An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their abiotic (non living) environment. ecosystems can be small, such as the tide pools found near the rocky shores of many oceans, or large, such as those found in the tropical rainforest of the amazon in brazil (figure 20.2). Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each. Energy transfer and the 10 percent rule. not all food chains and food webs consist of five trophic levels. however, five is the maximum number of trophic levels most ecosystems can support. this is because of inefficiencies in energy flow, which begin with photosynthesis. of all the solar energy that reaches earth, only a small percentage lands. An ecological energy budget focuses on the absorption of energy by photosynthetic organisms and the transfer of that fixed energy through the trophic levels of ecosystems (“trophic” refers to the means of organic nutrition). ecologists classify organisms in terms of the sources of energy they utilize.

Comments are closed.