Explicit Formulas Definition Examples Expii 48 Off
Explicit Formulas Definition Examples Expii 48 Off An explicit formula for a sequence is one for which an equals something that does not depend on any other elements in the sequence. for example, let's work with the recurrence formula. an=an−1−1a0=7. we can plug this formula into python and get the following values in the sequence: image source: by joshua siktar. Confusing the recursive and explicit formulas for a sequence the recursive formula shows how to find the next term based on the previous term. the explicit formula shows how to find any term based on the relationships between the term number and the term itself. it is easy to confuse the two. for example, 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, ….

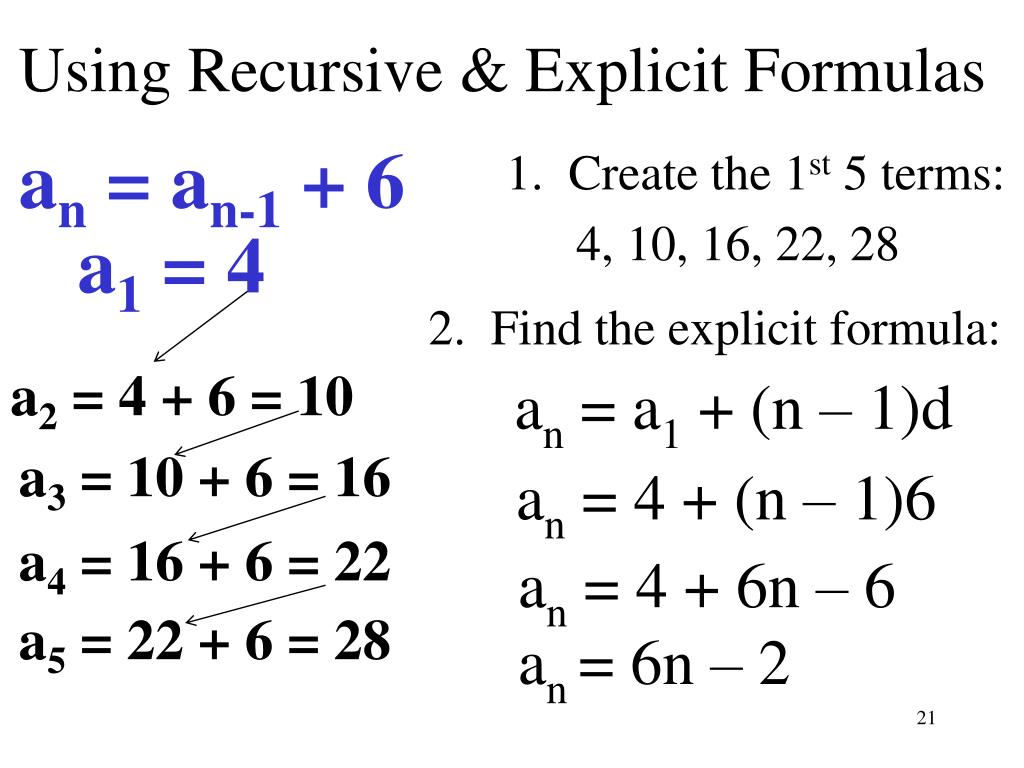
Explicit Formulas Definition Examples Expii 48 Off Introduction. explicit formulas provide a convenient way to express the terms of a sequence using a single formula. for instance, in an arithmetic sequence, each term can be calculated using the formula `a n = a 1 (n 1)d`, where `a n` represents the `n`th term, `a 1` represents the first term, `d` is the common difference between consecutive terms, and `n` indicates the term's position in. An example of a recursive formula for a geometric sequence is. bn=3×bn−1. because bn is written in terms of an earlier element in the sequence, in this case bn−1. we often want to find an explicit formula for bn, which is a formula for which bn−1,bn−2,…,b1,b0 don't appear. to do this, it's easiest to plug our recursive formula into a. An arithmetic sequence is one for which you can keep adding (or subtracting) the same number to get from one element of the sequence to the next. for instance, {2,4,6,8,10} is an arithmetic sequence. this is because 2 2=4, 4 2=6, and so on. we add 2 to one term of the sequence to get the next term. The explicit formula for the geometric sequence is a n = ar n 1 and it is also the nth term of a gp. here 'a' is the first term of the geometric sequence, and 'r' is the common ratio of the geometric sequence. the common ratio formula is r = ar a = ar 2 ar, and it is obtained by dividing a particular term with its previous term.

Comments are closed.