Esophagus Anatomy Diagram
Esophagus вђ Earth S Lab Learn about the esophagus, a 25 cm long fibromuscular tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach. see its anatomy, sphincters, blood supply, innervation, and related structures in diagrams and videos. Learn about the esophagus, a hollow, muscular tube that carries food and liquid from your throat to your stomach. find out how acid reflux, gerd and other disorders can affect your esophagus and what symptoms and treatments are available.

Trachea Esophageal Sphincter Diagram Vrogue Co The esophagus is a long, thin, and muscular tube that connects the pharynx (throat) to the stomach. it forms an important piece of the gastrointestinal tract and functions as the conduit for food and liquids that have been swallowed into the pharynx to reach the stomach. the esophagus is about 9 10 inches (25 centimeters) long and less than an. Learn about the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. find out its structure, location, function, and associated conditions, such as gerd and cancer. Learn about the esophagus, a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. find out how it works, what can go wrong, and how to prevent or treat esophageal issues. From here the esophagus travels down behind the heart and in front of the spine and eventually passes through the diaphragm to finally end at the stomach. picture 1: location of the esophagus in the human body. in an adult, the esophagus is usually around 25 to 30 centimeters in length and can measure up to about 2 centimeters in width.

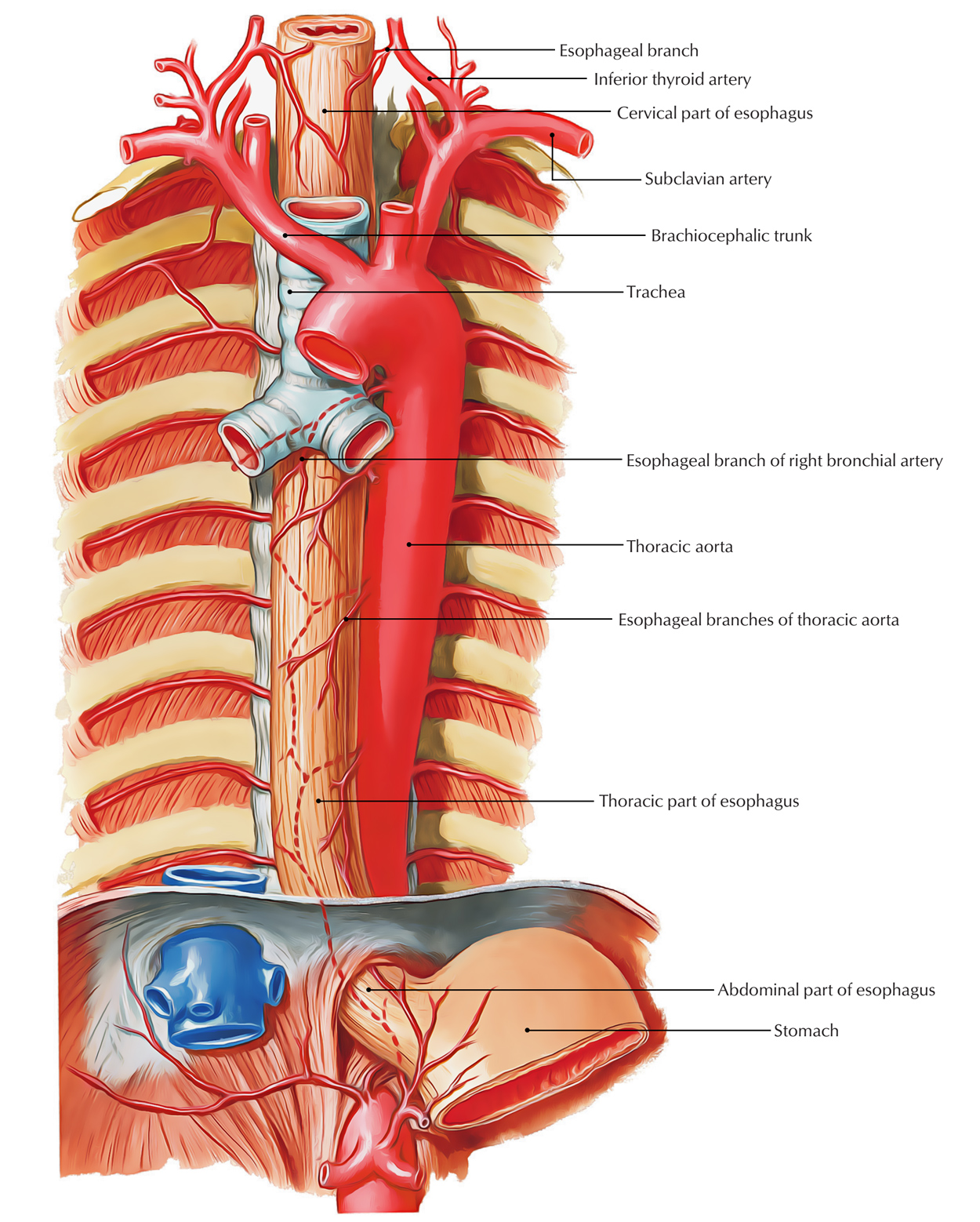
The Human Esophagus Functions And Anatomy And Problems Learn about the esophagus, a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. find out how it works, what can go wrong, and how to prevent or treat esophageal issues. From here the esophagus travels down behind the heart and in front of the spine and eventually passes through the diaphragm to finally end at the stomach. picture 1: location of the esophagus in the human body. in an adult, the esophagus is usually around 25 to 30 centimeters in length and can measure up to about 2 centimeters in width. The oesophagus is a fibromuscular tube, approximately 25cm in length that transports food from the pharynx to the stomach. it originates at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage, c6, extending to the cardiac orifice of the stomach, t11. anatomically, the oesophagus can be divided into two parts: thoracic and abdominal. The esophagus, historically also spelled oesophagus, is a tubular, elongated organ of the digestive system which connects the pharynx to the stomach. the esophagus is the organ that food travels through to reach the stomach for further digestion. it follows a path that travels behind the trachea and heart, in front of the spinal column, and through the diaphragm before entering the stomach.[1][2].
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/292/Gspt830scLPX0uk5rXr0w_esophagus-in-situ_english.jpg)
Esophagus Anatomy Sphincters Arteries Veins Nerves Kenhub The oesophagus is a fibromuscular tube, approximately 25cm in length that transports food from the pharynx to the stomach. it originates at the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage, c6, extending to the cardiac orifice of the stomach, t11. anatomically, the oesophagus can be divided into two parts: thoracic and abdominal. The esophagus, historically also spelled oesophagus, is a tubular, elongated organ of the digestive system which connects the pharynx to the stomach. the esophagus is the organ that food travels through to reach the stomach for further digestion. it follows a path that travels behind the trachea and heart, in front of the spinal column, and through the diaphragm before entering the stomach.[1][2].

Comments are closed.