Examples 5 1 5 2 And 5 3 Laws Of Motion Physics Class 11th Chapter 5
Law Of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5 Learn Cbse Hey students, through this video i aim to provide you not only solutions of important ncert examples but also a brief explanation of the concepts involved so cbse exam, class 10. Answer: (a) when the pebble is moving upward, the acceleration g is acting downward, so the force is acting downward is equal to f = mg = 0.05 kg x 10 ms 2 = 0.5 n. (b) in this case also f = mg = 0.05 x 10 = 0.5 n. (downwards). (c) the pebble is not at rest at highest point but has horizontal component of velocity.

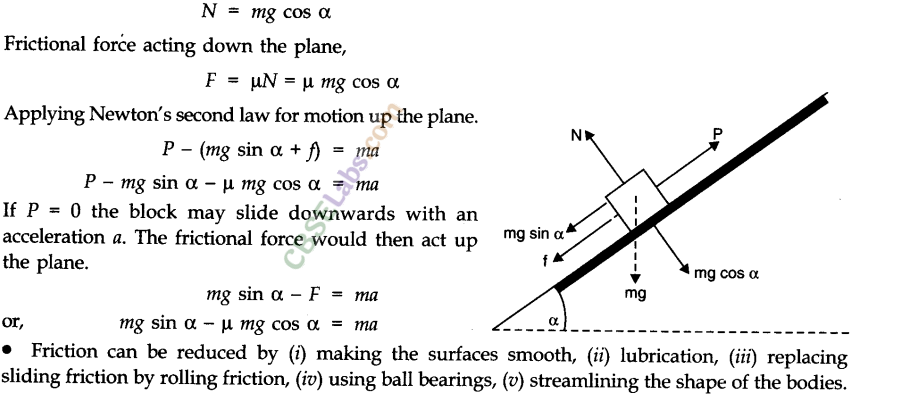
Examples 5 1 5 2 And 5 3 Laws Of Motion Phy Access the answers to ncert solutions for class 11 physics chapter 5 laws of motion. 1. give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on. (a) a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed. (b) a cork of mass 10 g floating on water. (c) a kite skillfully held stationary in the sky. (d) a car moving with a constant velocity of 30. Calculate the initial thrust (force) of the blast. solution : mass of the rocket, m = 20,000 kg. initial acceleration, a = 5 m s 2. acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m s 2. using newton’s second law of motion, the net force (thrust) acting on the rocket is given by the relation: f – mg = ma. Ncert solutions for class 11th: ch 5 laws of motion physics science. page no: 109. excercises. 5.1. give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on. (a) a drop of rain falling down with a constant speed, (b) a cork of mass 10 g floating on water, (c) a kite skillfully held stationary in the sky,. Law of motion class 11 notes physics chapter 5. • dynamics is the branch of physics in which we study the motion of a body by taking into consideration the cause i.e., force which produces the motion. • force. force is an external cause in the form of push or pull, which produces or tries to produce motion in a body at rest, or stops tries.

Comments are closed.